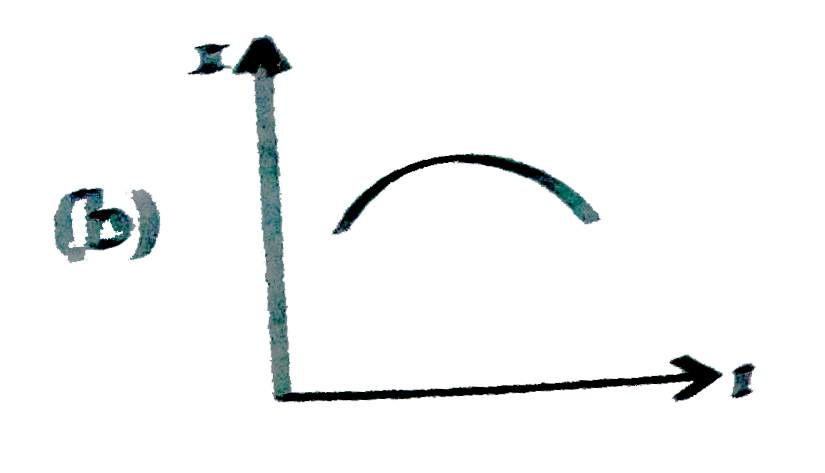A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise KINEMATIC EQUATIONS FOR UNIFORMLY ACCELERATED MOTION|32 VideosMOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise RELATIVE VELOCITY|18 VideosMOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise INSTANTANEOUS VELOCITY AND SPEED|16 VideosMOTION IN A PLANE
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosOSCILLATIONS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH-MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE-ACCELERATION
- The displacement of a body is proporticonal to the cube of time elapse...
Text Solution
|
- Match Column I with Column II.
Text Solution
|
- The slope of the tangent at a point on the curve of concentration of a...
Text Solution
|
- The area under acceleration-time graph gives
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements is not correct regarding the motion ...
Text Solution
|
- Match the Column I with Column II.
Text Solution
|
- A particle moving along a straight line has a velocity v m s^(-1), whe...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves rectilinearly. Its displacement x at time t is given ...
Text Solution
|
- A car starts from rest, attain a velocity of 36 km h^(-1) with an acce...
Text Solution
|
- A point moves with a uniform acceleration and v1 ,v2, v3 denote the a...
Text Solution
|
- A particle starts from point A moves along a straight line path with a...
Text Solution
|
- For the one dimensional motion, described by x=t-sint
Text Solution
|
- Position-time graph for motion with zero acceleration is
Text Solution
|
- The velocity -displacement graph of a particle is as shown in the figu...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity-time graph of a particle in one-dimensional motion is sho...
Text Solution
|
- Given below are four curves describing variation of velocity with time...
Text Solution
|
- The speed-time graph of a particle moving along a fixed direction is s...
Text Solution
|
- The given acceleration-time graph represents which of the following ph...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows a particle moving along x - axis subjected to three p...
Text Solution
|