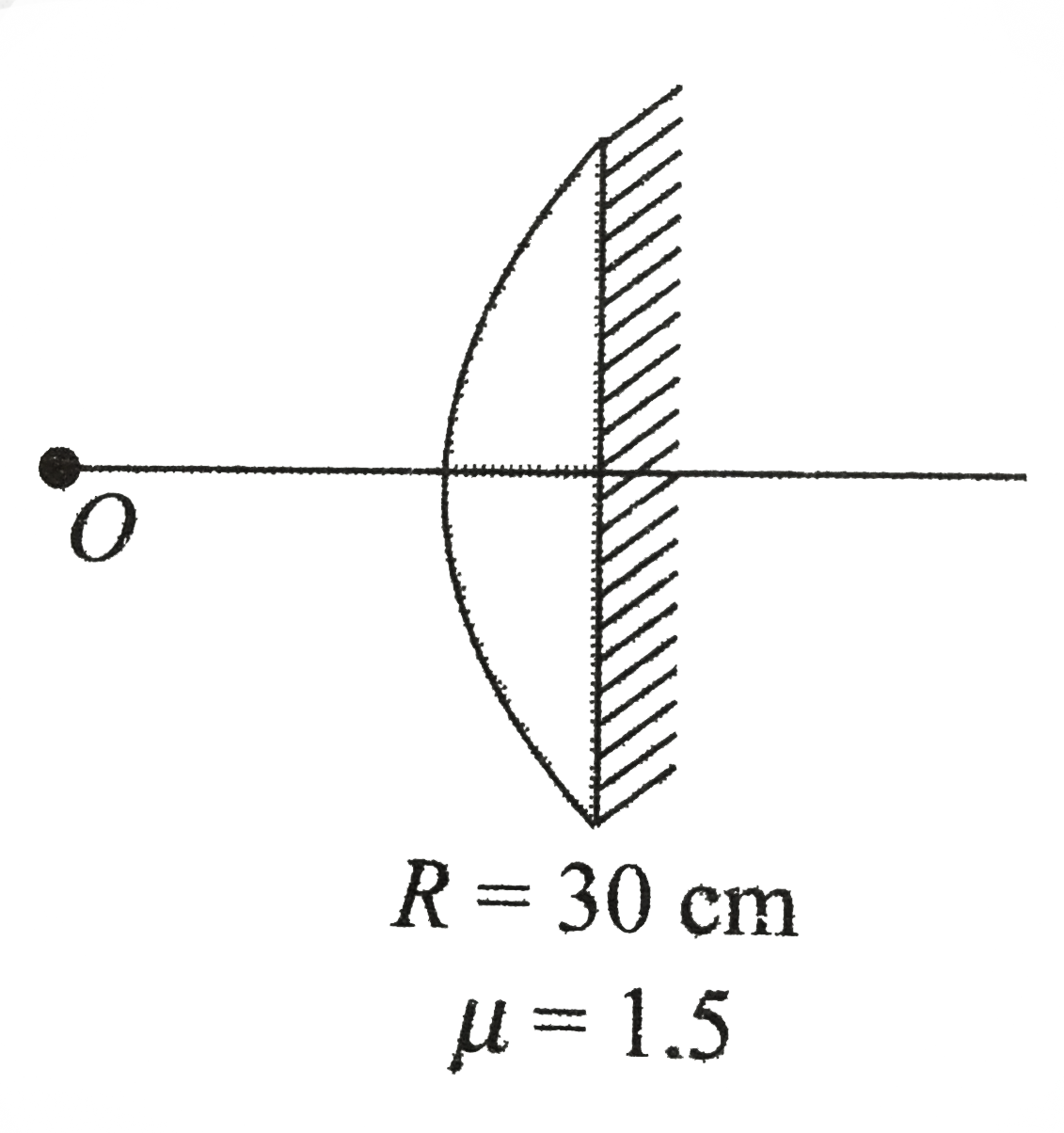
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective|26 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Single Correct|221 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise1.6|15 VideosELECTRON,PHONTS,PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT & X-RAYS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 3.3|15 VideosHEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Thermal Power in Resistance Connected in Circuit|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Exercise1.7
- Figure, shown two converging lenses. Incident rays are parallel to the...
Text Solution
|
- In Figure., find the position of final image formed.
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. what should be the value of d so that image is formed on the ...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig,, if the image of object O has to coincide with itself, then w...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length 20cm is placed 10cm away from a second ...
Text Solution
|
- When an object is placed at the proper distance ot the left of a conve...
Text Solution
|
- A telephoto combination consists of convex lens of focal length 30cm a...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens is cut in half along its principal axis and the two halv...
Text Solution
|
- A plano-convex lens is silvered on its plane side. The radius of curva...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length 10cm is placed 30 cm in front of a secon...
Text Solution
|
- A concave mirror of focal length 30 cm is placed on the flat horizont...
Text Solution
|
- The convex side of a thin concavo-convex lens of glass of refractive i...
Text Solution
|
- The source is placed 30 cm from a convex lens which has a focal length...
Text Solution
|
- If final image after two refractions through the lens and one reflecti...
Text Solution
|
- A point object O is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a convex lens o...
Text Solution
|
- The focal length of a thin convex-lens is 30cm. At a distance of 10 cm...
Text Solution
|
- A plano-convex glass lens (mu(g)=3//2) of radius of curvature R=10cm i...
Text Solution
|
- On a horizontal plane mirror, a thin equiconvex lens of glass is place...
Text Solution
|
- A pin is placed 10cm in front of a convex lens of focal length 20cm, m...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of glass (mu=1.5) is formed by combining two surfaces of...
Text Solution
|