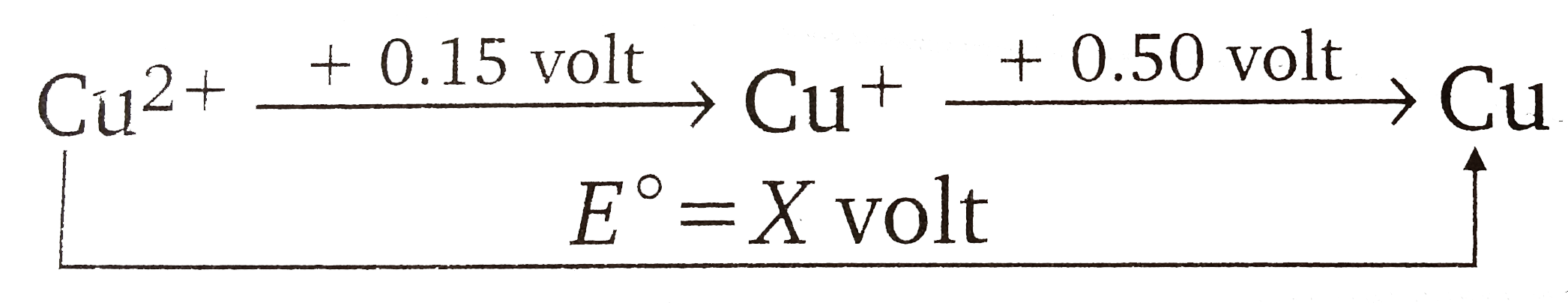Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMOTIVE FORCE
RC MUKHERJEE|Exercise PROBLEMS |26 VideosELECTROMOTIVE FORCE
RC MUKHERJEE|Exercise EXERCISE |1 VideosELECTROLYSIS AND ELECTROLYTIC CONDUCTANCE
RC MUKHERJEE|Exercise Objective Problems|39 VideosELEMENTARY PROBLEMS BASED ON DEFINITION OF MOLE: THE MOLE CONCEPT
RC MUKHERJEE|Exercise OBJECTIVE PROBLEMS |29 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems