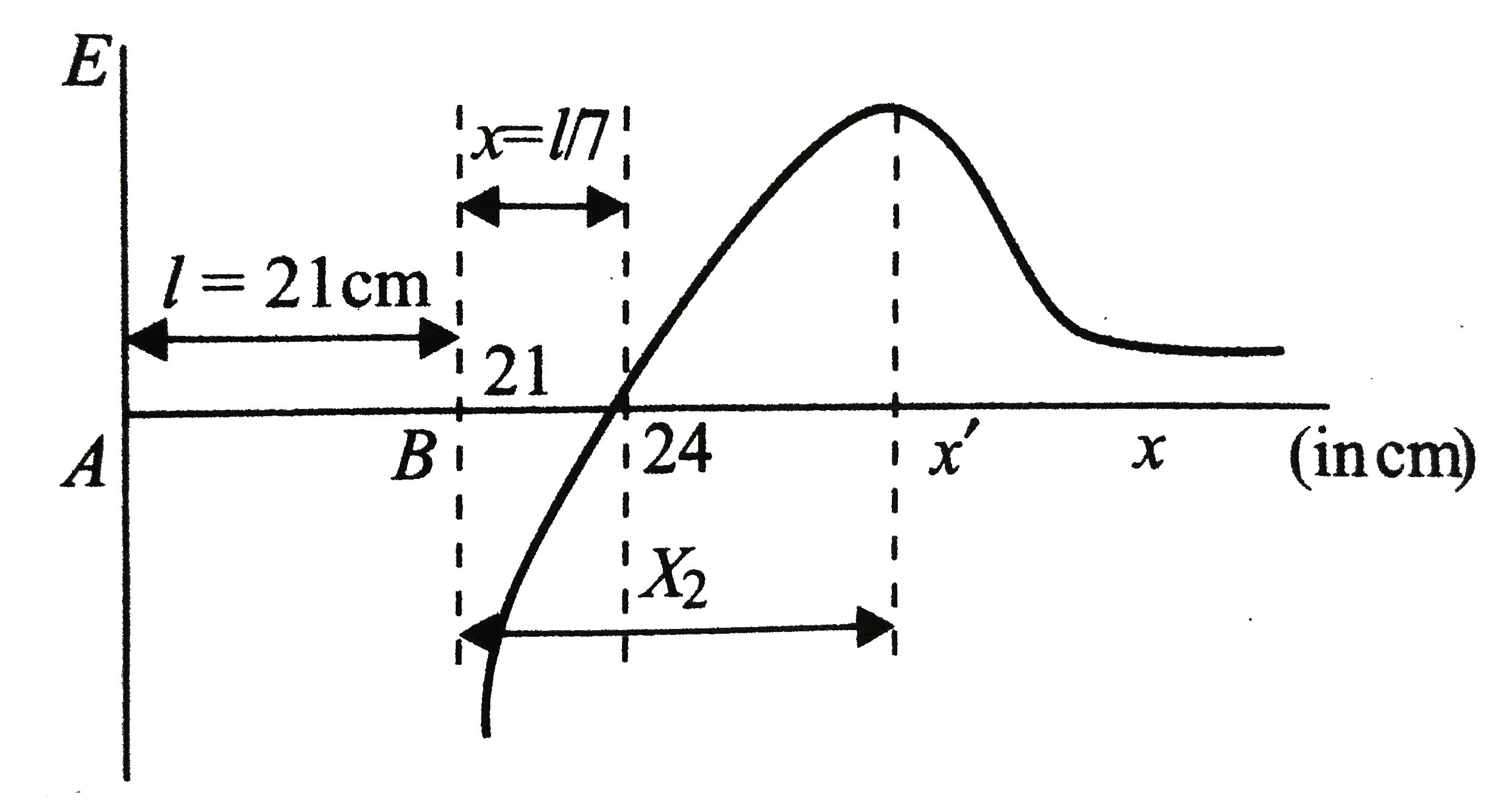
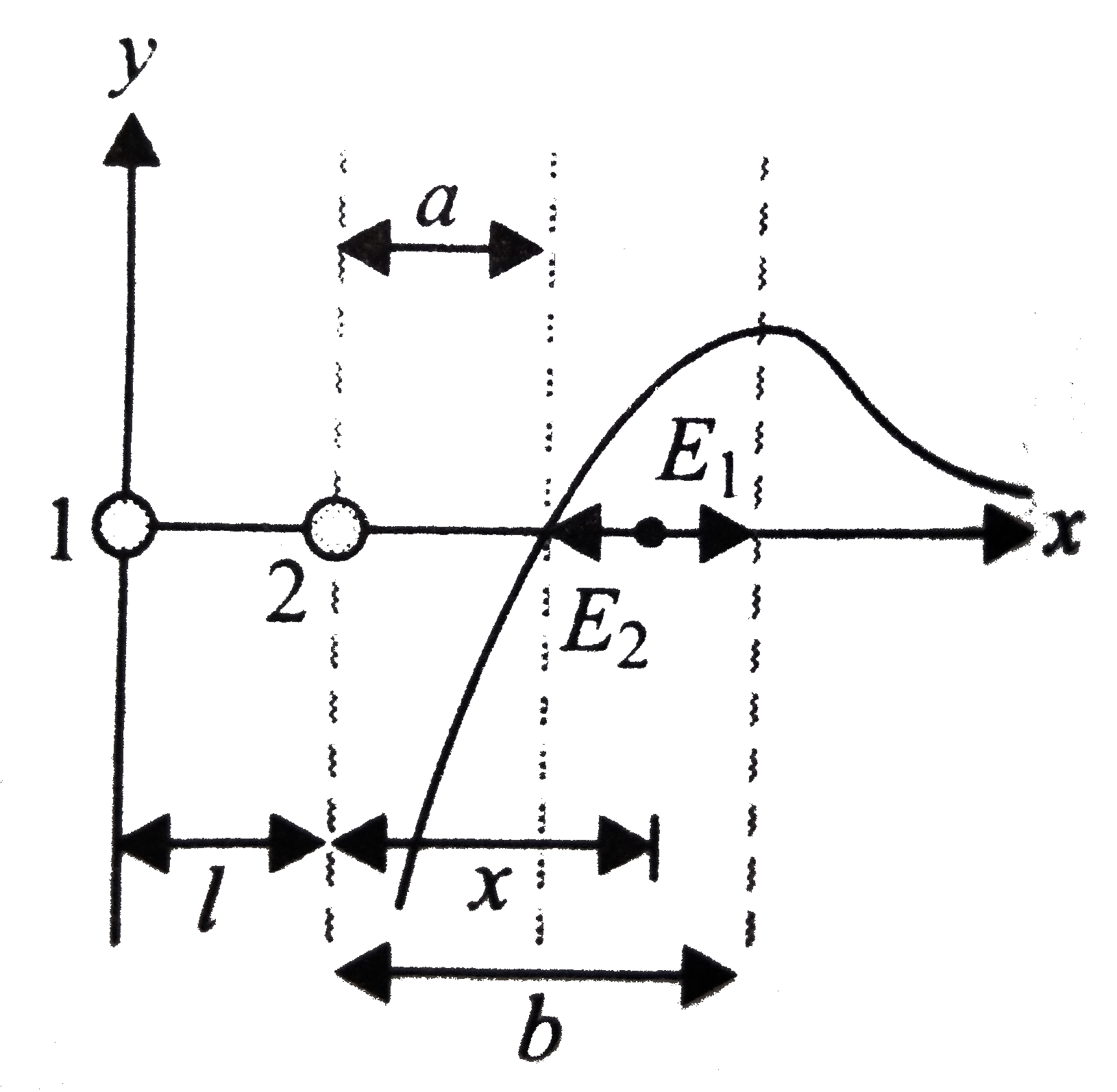
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
COULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|8 VideosCOULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Single Correct Ansewr Type|20 VideosCOULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct|8 VideosCENGAGE PHYSICS DPP
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise subjective type|51 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT & CIRCUITS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Kirchhoff s law and simple circuits|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-COULOMB LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELD-Comprehension
- Three charges are placed as shown in fig. the magnitude of q(1) is 2.0...
Text Solution
|
- Three charges are placed as shown in fig. the magnitude of q(1) is 2.0...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charge Q(a) and Q(b) are positional at point A and B. The fi...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charge Q(a) and Q(b) are positional at point A and B. The fi...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charge Q(a) and Q(b) are positional at point A and B. The fi...
Text Solution
|
- Four equal positive charges, each of value Q, are arranged at the four...
Text Solution
|
- Four equal positive charges, each of value Q, are arranged at the four...
Text Solution
|
- An electron is projected with an initial speed v(0)=1.60xx10^(6)ms^(-1...
Text Solution
|
- An electron is projected with an initial speed v(0)=1.60xx10^(6)ms^(-1...
Text Solution
|
- An electron is projected with an initial speed v(0)=1.60xx10^(6)ms^(-1...
Text Solution
|
- An electron is projected with an initial speed v(0)=1.60xx10^(6)ms^(-1...
Text Solution
|
- An electron is projected as shown in fig. with kinetic energy K, at an...
Text Solution
|
- An electron is projected as shown in fig. with kinetic energy K, at an...
Text Solution
|
- In 1909, Robert Millikan war the firest to find the charge of an elect...
Text Solution
|
- In 1909, Robert Millikan was the first to find the charge of an electr...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum of mass m charged negatively to q coulomb oscillates...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum of mass m charged negatively to q coulomb oscillates...
Text Solution
|
- There is an insulator rod of length L and of negligible mass with two ...
Text Solution
|
- There is an insulator rod of length L and of negligible mass with two ...
Text Solution
|
- There is an insulator rod of length L and of negligible mass with two ...
Text Solution
|