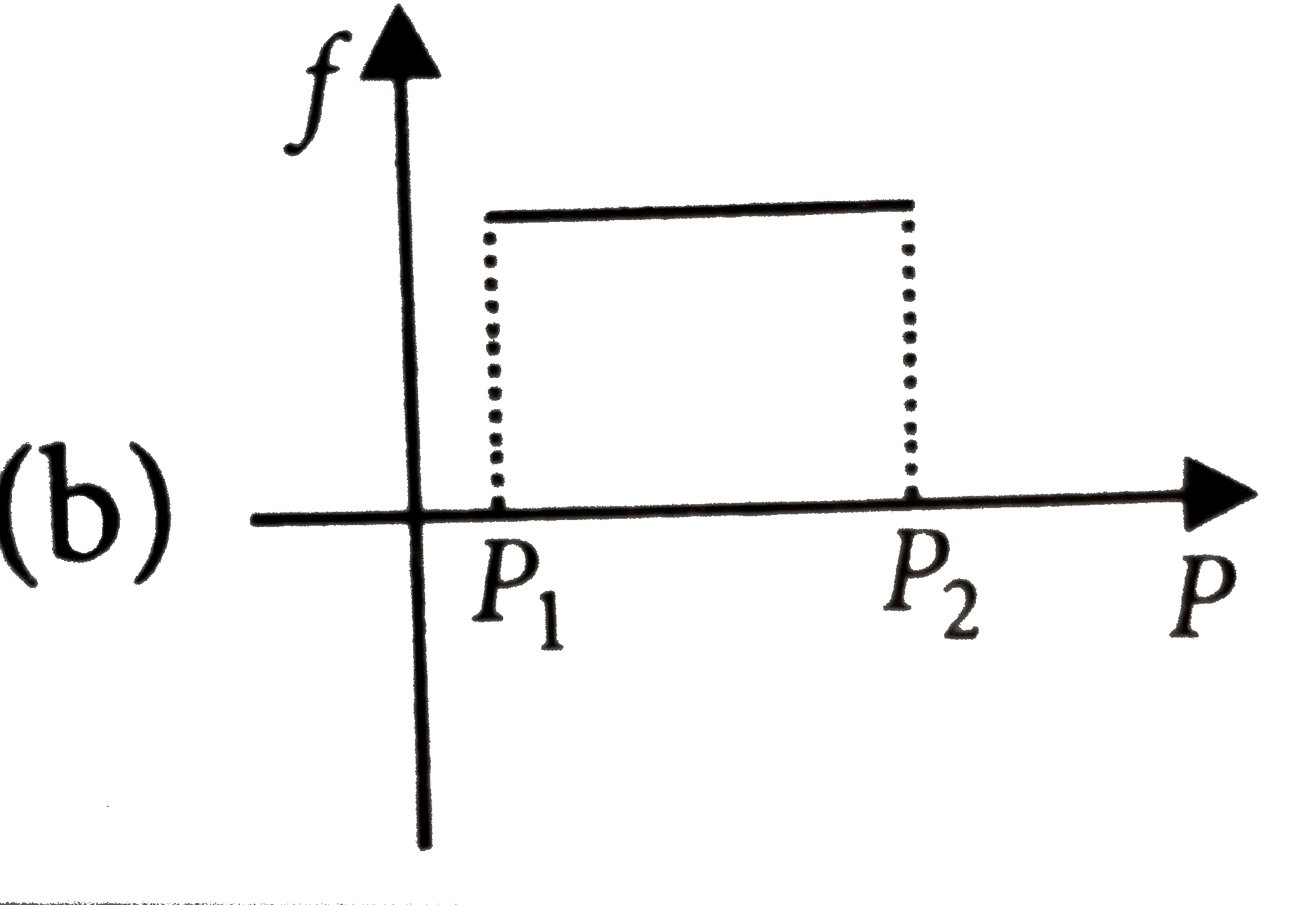
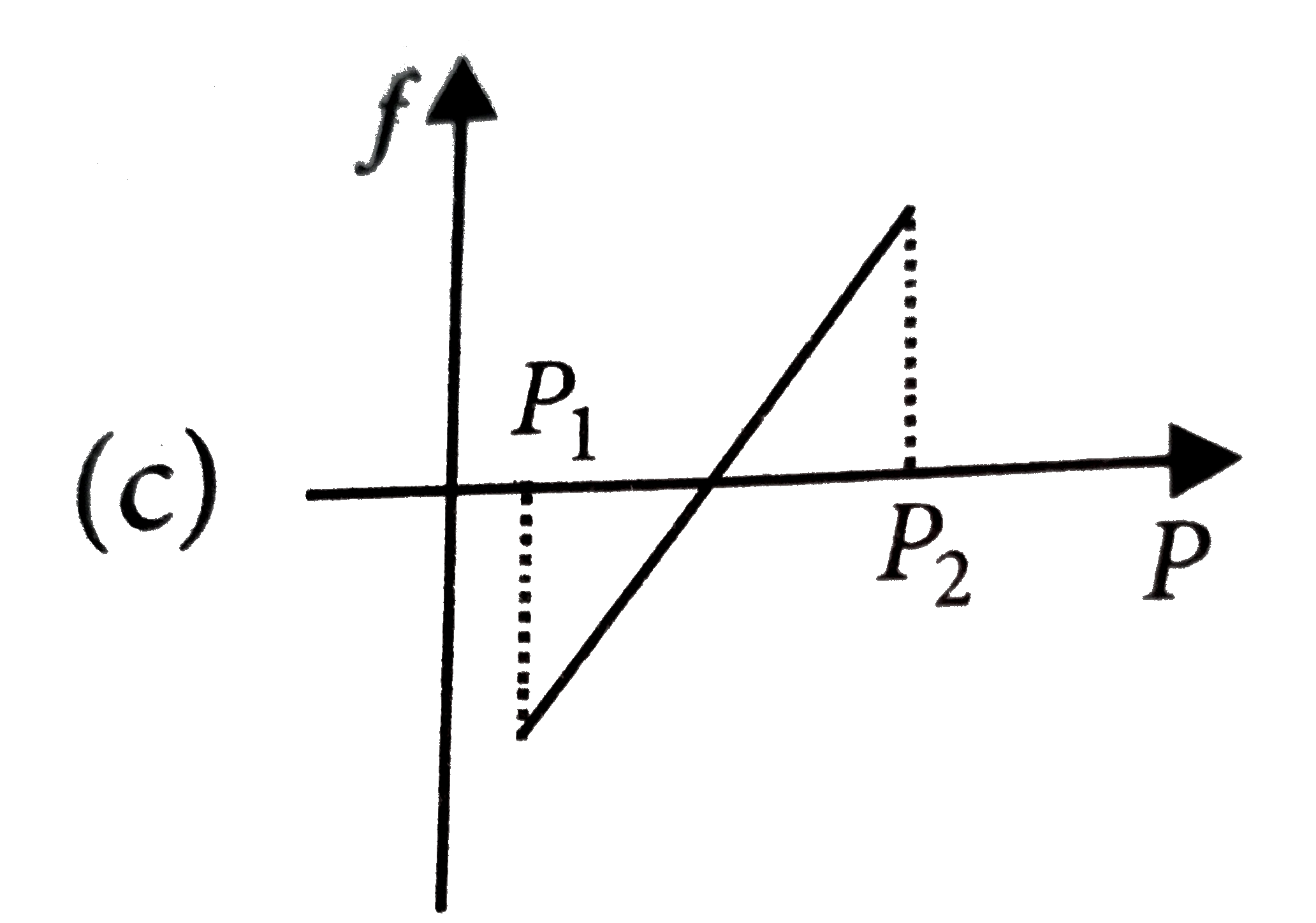
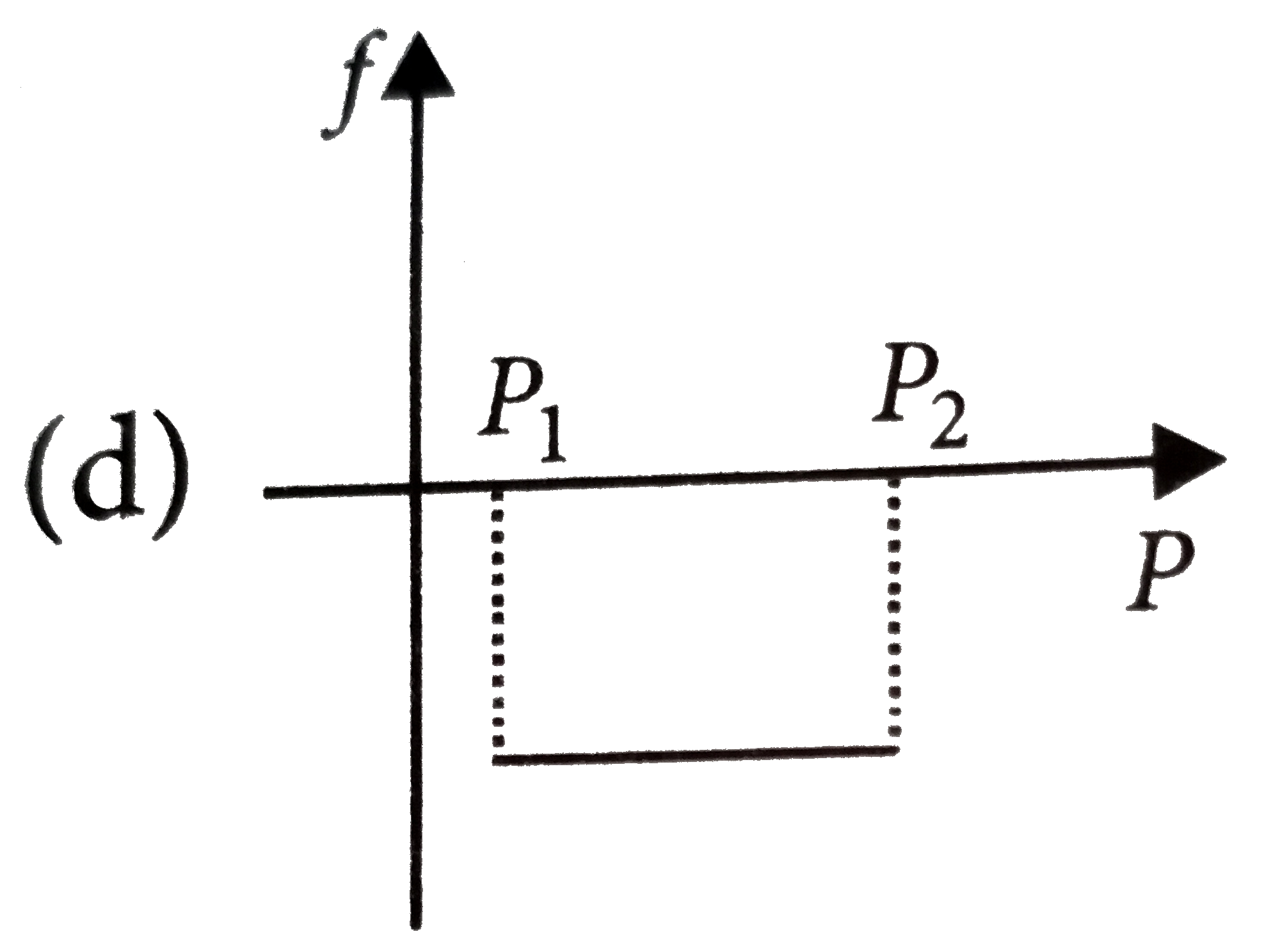
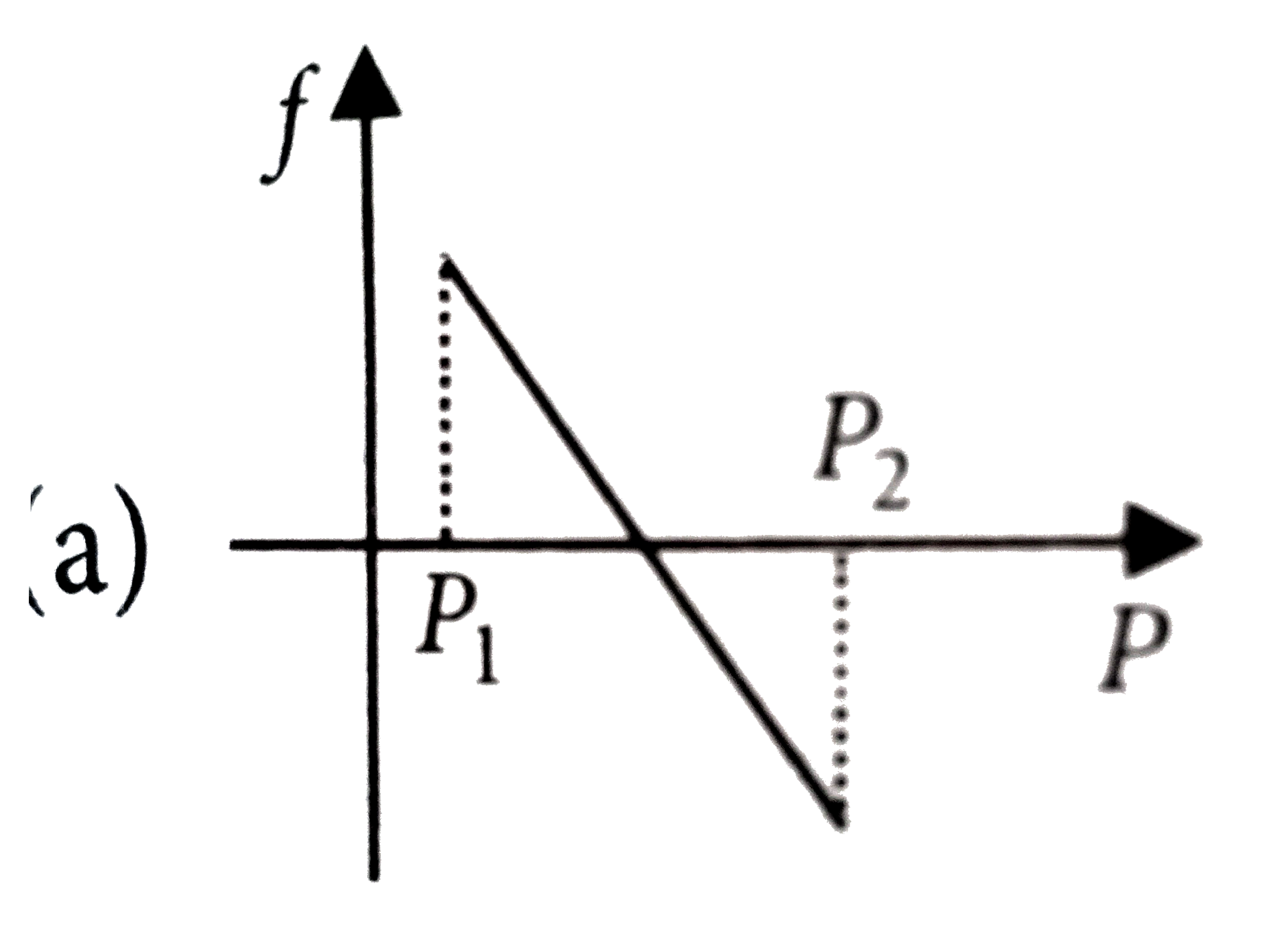A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
LAWS OF MOTION
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Exemplar Problems|9 VideosLAWS OF MOTION
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion & Reason|15 VideosLAWS OF MOTION
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosKINETIC THEORY
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|10 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise NCERT Exemplar|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH-LAWS OF MOTION-HOTS
- Two identical small masses each of mass m are connected by a light ine...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is on an inclined plane of angle theta. The coeffici...
Text Solution
|
- When body slides down from rest along smooth inclined plane making ang...
Text Solution
|
- What is the maximum value of the force F such that the block shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- A string of negligible mass going over a clamped pulley of mass m supp...
Text Solution
|
- Assuming all the surface to be frictionless. The smaller block m is m...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a surface with a vertical cross section...
Text Solution
|
- A piece of wire is bent in the shape of a parabola y=kx^(2) (y-axis ve...
Text Solution
|