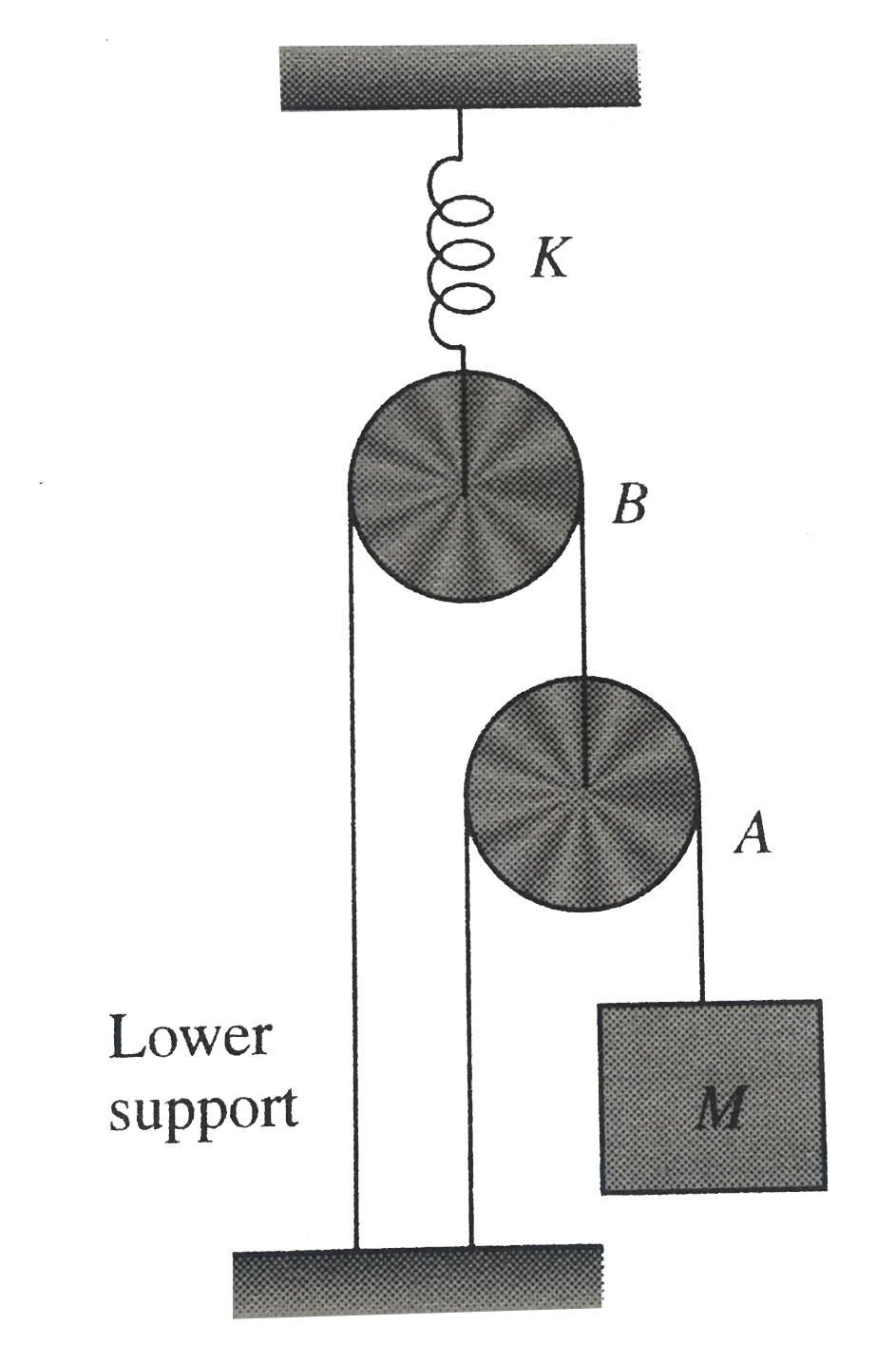
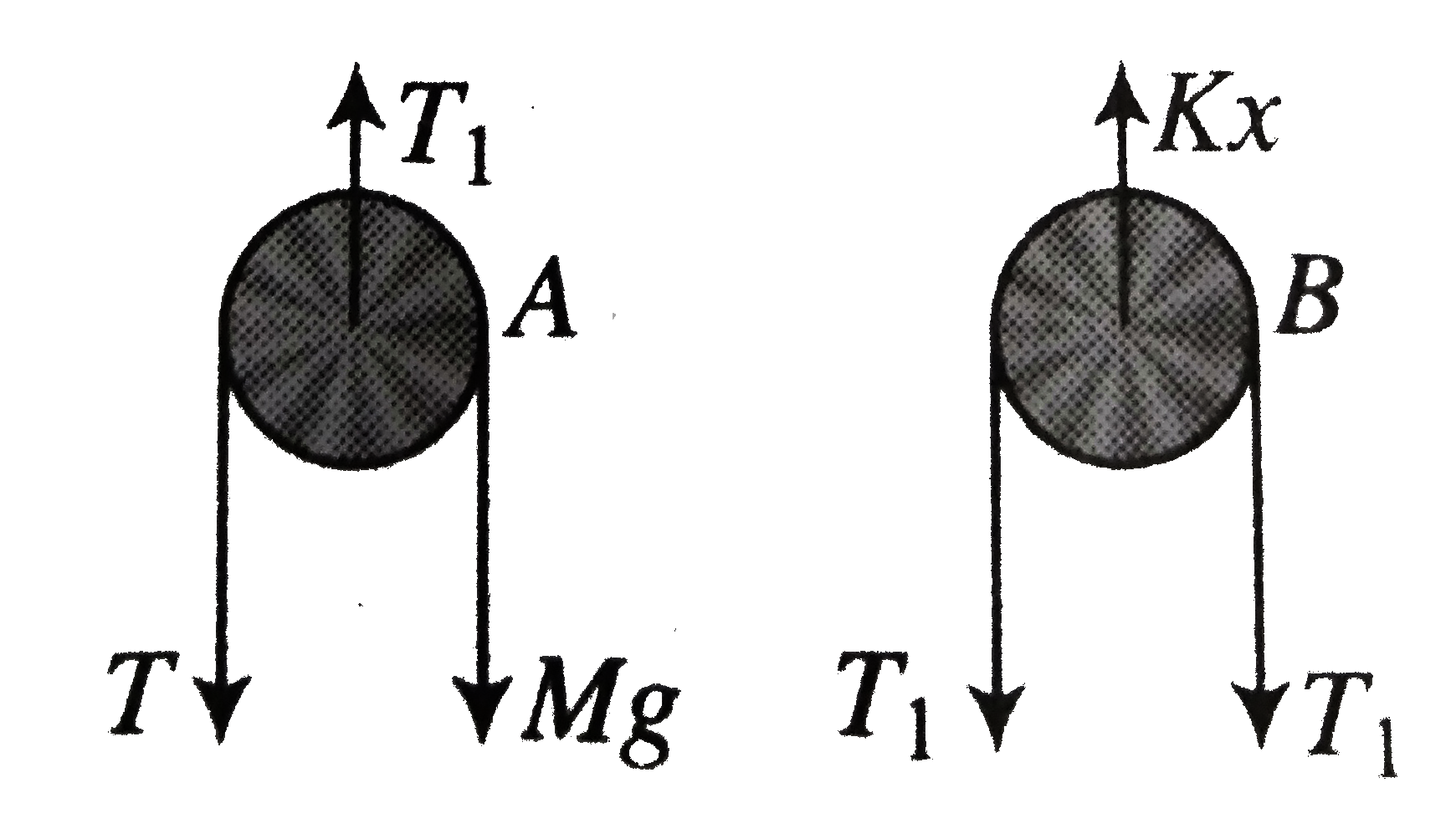
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|5 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion-reasoning|15 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|10 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer type|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1-Linked Comperhension
- In the arrangement shown in fig, pulleys D and E are small and frictio...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in fig., all pulleys are smooth and massless....
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in fig., all pulleys are smooth and massless....
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m(1) and m(2) are connected with a light spring o...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m(1) and m(2) are connected with a light spring o...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m(1) and m(2) are connected with a light spring o...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both t...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both t...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth block are placed at a smooth corner as shown in fig. Both t...
Text Solution
|
- Two containers of sand are arranged like the block as shown in fig. th...
Text Solution
|
- Two containers of sand are arranged like the block as shown in fig. th...
Text Solution
|
- A time varying force F=6t-2t^(2)N, at t=0 starts acting on a body of m...
Text Solution
|
- A time varying force F=6t-2t^(2)N, at t=0 starts acting on a body of m...
Text Solution
|
- A time varying force F=6t-2t^(2)N, at t=0 starts acting on a body of m...
Text Solution
|
- For the system shown in fig, there is no friction anywhere. Masses m(1...
Text Solution
|
- For the system shown in fig, there is no friction anywhere. Masses m(1...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m(1) and m(2) are connected with a light spring o...
Text Solution
|
- A mass M is suspended as shown in fig. The system is in equilibrium. A...
Text Solution
|
- A mass M is suspended as shown in fig. The system is in equilibrium. A...
Text Solution
|
- A mass M is suspended as shown in fig. The system is in equilibrium. A...
Text Solution
|