Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA ENGLISH-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-EXERCISE
- A wire of length 10cm translates in a direction making an angle of 60^...
Text Solution
|
- A circular copper ring of radius r translates in its plane with a cons...
Text Solution
|
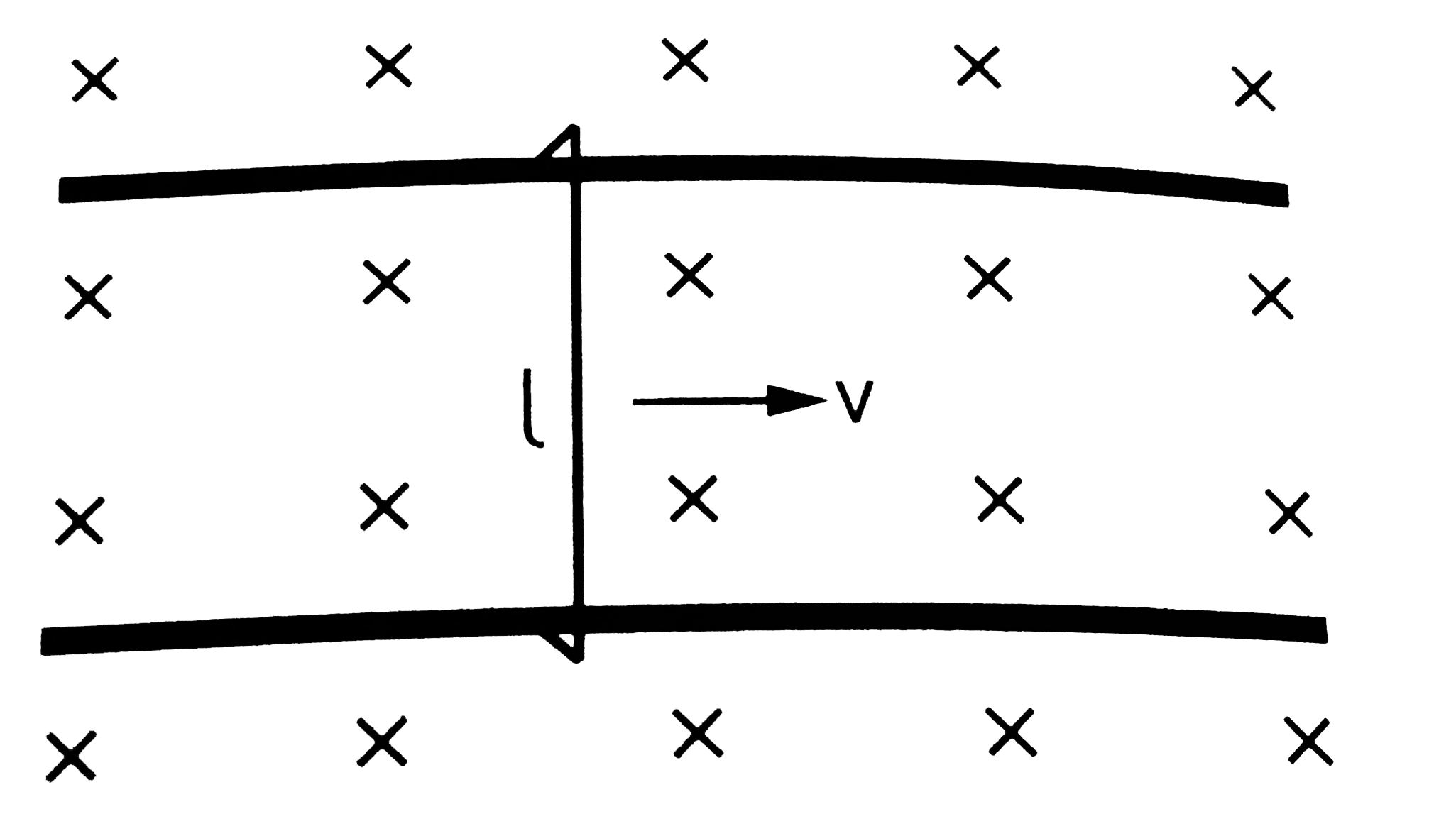
- Shows a wire sliding on two parallel, conducting rails placed at a se...
Text Solution
|
- shows a long U shaped wire of widt l placed in a perpendicular magnet...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation of the previous problem. (a) Calculate the forc...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in . The wire PQ has mass m, resistance r...
Text Solution
|
- A rectanguar frame of wire abcd has dimensions 32cm X 8.0 cm and a tot...
Text Solution
|
- Shows a metallic wire of resistance 0.20 Omega sliding on a horizontal...
Text Solution
|
- A wire ab of length l, mass m and resistance R slided on a smooth, thi...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in figure. The wires P1Q1 and P2Q2 are ma...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose the 19 Omega resistor of the previous problem is disconnected....
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in . The wire PQ has a negligible resist...
Text Solution
|
- The current generator I g, shown in . Sends a constant current I throu...
Text Solution
|
- The current generator ig, shown in , sends a constant current I throu...
Text Solution
|
- The system containing the rails and the wire of the previous problem i...
Text Solution
|
- The rectangualr wire- frame, shown in has a width d, mass m, resist...
Text Solution
|
- Shows a smooth pair of thick metallic rails connected across a battery...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting wire ab of length l, resistance r and mass m starts slidi...
Text Solution
|
- A bicycle is resting on its stand in the east - west direction and the...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting disc of radius r rotaes with a small but constant angul...
Text Solution
|