Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ANNUAL EXAM QUESTION PAPER MARCH-2020
SUNSTAR PUBLICATION|Exercise Part-D|11 VideosANNUAL EXAM QUESTION PAPER MARCH-2020
SUNSTAR PUBLICATION|Exercise Part-B|8 VideosANNUAL EXAM QUESTION PAPER MARCH -2015
SUNSTAR PUBLICATION|Exercise PART-A|37 VideosII PUC PHYSICS (P.U. BOARD LATEST MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER -2)
SUNSTAR PUBLICATION|Exercise PART-D|11 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SUNSTAR PUBLICATION-ANNUAL EXAM QUESTION PAPER MARCH-2020-Part-C
- Derive a relation between electric field and potential
Text Solution
|
- Derive the expression for energy stored in a charged capacitor.
Text Solution
|
- Give the principle of cyclotron and draw the neat labelled schematic d...
Text Solution
|
- Mention any three properties of diamagnetic substance.
Text Solution
|
- Define focal length of a mirror and hence relate focal length and radi...
Text Solution
|
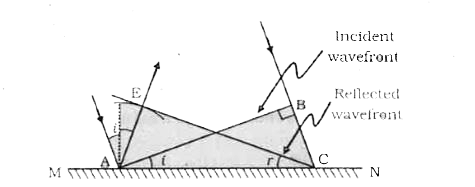
- Using Huygens principle, show that the angle of incidence is equal to ...
Text Solution
|
- Define work function. Write Einstein's photoelectric equation and expl...
Text Solution
|
- Give three differences between intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors
Text Solution
|