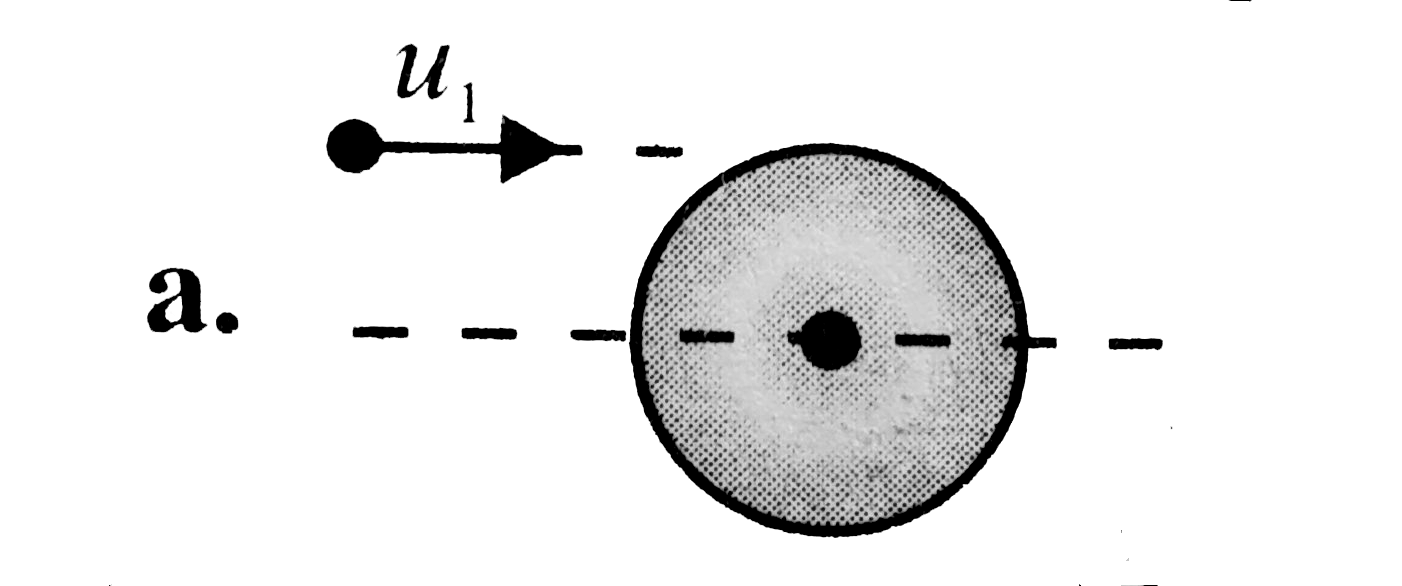
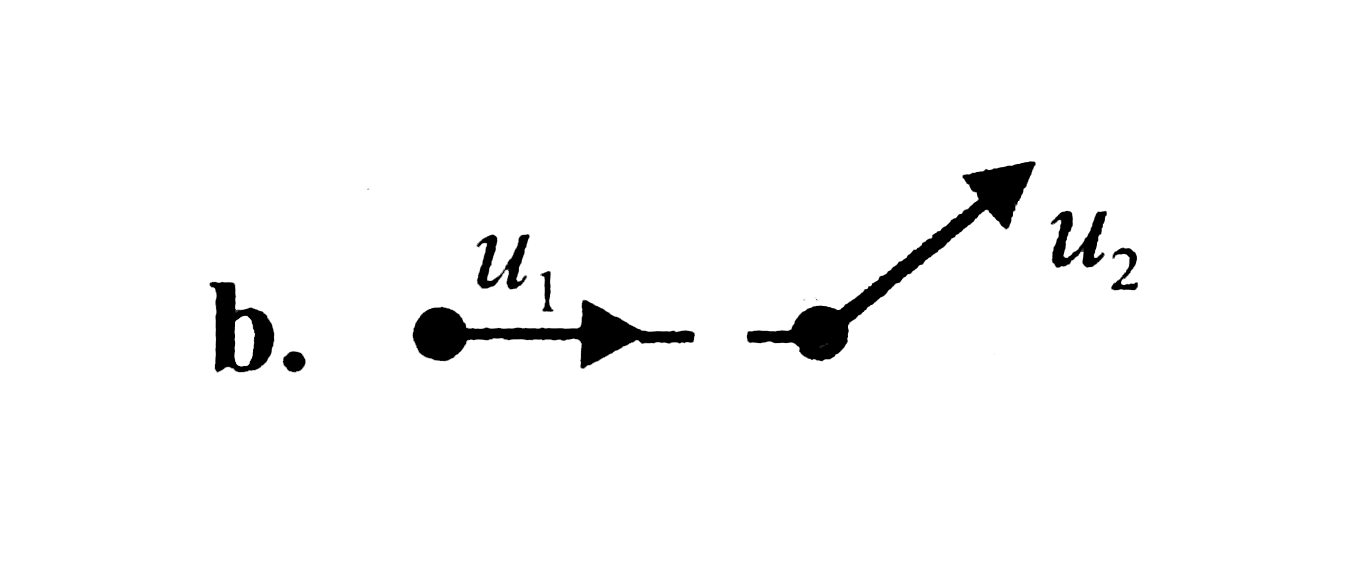
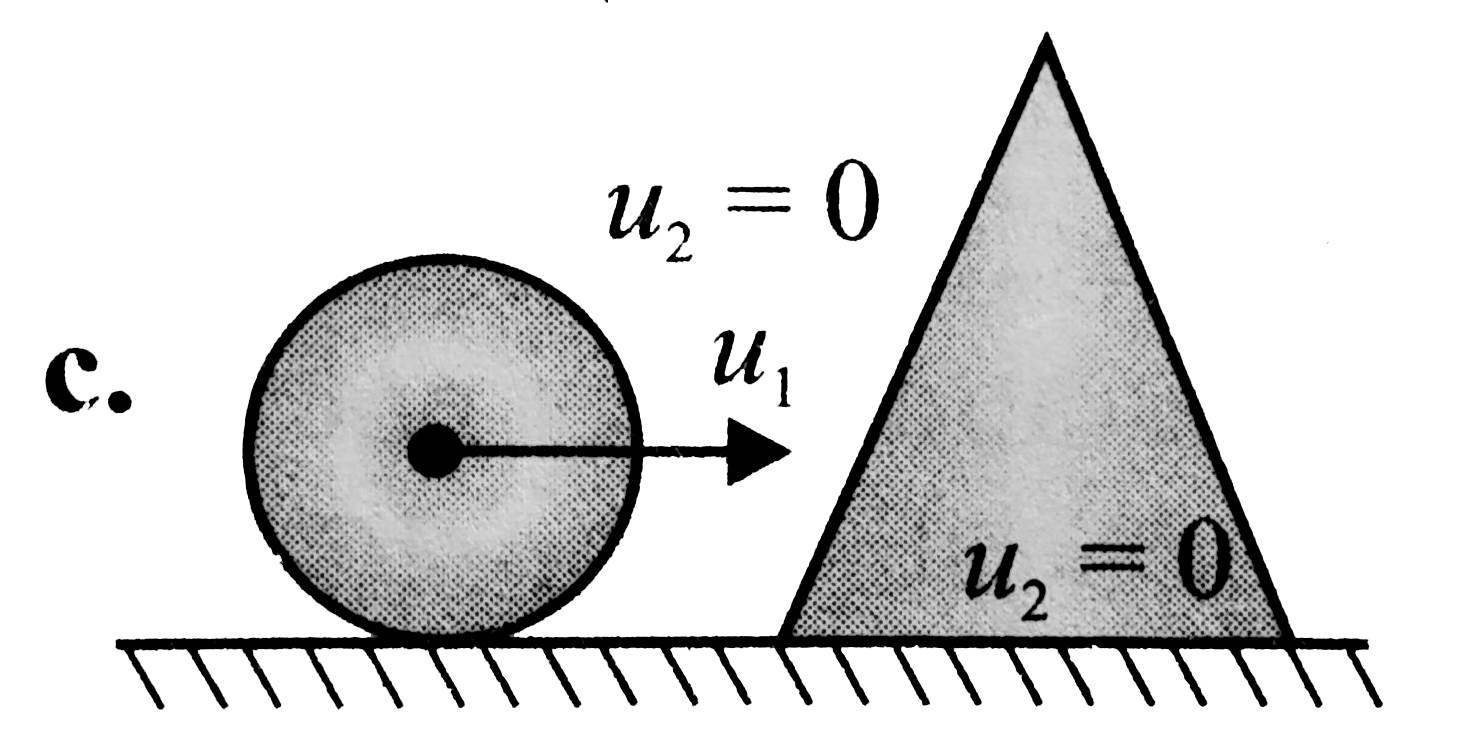
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|16 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Fill In The Blanks|2 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion - Reasoning|2 VideosCALORIMETRY
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Example|13 VideosDIMENSIONS & MEASUREMENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|2 Videos
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-CENTRE OF MASS-Linked Comprehension
- Collision is a physical process in which two or more objects, either p...
Text Solution
|
- Collision is a physical process in which two or more objects, either p...
Text Solution
|
- Collision is a physical process in which two or more objects, either p...
Text Solution
|
- Collision is a physical process in which two or more objects, either p...
Text Solution
|
- According to the principle of conservation of linear momentum if the e...
Text Solution
|
- According to the principle of conservation of linear momentum if the e...
Text Solution
|
- According to the principle of conservation of linear momentum if the e...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical balls A and B. each of mass 2 kg and radius R, are suspe...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical balls A and B. each of mass 2 kg and radius R, are suspe...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical balls A and B. each of mass 2 kg and radius R, are suspe...
Text Solution
|
- After falling from rest through a height h, a body of mass m begins to...
Text Solution
|
- After falling from rest through a height h, a body of mass m begins to...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical balls are connected by light inextensible strings with...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical balls are connected by light inextensible strings with...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical balls are connected by light inextensible strings with...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. a pulley is shown which is frictionless and a ring of mass m c...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. a pulley is shown which is frictionless and a ring of mass m c...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. a pulley is shown which is frictionless and a ring of mass m c...
Text Solution
|
- A system of men and trolley is shown in Fig. To the left, end of the s...
Text Solution
|
- A system of men and trolley is shown in Fig. To the left, end of the s...
Text Solution
|