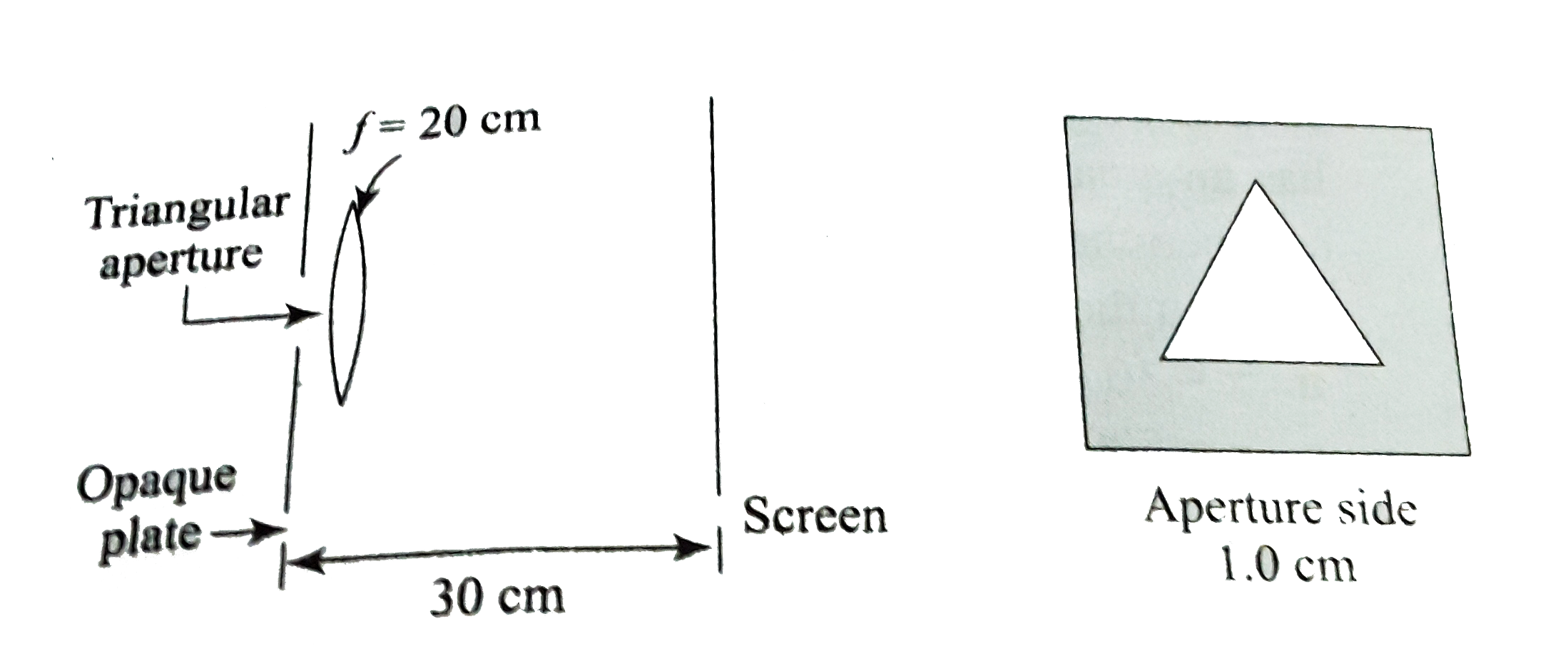
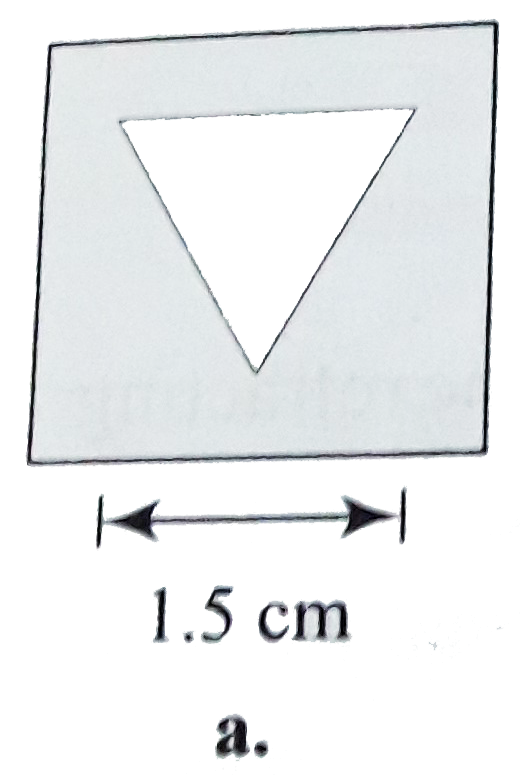
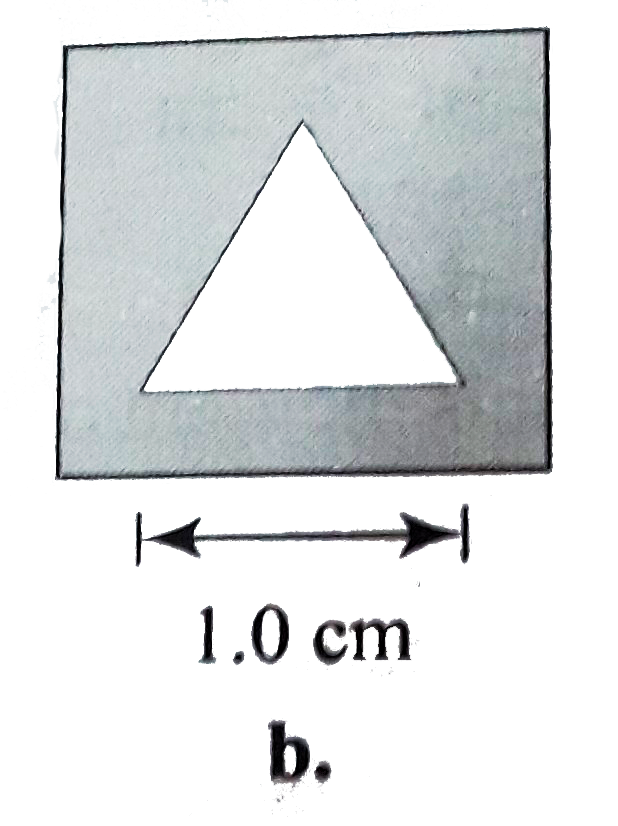
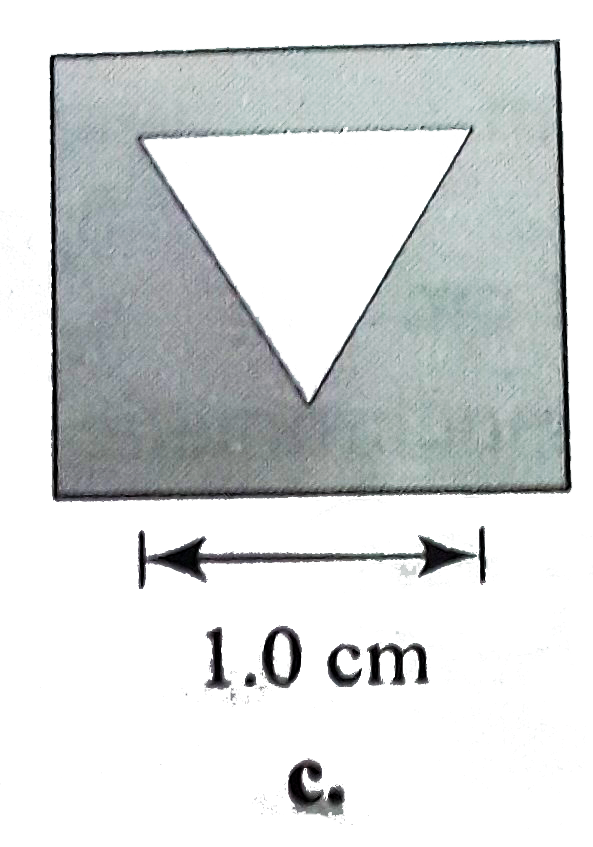
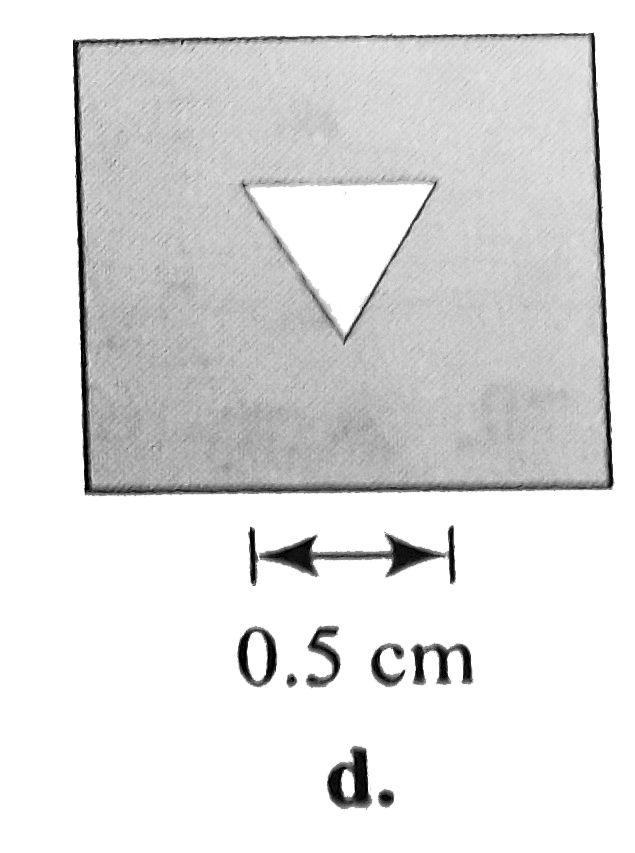
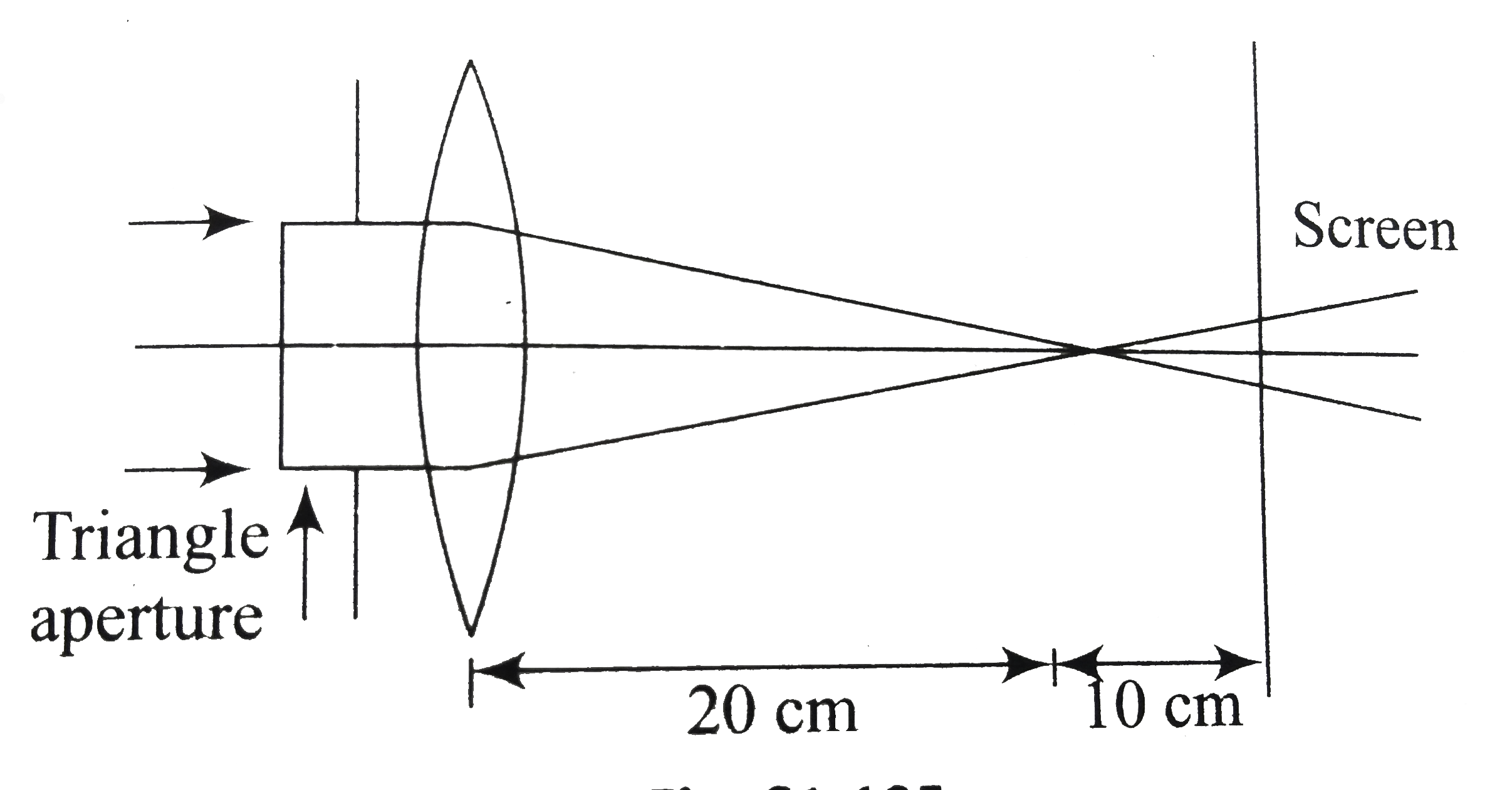
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion-Reasoninig|2 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Linked Comprehension|51 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective|26 VideosELECTRON,PHONTS,PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT & X-RAYS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 3.3|15 VideosHEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Thermal Power in Resistance Connected in Circuit|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Single Correct
- ACB is right-angled prism with other angles as 60^(@) and 30^(@) . Re...
Text Solution
|
- The lateral magnification of the lens with an object located at two di...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light falls axially on a thin converging lens of fo...
Text Solution
|
- A liquid of refractive index 1.6 is contained in the cavity of a glass...
Text Solution
|
- Figure(a) shows two plano-convex lenses in contact as shown. The combi...
Text Solution
|
- In a slide show programme, the image on the screen has an area 900time...
Text Solution
|
- A prism having refractive index 1.414 and refracting angle 30^(@) has ...
Text Solution
|
- In a lake, a fish rising vertically to the surface of water uniformly ...
Text Solution
|
- A concave lens with unequal radii of curvature made of glass (mu(g)=1....
Text Solution
|
- The refractive index of material of a prism of angles 45^(@), -45^(@),...
Text Solution
|
- An object is placed 1m in front of the curved surface of a plano-conve...
Text Solution
|
- The apparent thickness of a thick plano-convex lens is measured once w...
Text Solution
|
- An object is placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 50cm....
Text Solution
|
- A concave mirror of focal length 10cm and a convex mirror of focal len...
Text Solution
|
- A U-shaped wire is placed before a concave having radius of curvature ...
Text Solution
|
- An object ABED is placed in front of a concave mirror beyond the cente...
Text Solution
|
- A gun of mass M fires a bullet of mass m with a horizontal speed V. Th...
Text Solution
|
- The distance between two point sources of light is 24cm. Find out wher...
Text Solution
|
- Two thin symmetrical lenses of different nature and of different mater...
Text Solution
|
- A glass sphere of radius R=10cm is kept inside water. A ponit object ...
Text Solution
|