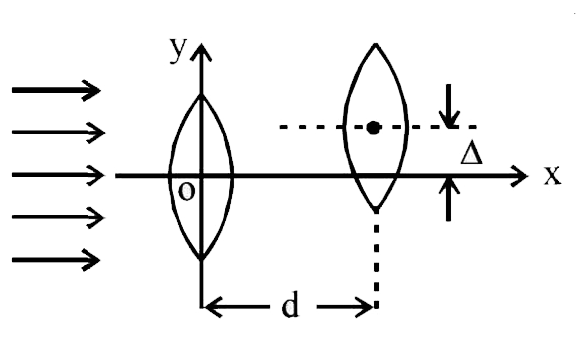A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|15 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Archives|7 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion-Reasoninig|2 VideosELECTRON,PHONTS,PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT & X-RAYS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 3.3|15 VideosHEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Thermal Power in Resistance Connected in Circuit|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Linked Comprehension
- The convex surface of a thin concave-convex lens of glass of refractiv...
Text Solution
|
- The convex surface of a thin concave-convex lens of glass of refractiv...
Text Solution
|
- Two thin convex lenses of focal lengths f(1) and f(2) are separated by...
Text Solution
|
- Two thin convex lenses of focal lengths f(1) and f(2) are separated by...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light falls successively on a thin convex lens of ...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light falls successively on a thin convex lens of ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical plano-convex lenses L(1)(mu(1)-1.4) and L(2)(mu(2)-1.5) ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical plano-convex lenses L(1)(mu(1)-1.4) and L(2)(mu(2)-1.5) ...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of light converges towards a point O, behind a convex mirror of...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of light converges towards a point O, behind a convex mirror of...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light enters a spherical drop of water of refractive index mu...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light enters a spherical drop of water of refractive index mu...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light enters a spherical drop of water of refractive index mu...
Text Solution
|
- The ciliary muscles of eye control the curvature of the lens in the ey...
Text Solution
|
- The ciliary muscles of eye control the curvature of the lens in the ey...
Text Solution
|
- The ciliary muscles of eye control the curvature of the lens in the ey...
Text Solution
|
- The ciliary muscles of eye control the curvature of the lens in the ey...
Text Solution
|
- The ciliary muscles of eye control the curvature of the lens in the ey...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light falls on a solid tranparent sphere. Q. W...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light falls on a solid tranparent sphere. Q. I...
Text Solution
|