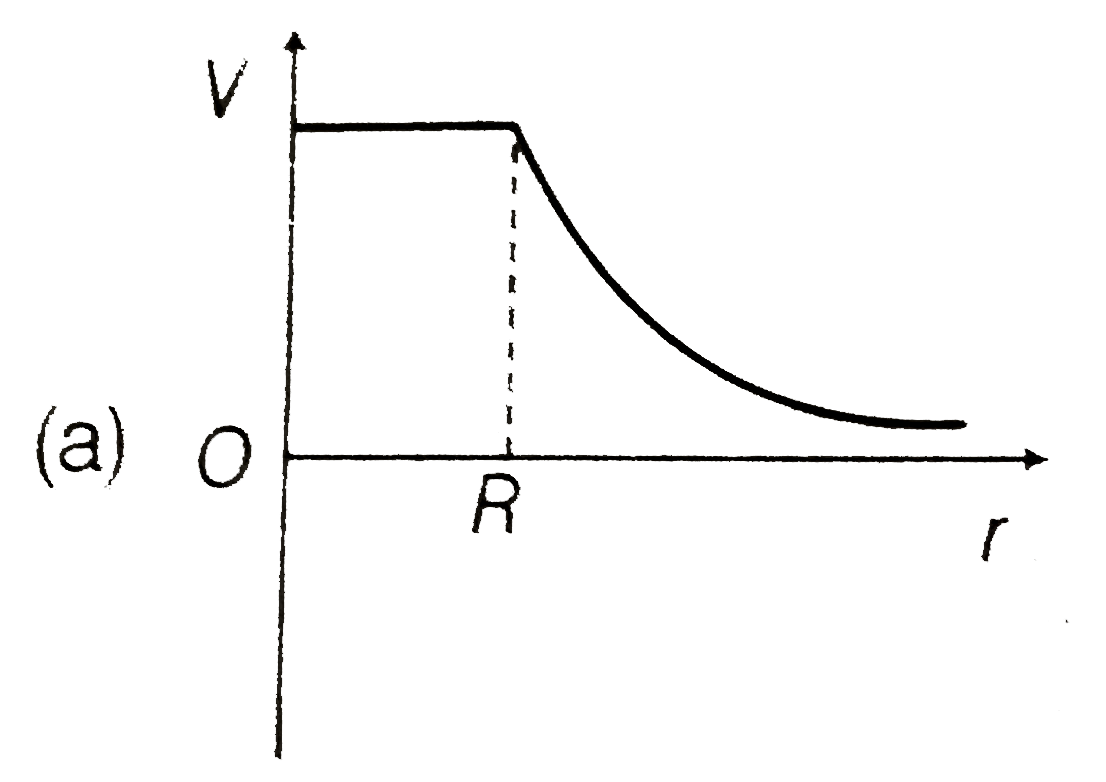
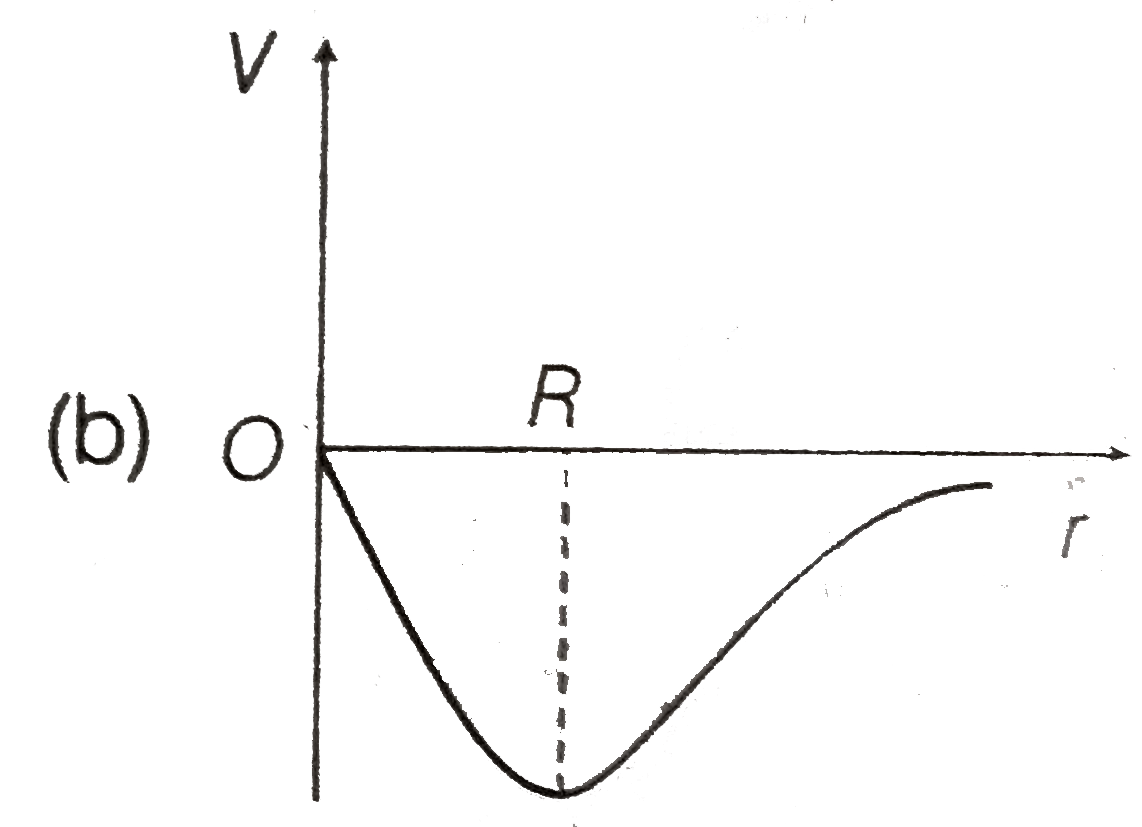
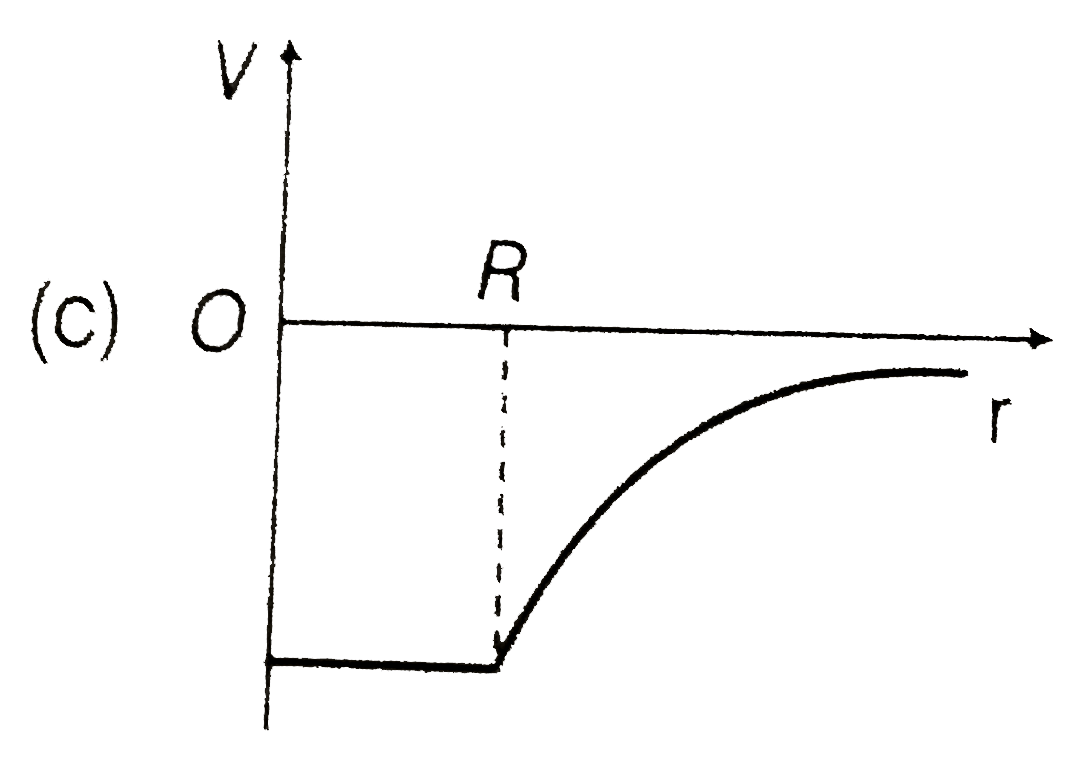A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GRAVITATION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Check Point 10.4|10 VideosGRAVITATION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Check Point 10.5|20 VideosGRAVITATION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Check Point 10.2|20 VideosGENERAL PHYSICS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|2 VideosKINEMATICS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-GRAVITATION-Check Point 10.3
- Three particles each of mass m are kept at vertices of an equilateral ...
Text Solution
|
- At what height the gravitational field reduces by 75 % the gravitation...
Text Solution
|
- Gravitational field due to a solid sphere
Text Solution
|
- A mass m is placed inside a hollow sphere of mass M as shown in figure...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform solid sphere of mass m and radius r is suspended symmetrical...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following plots represents the variation of gravitati...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows two shells of masses m1 and m2 . The shells are concentr...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies of masses m(1) and m(2) are placed distant d apart. Show th...
Text Solution
|
- A thin of length L is bent to form a semicircle. The mass of rod is M....
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 10 g is kept on the surface of a uniform sphere of ...
Text Solution
|
- The diagram showing the variation of gravitational potential of earth ...
Text Solution
|
- Inside a uniform shell
Text Solution
|
- If V is the gravitational potential on the surface of the earth, then ...
Text Solution
|
- By which curve will be variation of gravitational potential of a hollo...
Text Solution
|
- For a uniform ring of mass M and radius R at its centre
Text Solution
|