Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ICSE-MATHEMATICS-2020 -SECTION-B
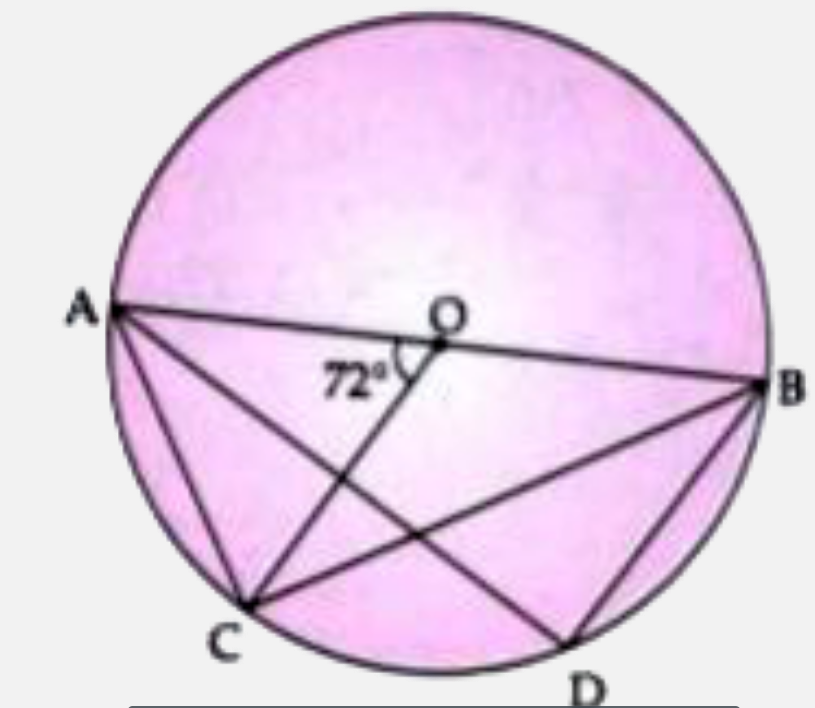
- In the figure given below, O is the centre of the circle and Ab is a d...
Text Solution
|
- A company with 500 shares of nominal value Rs. 120 declares an annual...
Text Solution
|
- The mean of the following data is 16. Calculate the value of f.
Text Solution
|
- The 4^(th), 6^(th) and the last term of a geometric progression are 1...
Text Solution
|
- If A=[(3, 0),(5, 1)] and B=[(-4,2),(1, 0)] Find A^(2)-2AB+B^(2)
Text Solution
|
- In the figure given figure AB = 9cm, PA = 7.5 cm and PC = 5 cm. Chords...
Text Solution
|
- From the top of a cliff, the angle of depression of the top and bottom...
Text Solution
|
- Find the value of 'p' if the lines, 5x-3y+2=0 and 6x-py+7=0 are perpe...
Text Solution
|
- Using properties of proportion find x:y given: (x^(2)+2x)/(2x+4)=(y^...
Text Solution
|
- What must be added to the polynomial 2x^(3)-3x^(2)-8x, so that it lea...
Text Solution
|
- Mr. Sonu has a recurring deposit account and deposits Rs. 750 per mon...
Text Solution
|
- Use graph paper for this question. Take 1 cm = 1 unit on both x and...
Text Solution
|
- If x=(sqrt(2a+1)+sqrt(2a-1))/(sqrt(2a+1)-sqrt(2a-1)), prove that x^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- If the 6^(th) term of an A.P. is equal to four times its first term a...
Text Solution
|
- The difference of two natural numbers is 7 and their product is 450. ...
Text Solution
|
- A model of a high rise building is made to a scale of 1:50. (i) I...
Text Solution
|
- From a solid wooden cylinder of height 28 cm and diameter 6 cm, two c...
Text Solution
|
- Prove the identity ((1-tan theta)/(1-cot theta))^(2)=tan^(2)theta
Text Solution
|