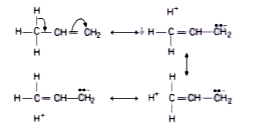
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
ICSE|Exercise ASSERTION - REASON TYPE QUESTIONS|11 VideosHYDROGEN
ICSE|Exercise NCERT TEXT-BOOK EXERCISE (With Hints and Solutions)|53 VideosREDOX REACTIONS (OXIDATION AND REDUCTION)
ICSE|Exercise NCERT TEXT-BOOK. EXERCISES ((With Hints and Solutions)|69 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ICSE-ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES -NCERT TEXT-BOOK EXERCISES (WITH HINTS AND SOLUTIONS )
- Identify the functional groups is the following compounds:
Text Solution
|
- Which of the two: O(2)NCH(2)CH(2)O^(–) or CH(3)CH(2)O^(–) is expecte...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why alkyl groups act as electron donors when attached to a n s...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the resonance structures for the following compounds. Show the el...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the resonance structures for the following compounds. Show the el...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the resonance structures for the following compounds. Show the el...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the resonance structures for the following compounds. Show the el...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the resonance structures for the following compounds. Show the el...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the resonance structures for the following compounds. Show the el...
Text Solution
|
- What are electrophiles and nucleophiles ? Explain with examples.
Text Solution
|
- Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equations as nucl...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equations as nucl...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equations as nucl...
Text Solution
|
- Classify the following reactions in one of the reaction type studied i...
Text Solution
|
- Classify the following reactions in one of the reaction type studied i...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the following reactions as either oxidation or reduction : Cl...
Text Solution
|
- What is Electrophiles?
Text Solution
|
- What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of str...
Text Solution
|
- What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of str...
Text Solution
|
- What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of str...
Text Solution
|