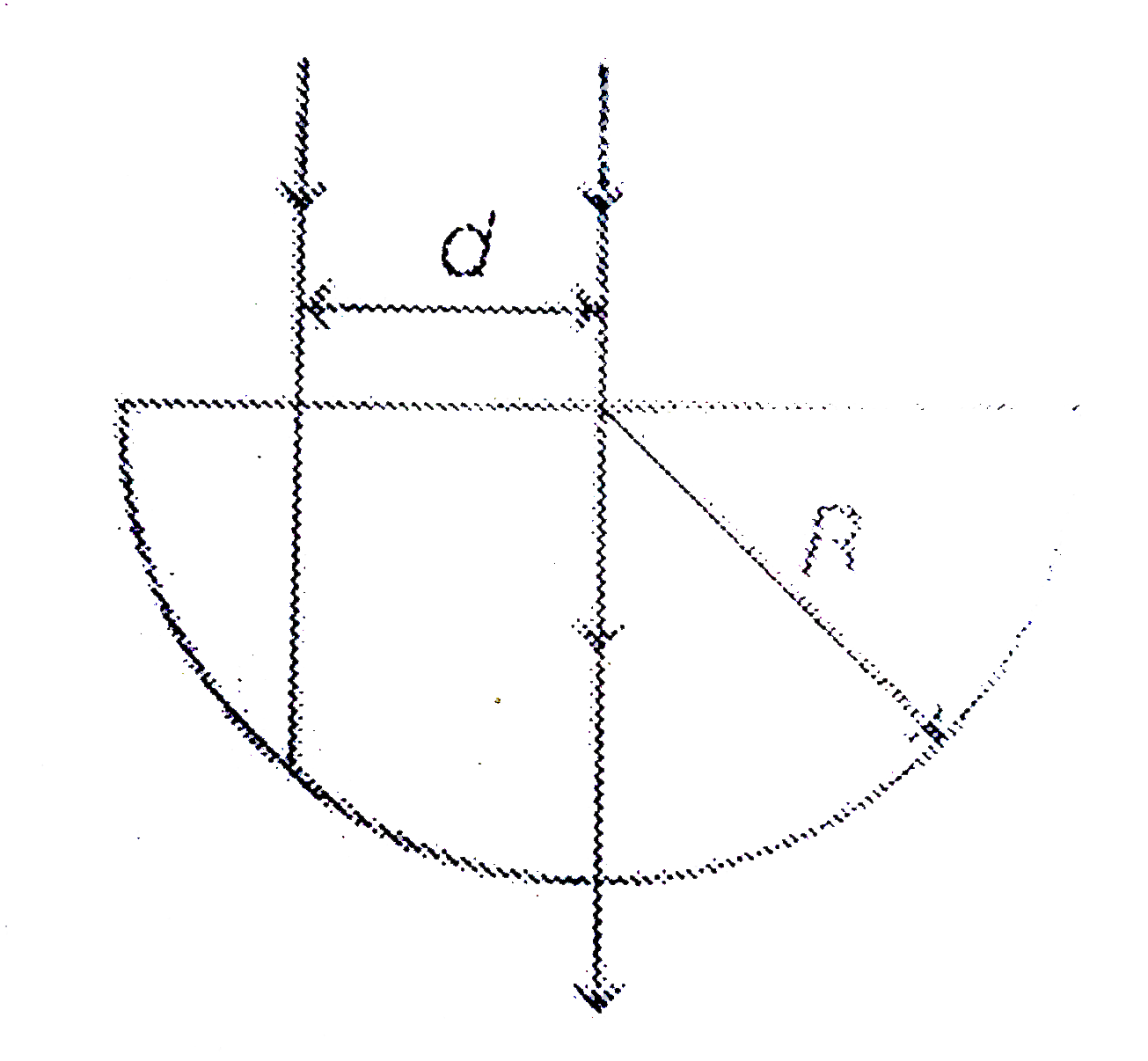A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise A. Only one option is correct (JEE Advance)|73 VideosRAY OPTICS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise B. More than one option is correct|20 VideosPROPERTIES OF MATTER
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|8 VideosROTATION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise (C) Chapter Exercises|39 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-RAY OPTICS-Integer type q.
- As shown, a narrow beam of light is incident onto a semi-circular glas...
Text Solution
|
- When an object is kept at a distance of 30cm from a concave mirror, th...
Text Solution
|
- A point object O is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens of f...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length 30 cm forms a real image three times lar...
Text Solution
|
- In a plano-convex lens radius of curvature of the lens is 10 cm. if th...
Text Solution
|
- How much water should be filled in a container of height 21 cm, so tha...
Text Solution
|
- A plane mirror is placed along the y-axis such that x-axis is normal t...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travelling in glass (mu=3//2) is incident on a horizont...
Text Solution
|
- Assume that you are sitting in a car at rest. You see a person in the ...
Text Solution
|
- A point source of light is placed inside water and a thin converging l...
Text Solution
|
- Image distance |v| vs object distance |u| curve for two biconvex lense...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical equi-concave lenses made of magnitude of combined glass ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the magnitude of velocity of image of a point object O with respe...
Text Solution
|
- A point object located at a distance of 15 cm from the pole of concave...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray is incident on face AB of a prism ABC as shown in figure. ...
Text Solution
|