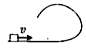
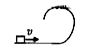A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
COMPETITION CARE UNIT
ICSE|Exercise UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION (ROTATIONAL MOTION AND MOMENT OF INERTIA ) |25 VideosCOMPETITION CARE UNIT
ICSE|Exercise GRAVITATION |25 VideosCOMPETITION CARE UNIT
ICSE|Exercise MOTION IN FLUIDS |25 VideosCIRCULAR MOTION
ICSE|Exercise MODULE 2 (FROM ROTATIONAL KINETIC ENERGY , WORK ,POWER)|24 VideosDIMENSIONS
ICSE|Exercise SELECTED PROBLEMS (FROM CONVERSIONS OF ONE SYSTEMS OF UNITS INTO ANOTHER)|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ICSE-COMPETITION CARE UNIT-UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION
- A particle is moving in a circle with uniform speed. IT has constant
Text Solution
|
- A car moving on a horizontal road may be thrown out of the road in tak...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is taken round a circle by the application of force. The wo...
Text Solution
|
- The ride is circus rides along a circular track in a vertical plane. T...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving in a circular path with a constant speed. If thet...
Text Solution
|
- A particle 'P' is moving in a circle of radius 'a' with a uniform spee...
Text Solution
|
- A car sometimes overturns while taking a turn. When it overturns, it i...
Text Solution
|
- Keeping the banking angle same, to increase the maximum speed with whi...
Text Solution
|
- For traffic moving at 60 km/hour along a circular track of radius 0.1 ...
Text Solution
|
- A 1 kg stone at the end of 1 m long string is whirled in a vertical ci...
Text Solution
|
- A car when passes through a convex bridge with velocity v exerts a for...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of equal masses are revolving in circular paths of radii...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass M is moving in a horizontal circle fo radius R with...
Text Solution
|
- A car is moving in a circular horizontal track of radius 10 m with a c...
Text Solution
|
- The driver of a car travelling at velocity v suddenly sees a braood w...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is moving in a circular path of constant radius r...
Text Solution
|
- A small block is shot into each of the four track as shown in Fig 15.7...
Text Solution
|
- A car has linear velocity v on a circular road of radius r. IF r it i...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum is oscillating without damping. When the displacemen...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of charge q and mass m moves in a circular orbit of radius...
Text Solution
|