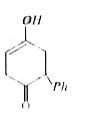
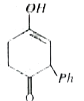
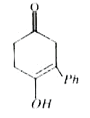
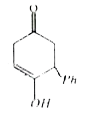
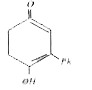
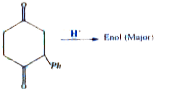A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ISOMERISM
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise LECTURE SHEET (EXERCISE-I (INTEGER TYPE QUESTIONS))|3 VideosISOMERISM
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise LECTURE SHEET (EXERCISE-II (STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS))|22 VideosISOMERISM
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise LECTURE SHEET (EXERCISE-I (MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS))|3 VideosIONIC EQUILIBRIUM
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise ADDITIONAL PRACTICE EXERCISE (LEVEL -II PRACTICE SHEET (ADVANCED) (Integer Type Questions))|8 VideosPERIODIC CLASSIFICATION
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise OBJECTIVE EXERCISE - 3 (RECENT AIPMT/NEET QUESTIONS)|14 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems