A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MOTION IN A PLANE
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise HOTS|6 VideosMOTION IN A PLANE
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise EXEMPLER PROBLEMS|9 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosMOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise NCERT Exemplar|6 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH-MOTION IN A PLANE -Assertion And Reason
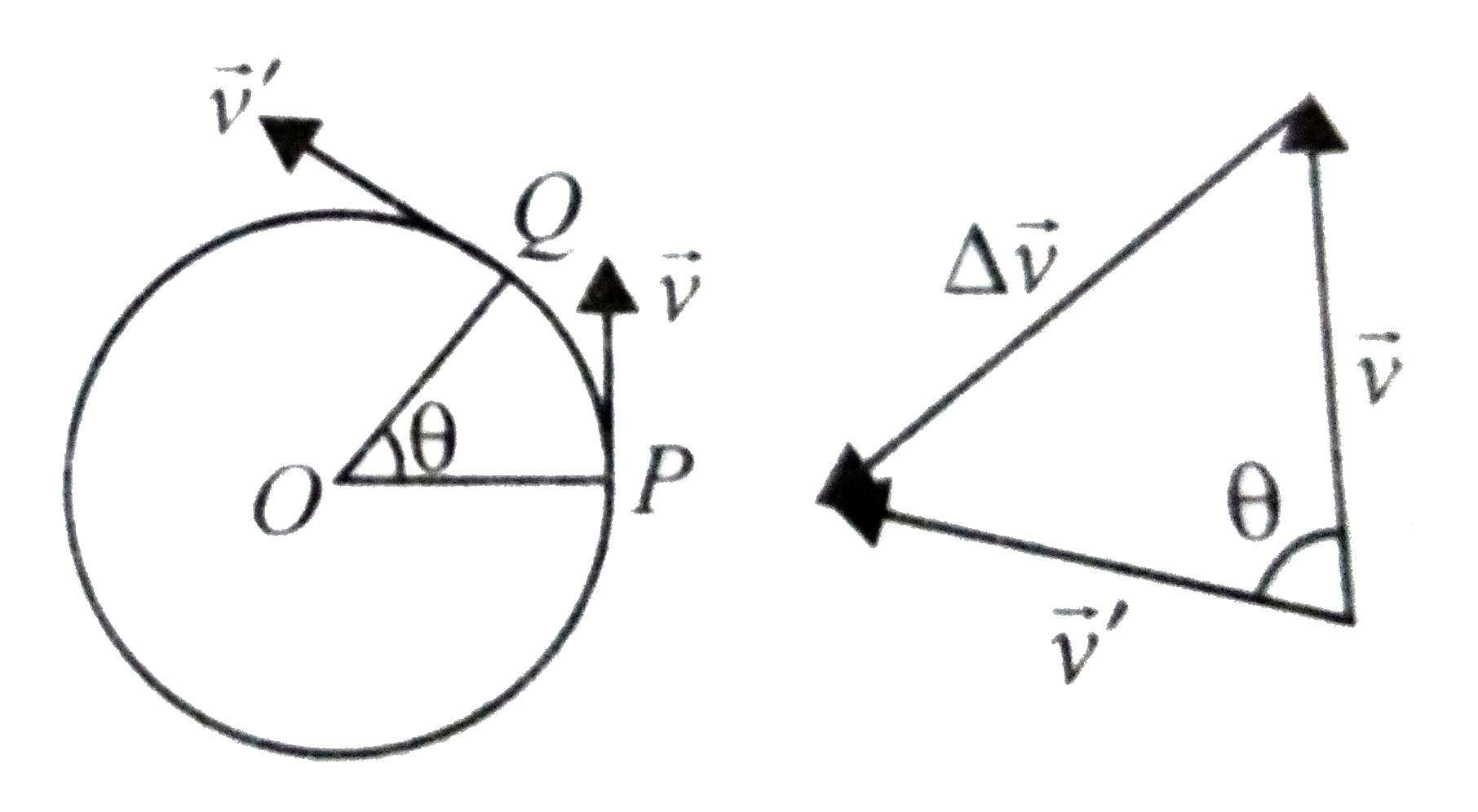
- A particle is moving on a circular path with a constant speed v. It...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Two vectors are said to be equal if , and only if, they hav...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Vector addition is commutative. Reason: Two vectors may b...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: The difference of two vectors A and B can be treated as the...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: For motion in two or three diemensions, velocity and accel...
Text Solution
|
- Asserion: Magnitude of the resultant of two vectors may be less than t...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : An object has given two velocities vecv(1) and vecv(2) has...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : A vector vecA can be resolved into component along with gi...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: If hat(i) and hat(j) are unit Vectors along x-axis and y-ax...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Rain is falling vertically with a certain speed. A boy hold...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : The instantaneous velocity is given by the limiting value ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: The trajectory of an object moving under the same acclerati...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: A projectile that traverses a parabolic path show deviation...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : A projectile should have two component velocities in two m...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Centripetal acceleration is always direction towards the ce...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: A uniform circular motion is an acceleration motion. Reas...
Text Solution
|