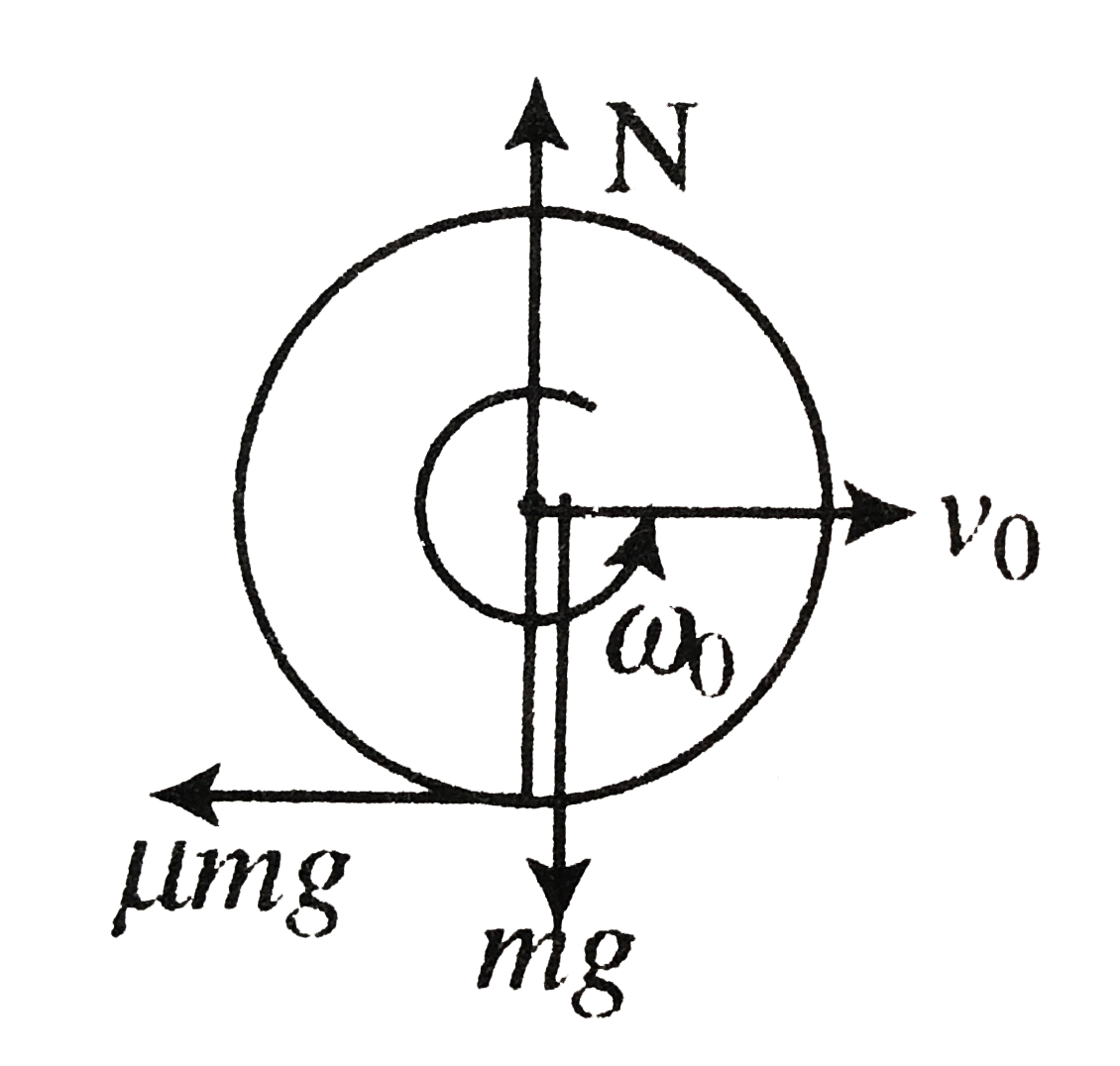Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 3.1|11 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 3.2|13 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Interger|2 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|11 VideosSOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|16 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2-Solved Examples
- A carpet of mass M is rolled along its length so as to from a cylinder...
Text Solution
|
- A block X of mass 0.5 kg is held by a long massless string on a fricti...
Text Solution
|
- A man pushes a cylinder of mass m(1) with the help of a plank of mass ...
Text Solution
|
- A plank of mass M, is placed on a smooth surface over which a cylinder...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform slender bar B of mass m and length L supported by a firction...
Text Solution
|
- A hoop of mass m is projected on a floor with linear velocity v(0) and...
Text Solution
|
- A trolley intially at rest with a solid cylinder placed on its bed su...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform solid cyinder of radius R=15 cm rolls over a horizontal plan...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere of radius R is set into motion on a rough horizontal su...
Text Solution
|
- A composite rod of mass 2m and length 2l comprises two indentica rods ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of radius R=20 cm has mass m=0.75 kg and moment of inertia (abo...
Text Solution
|
- Two thin circular disks of mass 2kg and radius 10 cm each are joined b...
Text Solution
|