Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ICSE-ICSE EXAMINATION PAPER 2020 -SECTION - B
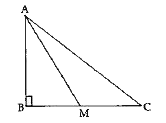
- ABC is a triangle, right angled at B, M is a point on BC. Prove that :...
Text Solution
|
- If 13 sin A = 12 Find sec A - tan A.
Text Solution
|
- A sum of Rs. 10,000 yields Rs. 3310 as compound interest in 3 years. I...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure O is the centre of the two concentric circles. A l...
Text Solution
|
- If the mean of the observations a, a + 6, a + 2, a + 8 and a + 4 is 11...
Text Solution
|
- Factorize : 25a^(2) - 9b^(2) + 12bc - 4c^(2)
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure ABCD is trapezium, P is the mid-point of side AD a...
Text Solution
|
- Solve the following pair of linear equations using cross multiplicatio...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure ABCD is a quadrilateral. BP is drawn parallel to A...
Text Solution
|
- The cost of moving a circular field at Rs. 16 per sq m is Rs. 2464, fi...
Text Solution
|
- In the given triangle ABC, AD bot BC. AB = 13 cm, BD = 5 cm, DC = 4 cm...
Text Solution
|
- log(2)a = 3, log(3)b = 2, log(4) c = 1 Find the value of 3a + 2b - 1...
Text Solution
|
- Use graph paper for this equation. Draw the graph of 3x-2y=5 and 2x=3y...
Text Solution
|
- Solve for x. (root(3)((3)/(5)))^(2x + 1) = (125)/(27)
Text Solution
|
- If 1 is subtracted from the numerator of a fraction is becomes (2)/(3)...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, PQR is a triangle where PS, QS and RS are the bis...
Text Solution
|
- Evaluate without using trigonometric tables : tan 20.tan 40^(@) tan ...
Text Solution
|
- Factorize : x^(3) - 3x^(2) + x - 3
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, 'O' is the centre of the circle, Arc AB = Arc BC ...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a parallelogram in which angle DAB = 80^(@). Bisector of angle...
Text Solution
|
- Given three points P(-1, 2), A(2, k) and B(k, -1). Given that PA = PB....
Text Solution
|