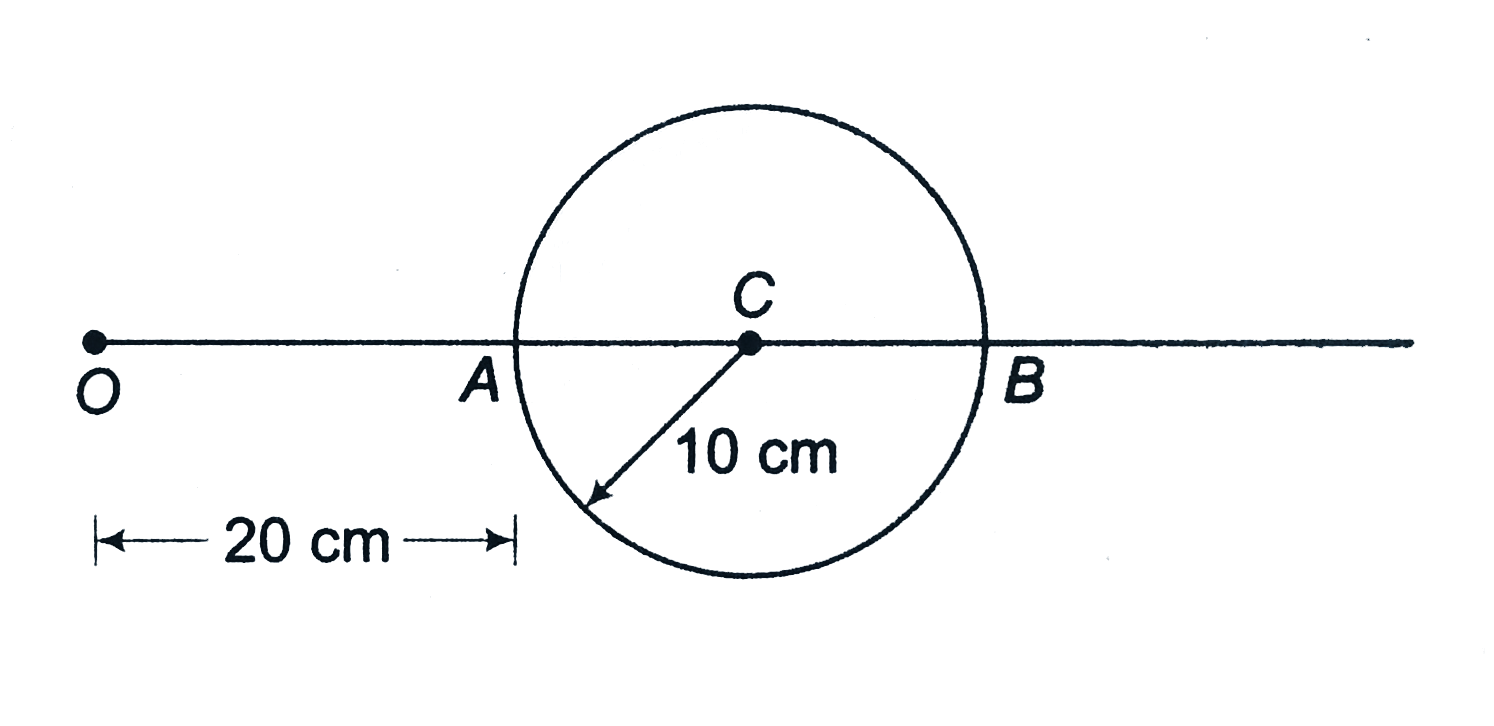
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-RAY OPTICS-Medical entrance gallary
- A glass sphere of radius R=10cm is kept inside water. A ponit object ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical glass (mu(g)=3//2) equi- convex lenses of focal length f...
Text Solution
|
- An air bubble in a glass slab with refractive index 1.5 (near normal i...
Text Solution
|
- A person can see clearly objects only when they lie between 50 cm and ...
Text Solution
|
- An astronomical telesope has objective and eyepiece of focal lengths 4...
Text Solution
|
- Match the corresponding entries of Column I with Column II.
Text Solution
|
- The angle of incidence for a ray of light at a refracting surface of a...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical thin planoconvex glass lenses (refractive index 1.5) eac...
Text Solution
|
- The refracting angle of a prism is A and refractive index of the mater...
Text Solution
|
- The near point and far point of a person are 40cm and 250cm, respectiv...
Text Solution
|
- An object is seen thorugh a simple microscope of focal length 12 cm. F...
Text Solution
|
- Angle of minimum deviation for a prism of refractive index 1.5 is equa...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light passes from a medium A having refractive index 1.6 to t...
Text Solution
|
- The focal length of a converting lens are f(v) and f(r) for violet and...
Text Solution
|
- Aperture of human eye is 0.2cm. The minimum magnifying power of a visa...
Text Solution
|
- An object is located 4cm from the first of two thin converging lenses ...
Text Solution
|
- If mu(v)=1.530 and mu(R)=1.5145, then disperisve power of a crown glas...
Text Solution
|
- Disperion of light is caused due to
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the focal length of a reading glass of a person, if the dist...
Text Solution
|
- A person wants a real image of his own, 3 times enlarged. Where should...
Text Solution
|
- The magnification power of a convex lens of focal length 10cm, when th...
Text Solution
|