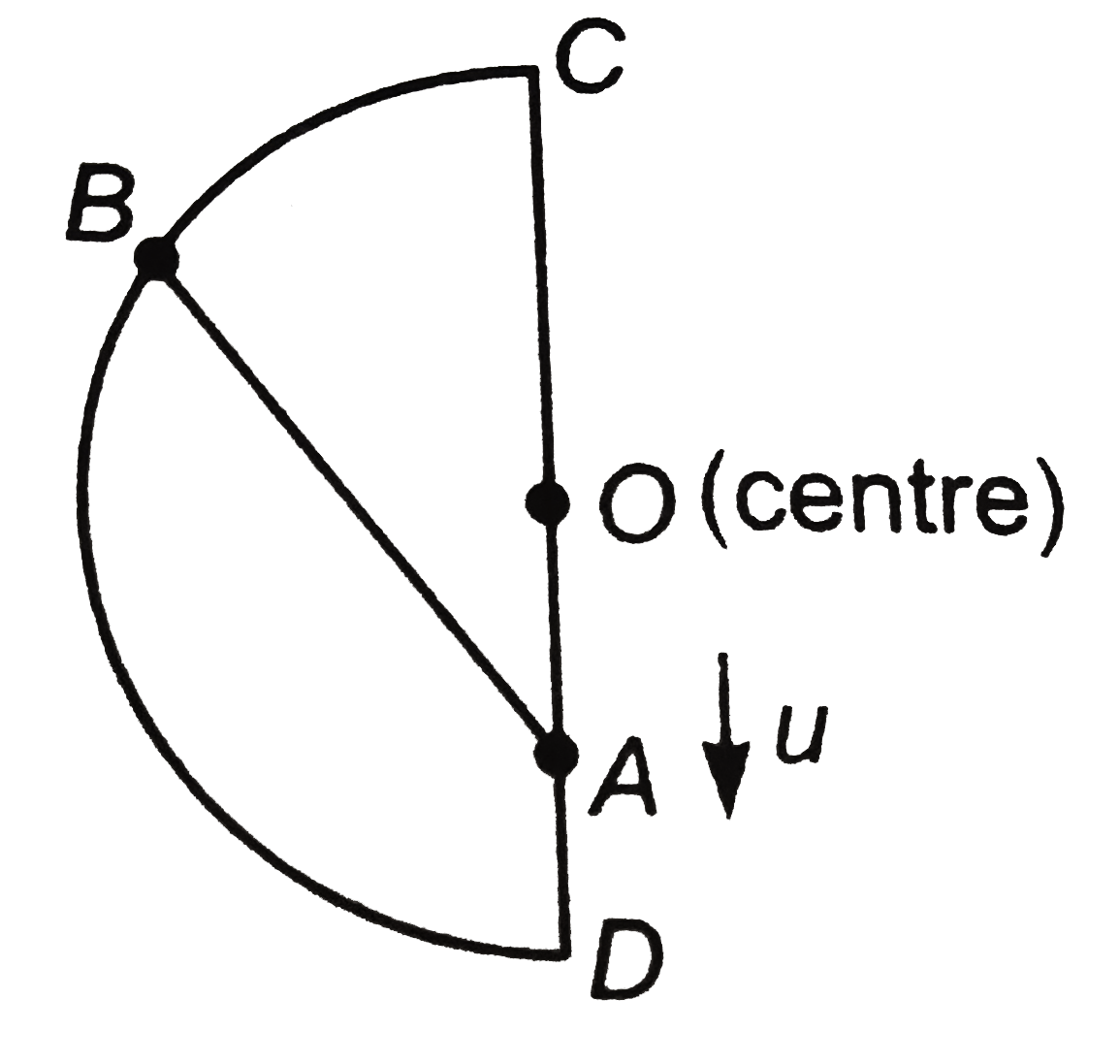
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
LAWS OF MOTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Match the columns|7 VideosLAWS OF MOTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Medical entrances gallery|39 VideosLAWS OF MOTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Check point 5.4|20 VideosKINEMATICS 1
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|15 VideosLAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Level 2 Subjective|18 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-LAWS OF MOTION-Chapter exercises (A) Taking it together
- Two masses m and M are attached with strings as shown. For the system ...
Text Solution
|
- A man has fallen into a ditch of width d and two of his friends are sl...
Text Solution
|
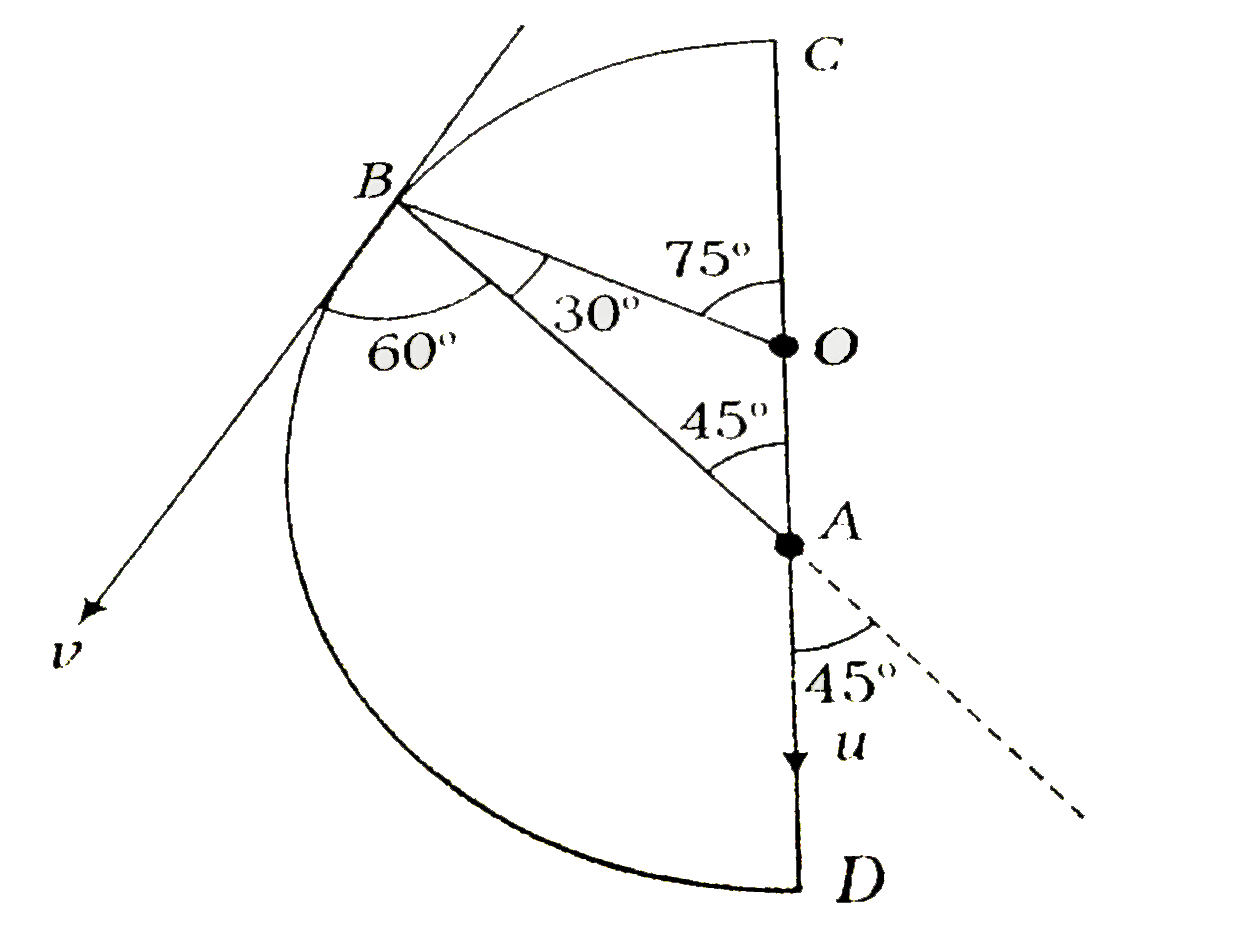
- Two beads A and B move along a semicircular wire frame as shown in fig...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m and 2m are placed one over the other as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- If a body looses half of its velocity on penetrating 3 cm in a wooden ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is moving towards the wall as shown in diagram then its momentu...
Text Solution
|
- Two weights w(1) and w(2) are suspended from the ends of a light strin...
Text Solution
|
- A dynamometer D is attached to two bodies of masses M=6 kg and m=4 kg....
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks are connected over a massless pulley as shown in figure. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 5 kg resting on a horizontal surface is connected by a...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 3kg is at rest on a rough inclined plan as shown in th...
Text Solution
|
- Two block of masses M and m are connected to each other by a massless ...
Text Solution
|
- An insect crawls up a hemispherical surface very slowly. The coefficie...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m lying on a rough horizontal plane is acted upon by a...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown if coefficient of friction is mu, then m(2) will s...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M rests on a rough horizontal surface as shown. Coeffi...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B each of mass m are placed on a smooth horizontal su...
Text Solution
|
- A cube of mass m is placed on top of a wedge of mass 2m, as shown in f...
Text Solution
|
- If the coefficient of friction between all surface figure is 0.4 then...
Text Solution
|
- Block B moves to the right with a constant velocity v(0). The velocity...
Text Solution
|