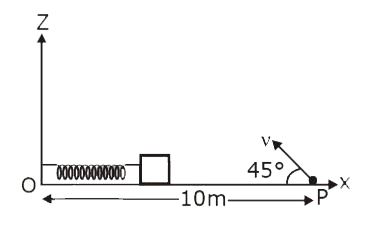
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SL ARORA-Motion in a Plane-Excercise
- A boat which has a speed of 6km/h in still water crosses a river of wi...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travelling in the direction 1/2 (hati+sqrt(3)hatj) is i...
Text Solution
|
- A small block is connected to one end of a massless spring of un-stret...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a disc rotating in the horizontal plane with a constant angul...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical discs of same radius R are rotating about their axes in ...
Text Solution
|
- The coordinate of a particle moving in a plane are given by x(t) = ...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass 1 kg is a circular are of ratius 40 m . The blo...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass 1 kg is a circular are of ratius 40 m . The blo...
Text Solution
|
- Airplanes A and B are flying with constant velocity in the same vertic...
Text Solution
|
- Two vectors vecA and vecB are defined as vecA=ahati and vecB=a( cos om...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected form the ground at an angle of 45^(@) with the hor...
Text Solution
|
- Two forces are such that the sum of their magnitudes is 18N and their ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving eastwards with a velocity of 5 ms(-1). In 10 sec...
Text Solution
|
- The coordinates of a moving particle at any time t are given by x=alph...
Text Solution
|
- A vector vecA ur is rotated by a small angle triangletheta radian (tri...
Text Solution
|
- A particle has an initial velocity 3hati+4hatj and an accleration of 0...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a rubber ball freely falling from a height h = 4.9 m on a hor...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving with velocity vecv = k( y hat(i) + x hat(j)) , w...
Text Solution
|
- A boy playing on the roof of a 10 m high building throws a ball with a...
Text Solution
|
- A projectile can have the same range R for two angles of projection .I...
Text Solution
|