A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|10 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise MCQ_TYPE|20 VideosMISCELLANEOUS KINEMATICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Interger type|3 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 2-LC_TYPE
- Two ropes are puling a large ship at rest of mass 1xx106kg into harbou...
Text Solution
|
- Two ropes are puling a large ship at rest of mass 1xx106kg into harbou...
Text Solution
|
- Two ropes are puling a large ship at rest of mass 10^6kg into harbour....
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure F=10N , R=1 m , mass of the body is 2 kg and momen...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure F=10N , R=1 m , mass of the body is 2 kg and momen...
Text Solution
|
- A disc having radius R is rolling without slipping on a horizontal (x-...
Text Solution
|
- A disc having radius R is rolling without slipping on a horizontal (x-...
Text Solution
|
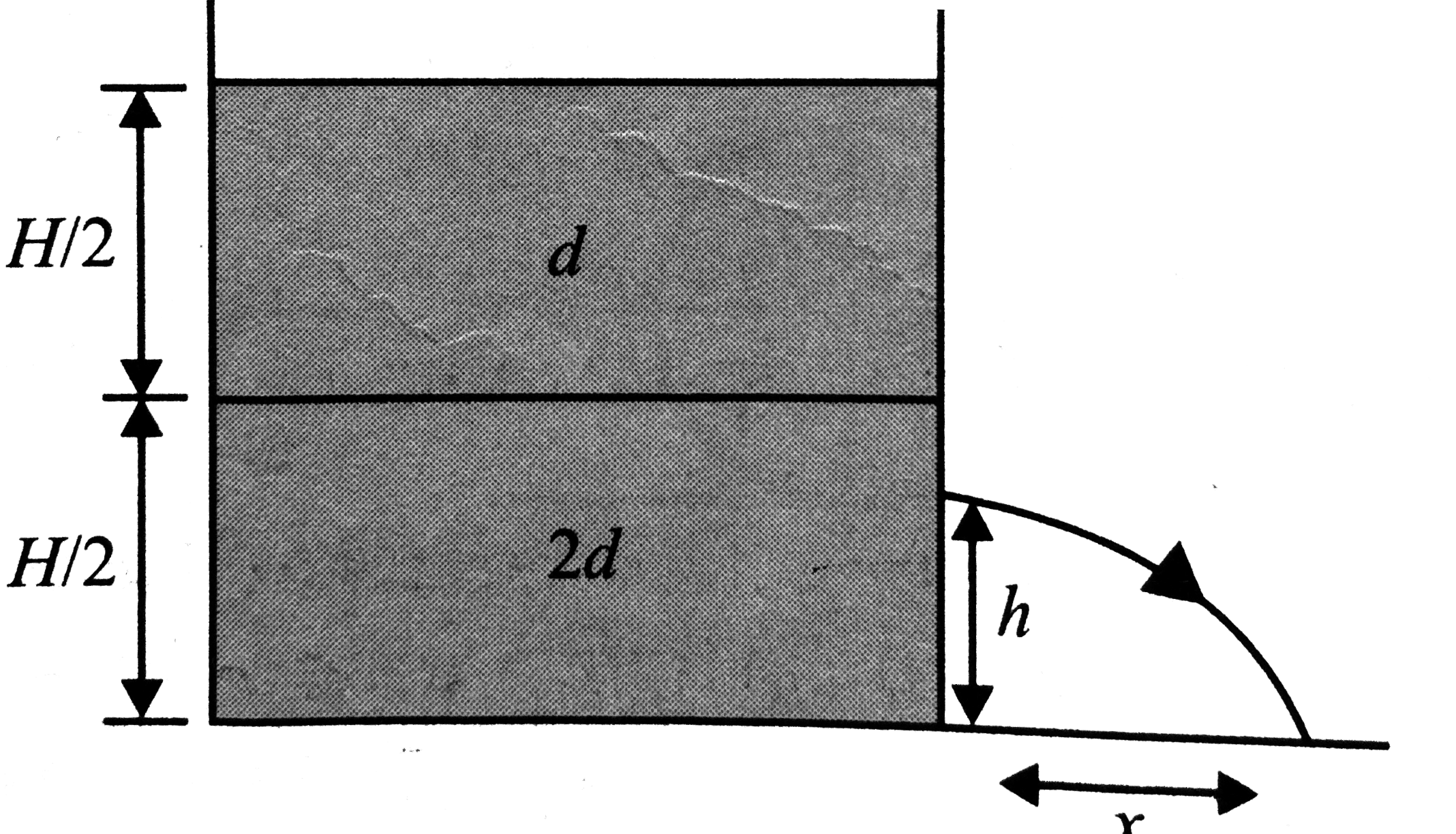
- A cylindrical container of length L is full to the brim with a liquid ...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical container of length L is full to the brim with a liquid ...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical container of length L is full to the brim with a liquid ...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical container of length L is full to the brim with a liquid ...
Text Solution
|
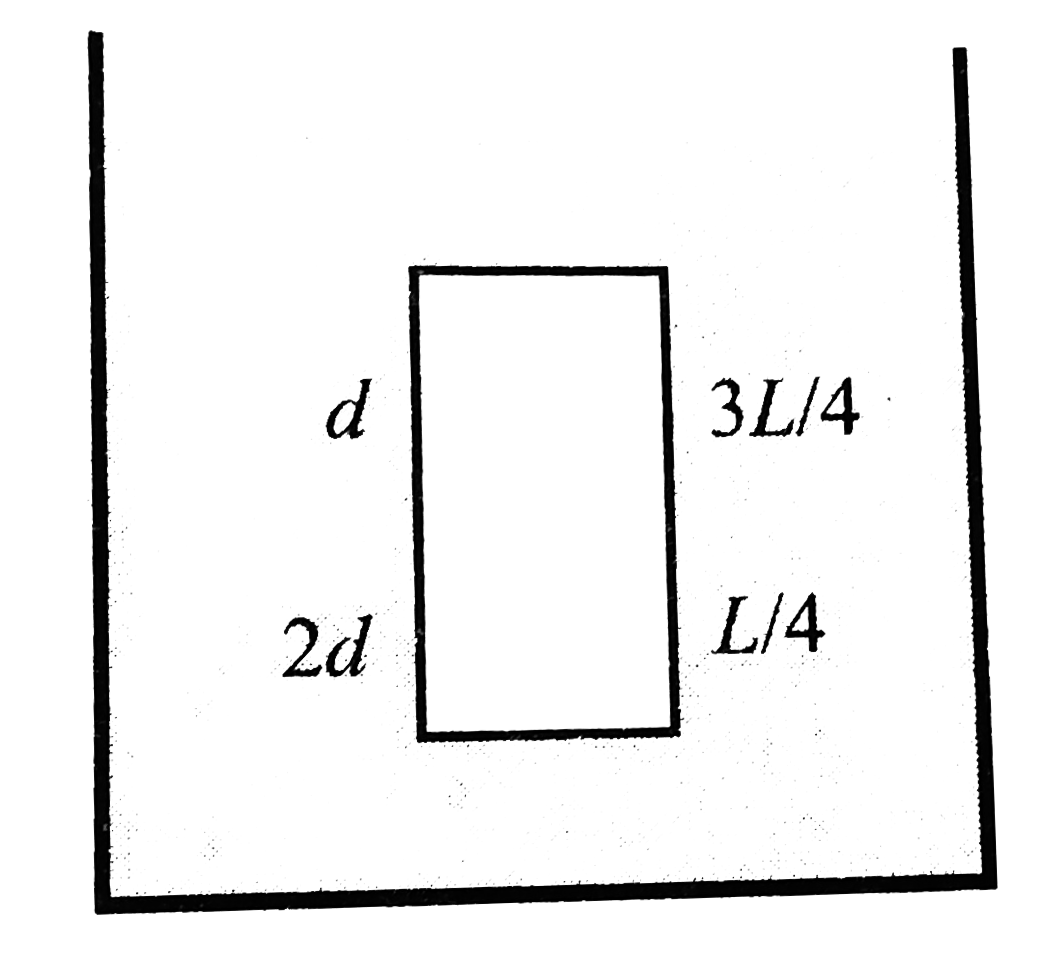
- Fluids at rest exert a normal force to the walls of the container or ...
Text Solution
|
- Fluids at rest exert a normal force to the walls of the container or ...
Text Solution
|
- Fluids at rest exert a normal force to the walls of the container or ...
Text Solution
|
- Fluids at rest exert a normal force to the walls of the container or ...
Text Solution
|
- Fluids at rest exert a normal force to the walls of the container or ...
Text Solution
|
- Fluids at rest exert a normal force to the walls of the container or ...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow sphere is completely filled with a liquid having a density rh...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow sphere is completely filled with a liquid having a density rh...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow sphere is completely filled with a liquid having a density rh...
Text Solution
|