Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
ICSE|Exercise ASSERTION - REASON TYPE QUESTIONS|11 VideosHYDROGEN
ICSE|Exercise NCERT TEXT-BOOK EXERCISE (With Hints and Solutions)|53 VideosREDOX REACTIONS (OXIDATION AND REDUCTION)
ICSE|Exercise NCERT TEXT-BOOK. EXERCISES ((With Hints and Solutions)|69 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ICSE-ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES -NCERT TEXT-BOOK EXERCISES (WITH HINTS AND SOLUTIONS )
- What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of str...
Text Solution
|
- What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of str...
Text Solution
|
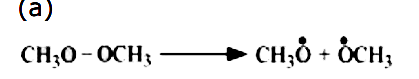
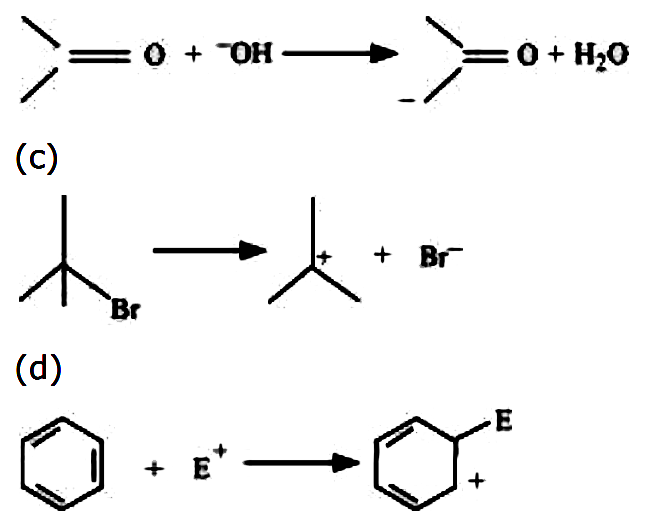
- For the following bond cleavages, use curved-arrows to show the electr...
Text Solution
|
- For the following bond cleavages, use curved-arrows to show the electr...
Text Solution
|
- For the following bond cleavages, use curved-arrows to show the electr...
Text Solution
|
- For the following bond cleavages, use curved-arrows to show the electr...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the terms Inductive and Electromeric effects. Which electron d...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the terms Inductive and Electromeric effects. Which electron d...
Text Solution
|
- Give a brief description of the principles of the following techniques...
Text Solution
|
- Give a brief description of the principles of the following techniques...
Text Solution
|
- Give a brief description of the principles of the following techniques...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the method, which can be used to separate two compounds with ...
Text Solution
|
- What is the difference between distillation, distillation under reduce...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the chemistry of Lassaigne’s test.
Text Solution
|
- Differentiate between the principle of estimation of nitrogen in an or...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the principle of estimation of halogens, sulphur and phosphoru...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the principle of paper chromatography.
Text Solution
|
- Why is nitric acid added to sodium extract before adding silver nitrat...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the reason for the fusion of an organic compound with metallic...
Text Solution
|
- Name a suitable technique of separation of the components from a mixtu...
Text Solution
|