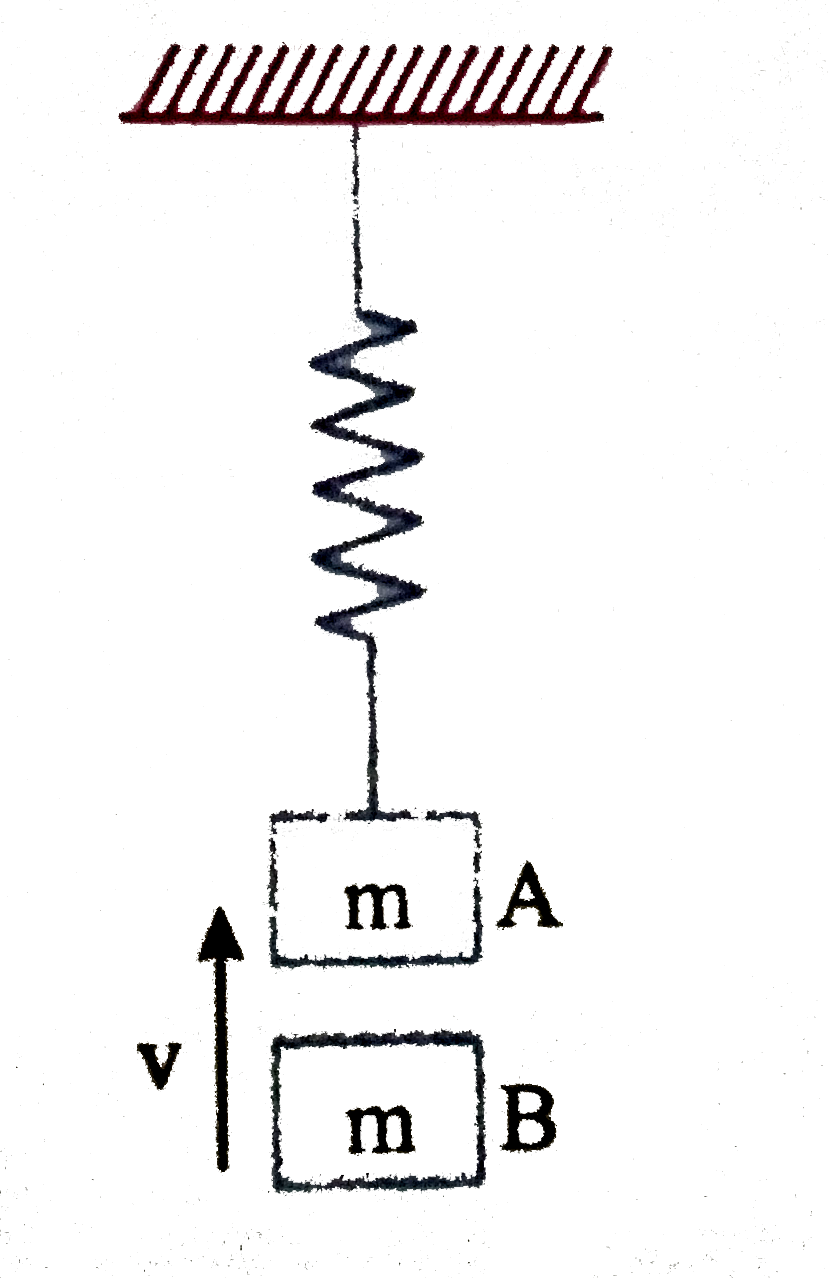A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
WORK, POWER & ENERGY
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct|25 VideosWORK, POWER & ENERGY
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Linked Comprehension|55 VideosWORK, POWER & ENERGY
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective|23 VideosVECTORS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise Multiple Correct|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-WORK, POWER & ENERGY-Single Correct
- An engine can pull four coaches at a maximum speed of 20ms^-1. The mas...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, the variation of potential energy of a particle of mass m=2...
Text Solution
|
- Block A is hanging from vertical spring of spring constant K and is re...
Text Solution
|
- A machine delivers power to a body which is proportional to velocity o...
Text Solution
|
- The kinetic energy acquired by a mass m travelling a certain distance ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m slides on a frictionaless surface ABCD, starting ...
Text Solution
|
- A projectile is fired with some velocity making certain angle with the...
Text Solution
|
- Two constant forces vecF1 and vecF2 act on a body of mass 8kg. These f...
Text Solution
|
- Given vecF=(xy^2)hati+(x^2y)hatjN. The work done by vecF when a partic...
Text Solution
|
- A force vecF=(3xy-5z)hatj+4zhatk is applied on a particle. The work do...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy of a particle is determined by the expression U=a...
Text Solution
|
- In the position shown in figure, the spring is at its natural length. ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, a spring of spring constant K is fixed at on end...
Text Solution
|
- Let r be the distance of a particle from a fixed point to which it is ...
Text Solution
|
- A mass m starting from A reaches B of a frictionless track. On reachin...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m slides along a curved-flat-curved track. The curv...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m has initial velocity u having direction towards +x a...
Text Solution
|
- A moving railway compartment has a spring of constant k fixed to its f...
Text Solution
|
- A rope ladder of length L is attached to a balloon of mass M. As the m...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is lying at rest at point P of a wedge having a smoo...
Text Solution
|