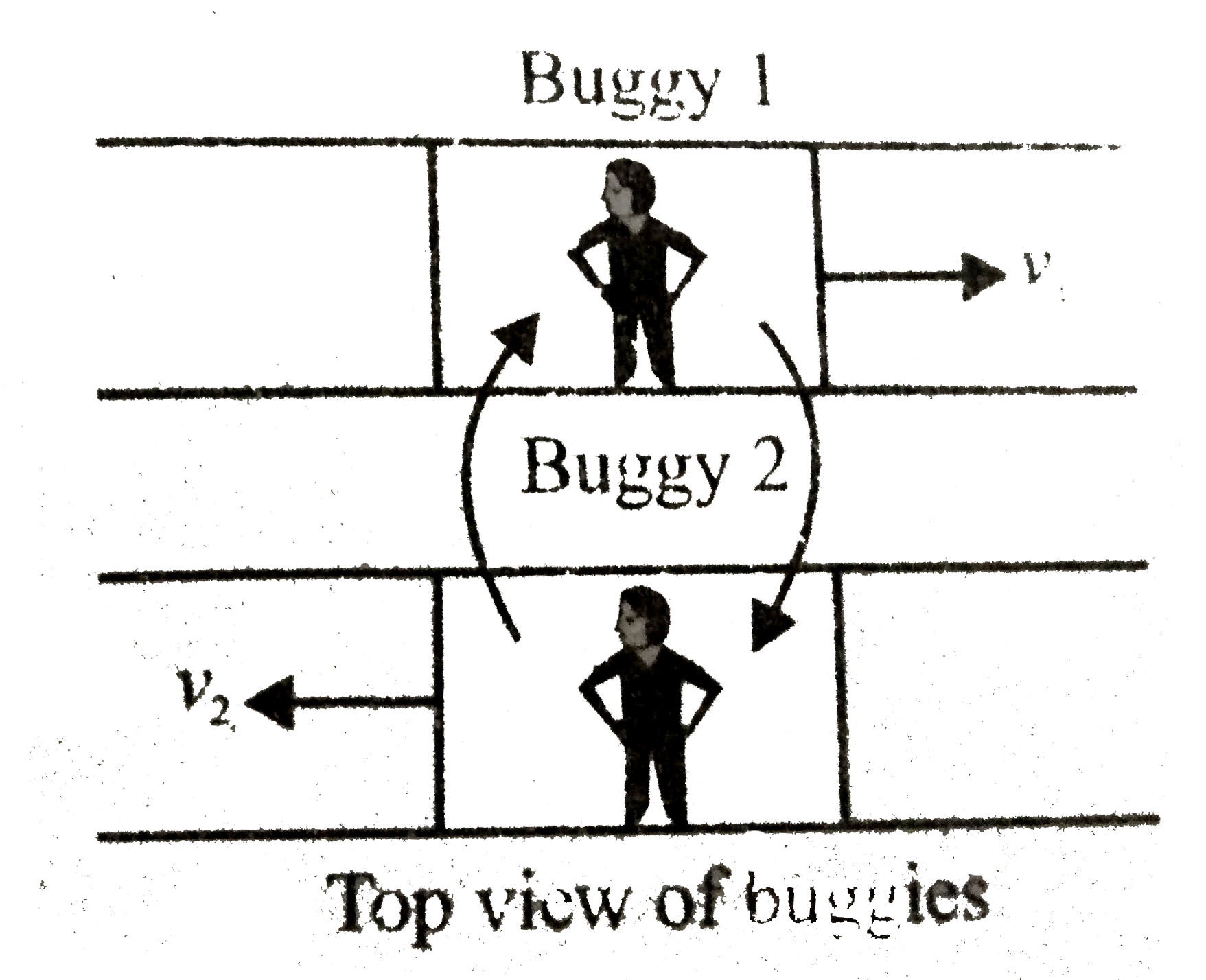Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 1.3|24 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective|23 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 1.1|20 VideosCALORIMETRY
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Example|13 VideosDIMENSIONS & MEASUREMENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-CENTRE OF MASS-Exercise 1.2
- Discuss the possibility of conservation of linear momentum of a block ...
Text Solution
|
- A shell is fired from a cannon with a speed of 100 m//s at an angle 30...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a block A of mass 6 m having a smooth semicircular groove...
Text Solution
|
- Two friends A and B (each weighing 40 kg) are sitting on a frictionles...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth wedge of mass M rests on a smooth horizontal surface. A block...
Text Solution
|
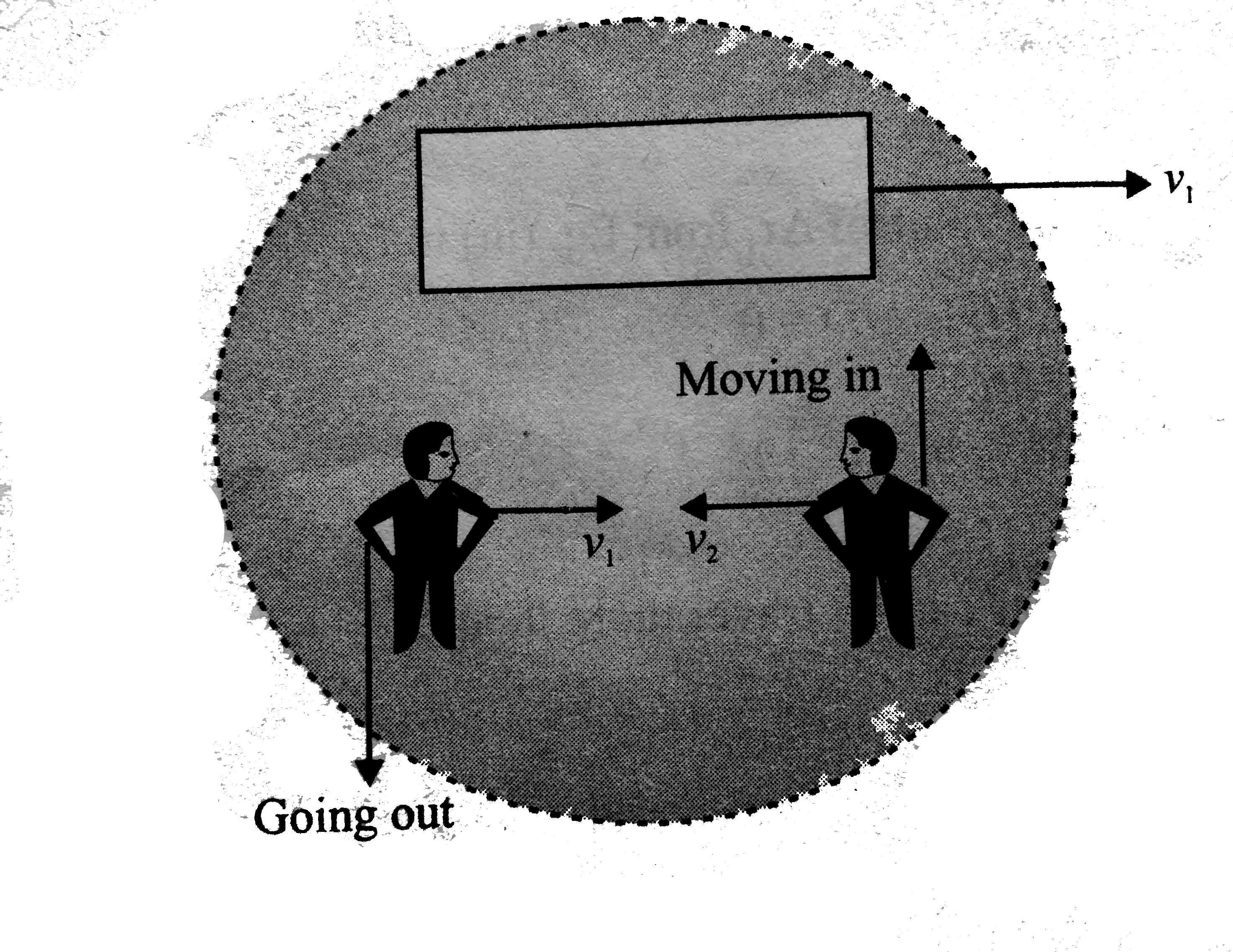
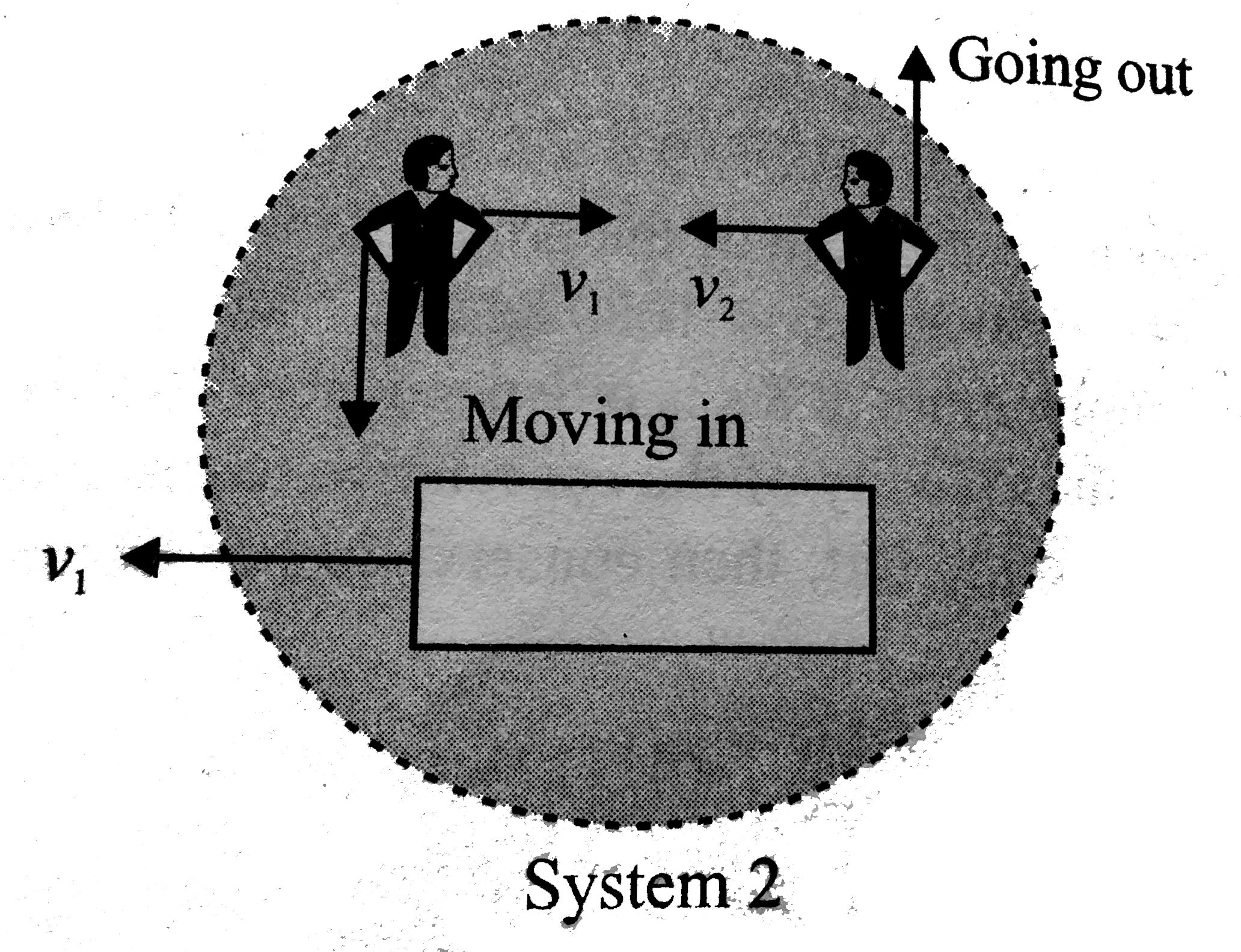
- Two identical buggies 1 and 2 with one man in each move along parallel...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. a man stands on a boat floating in still water. The mass of t...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m(1) = 2 kg and m(2) = 5 kg are moving in the sam...
Text Solution
|
- An 80 kg boy and his 40 kg sister, both wearing roller blades, face ea...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses M and 3M are placed on a horizontal, frictionless...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum bob os mass 10^(-2) kg is raised to a height 5 xx 10^(-2)m ...
Text Solution
|
- A rifle man, who together with his rifle has a mass of 100 kg, stands ...
Text Solution
|
- A projectile of mass 50 kg is shot vertically upwards with an initial ...
Text Solution
|
- a. A rail road flat car of mass M can roll without friction along a st...
Text Solution
|
- a. A rail road car of mass M is moving without friction on a straight ...
Text Solution
|
- A shell of mass 2 kg moving at a rate of 4 m//s suddenly explodes into...
Text Solution
|
- A mud ball at rest explodes into three fragmennts of masses in the rag...
Text Solution
|
- A hemisphere of radius R and mass 4 m is free to slide with its base o...
Text Solution
|
- A gun (mass=M) fires a bullet (mass=m) with speed vr relative to barr...
Text Solution
|
- Two trolleys A and B are free to move on a level frictionless track, a...
Text Solution
|