Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-C (NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION) (LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESITONS)|5 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-D (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs))(MCQs FROM .DARPAN. BASED ON TEXTBOOK)|26 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-C (NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION) (VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESITONS)|5 VideosMOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION D (MCQs ASKED IN COMPETITIVE EXAMS)|34 VideosSAMPLE QUESTION PAPER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise PART-B SECTION-C|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS-SECTION-C (NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION) (SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESITONS)
- A short object of length L is placed along the principal axis of a con...
Text Solution
|
- A cicular disc of radius R is placed co-axially and horizontally insi...
Text Solution
|
- A thin convex lens of focal length 25 cm is cut into tow pieces 0.5 c...
Text Solution
|
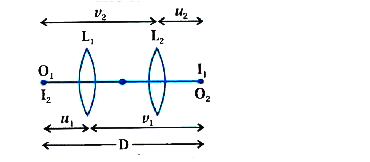
- In many experimental set-ups, the source and screen are fixed at a dis...
Text Solution
|
- A jar of height h is filled with a transparent liquid of refractive in...
Text Solution
|
- A myopic adult has a far point at 0.1 m. His power of accomodation is ...
Text Solution
|