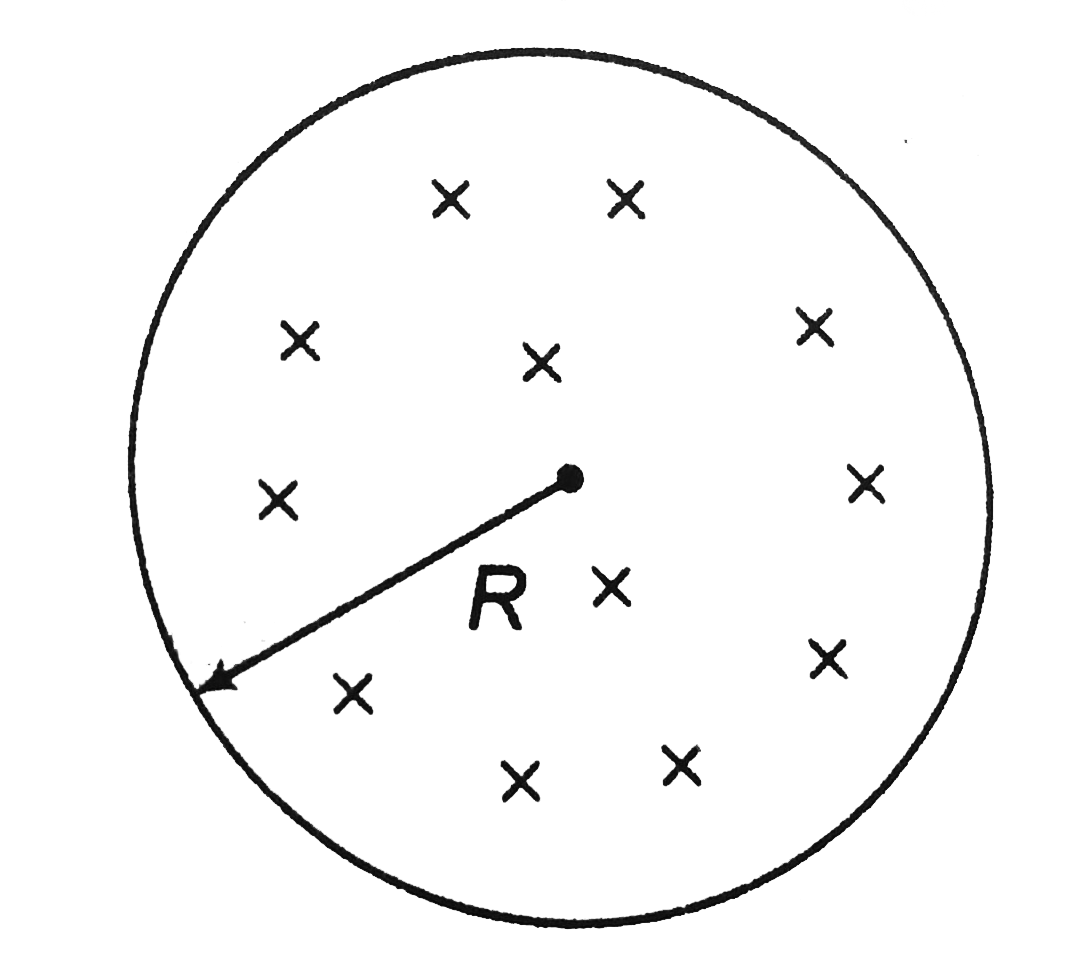
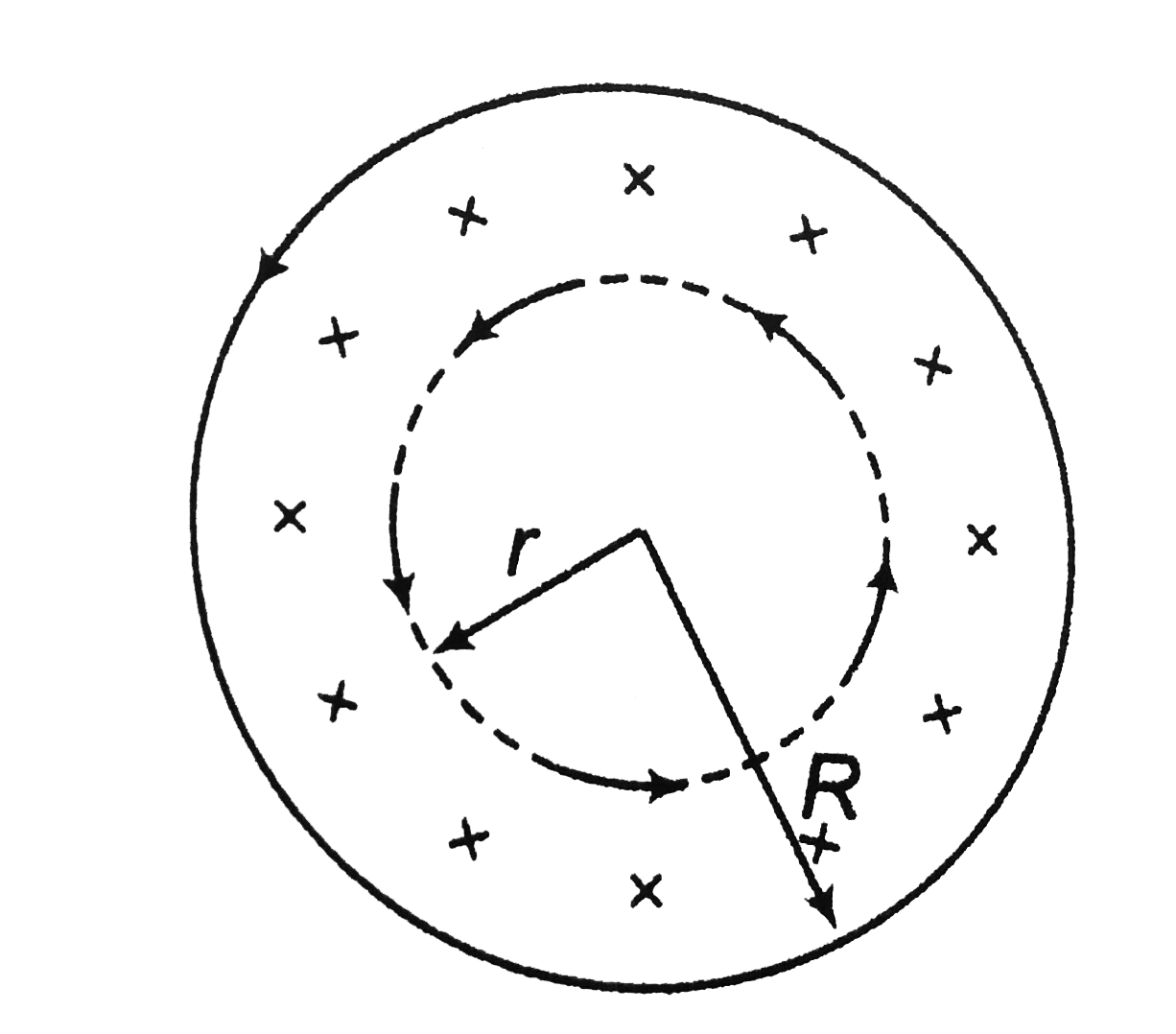
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Check point|60 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Taking it together|119 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Level 2 Subjective|20 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Medical entrances gallery|97 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Sec C|22 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-Example
- A 5H inductor is placed in series with a 10Omega resistor. An emf of 5...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor of capacitance 25muF is charged to 300V. It is then connec...
Text Solution
|
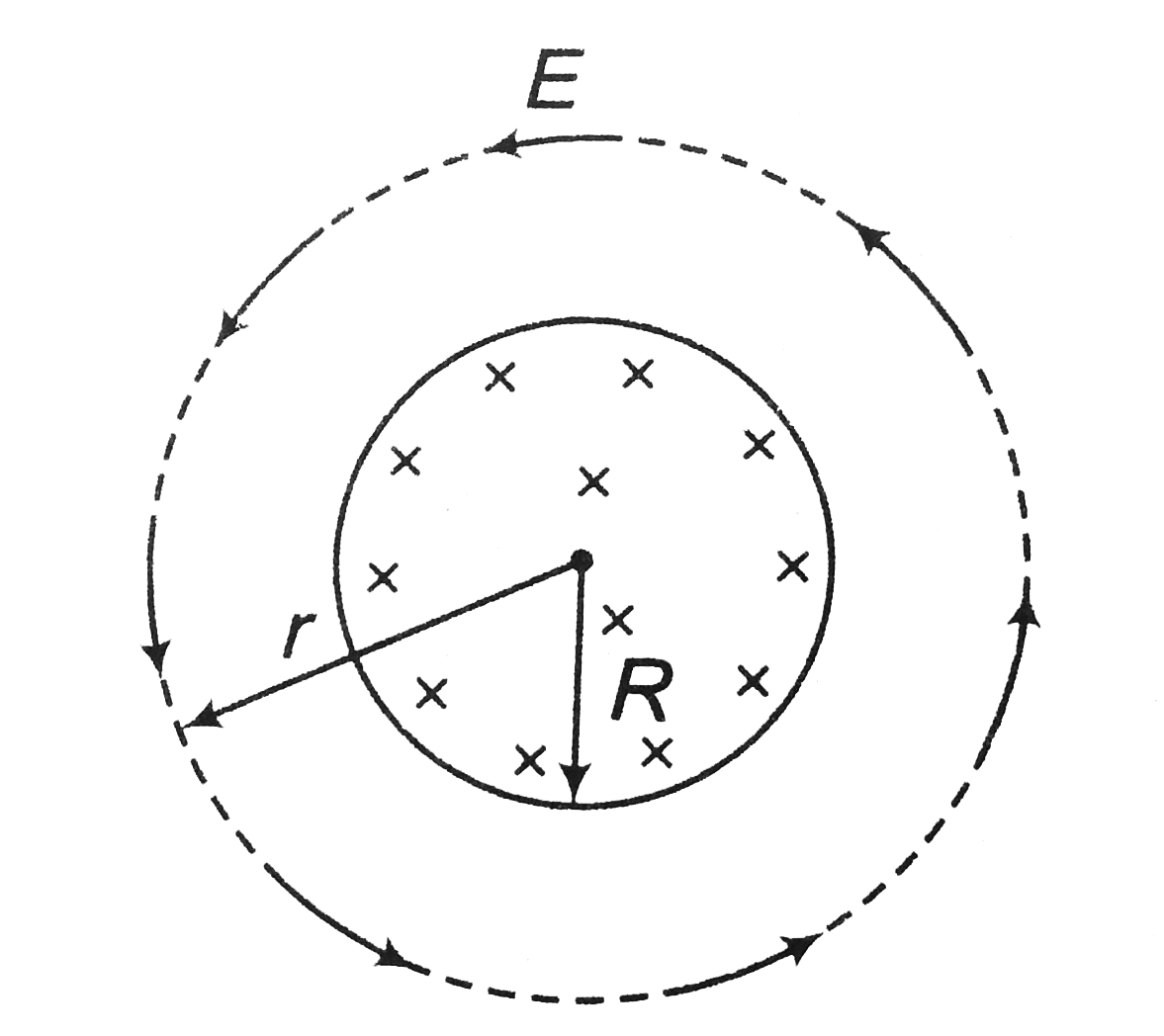
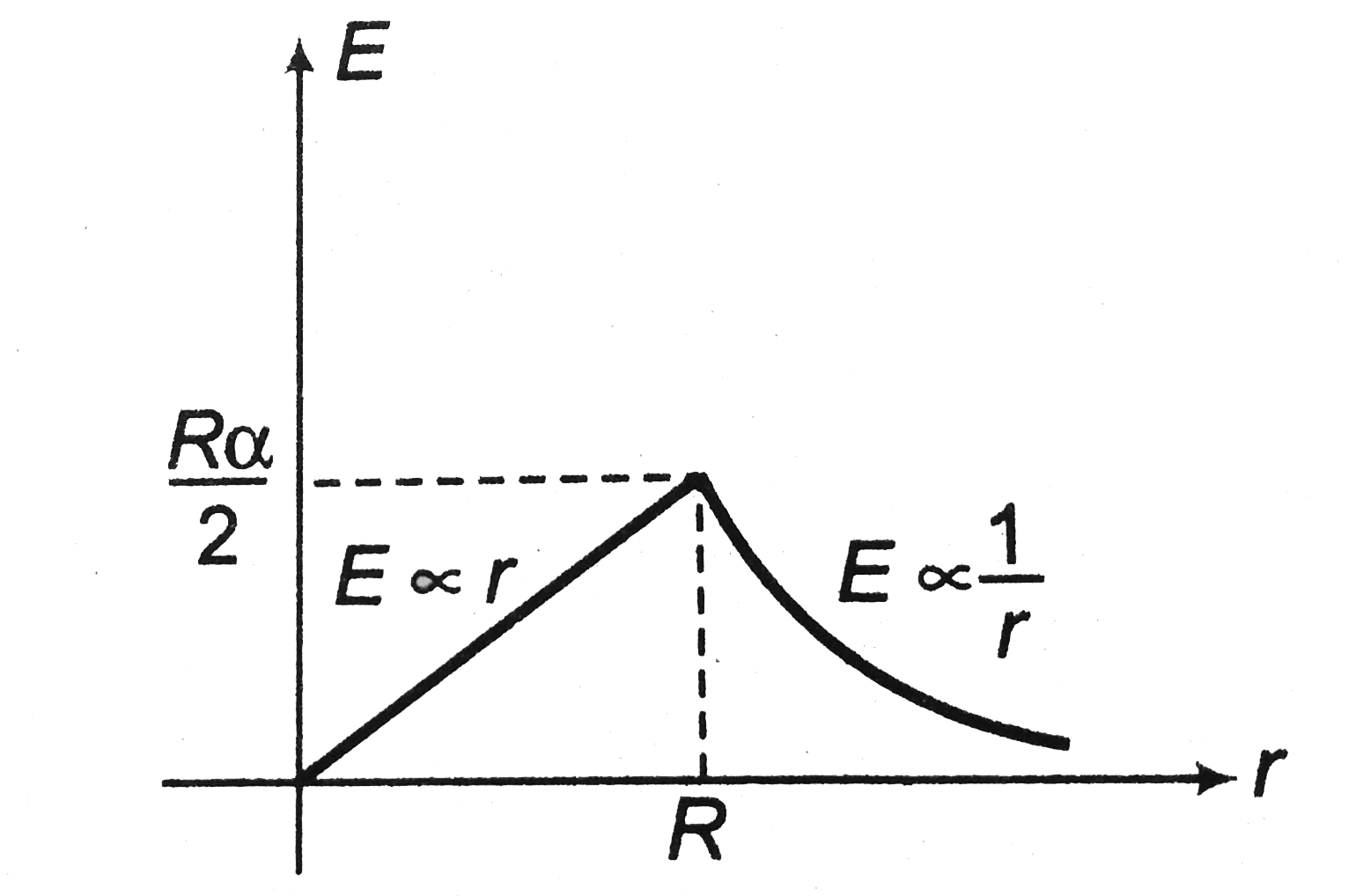
- The magnetic field at all points within the cyllindrical region whose ...
Text Solution
|
- A long thin solenoid has 900"tuns"//"metre" and radius 2.50cm,. The cu...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform magnetic field exists in the space bar B = B(1) hat i+B(2) h...
Text Solution
|
- A long solenoid of radius 4 cm, length 400 cmcarries a current of 3 A....
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a long straight wire carrying current I and a square cond...
Text Solution
|
- A coil with an average diameter of 0.02 m is placed perpendicular to a...
Text Solution
|
- A coil consists of 200 turns of wire having a total reistance of 2.0Om...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic flux passing through a metal ring varies with time t as:...
Text Solution
|
- A square loop of side 10 cm and resistance 0.5 Omega is placed vertica...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of length l in the form of a square loop lies in a plane normal...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose a coil of area 5m^(2), resistance 10Omega and number of turns ...
Text Solution
|
- Through a long solenoid of diameter 4.1 cm, having 100 turns per cm, a...
Text Solution
|
- A square loop of edge b having M turns is rotated with a uniform angul...
Text Solution
|
- A square loop ACDE of area 20 cm^2 resistance 5Omega is rotate in as...
Text Solution
|
- The two conducting rails are placed perpendicular to each other, such ...
Text Solution
|
- A bar magnet is freel falling along the axis of a circular loop as sho...
Text Solution
|
- A bar magnet is brought near a solenoid as shown in figure. Will the s...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure currnet from A to B in the straight wire is decrea...
Text Solution
|