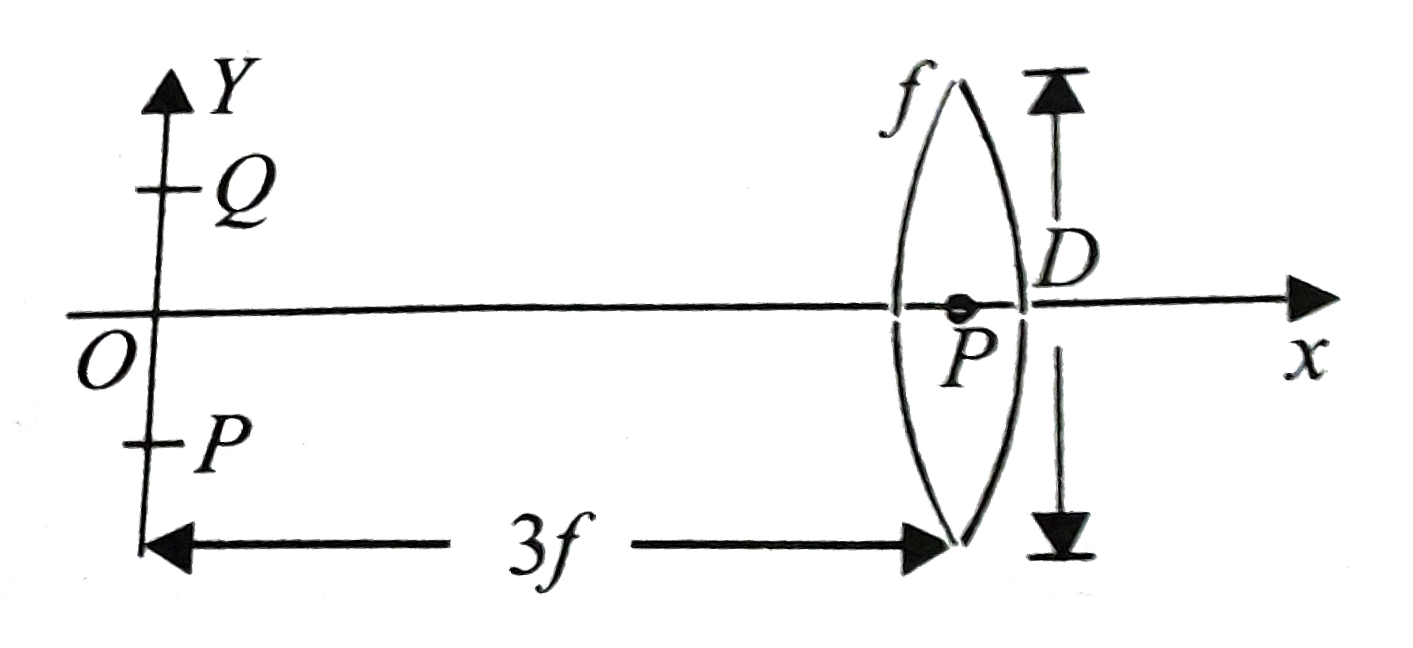
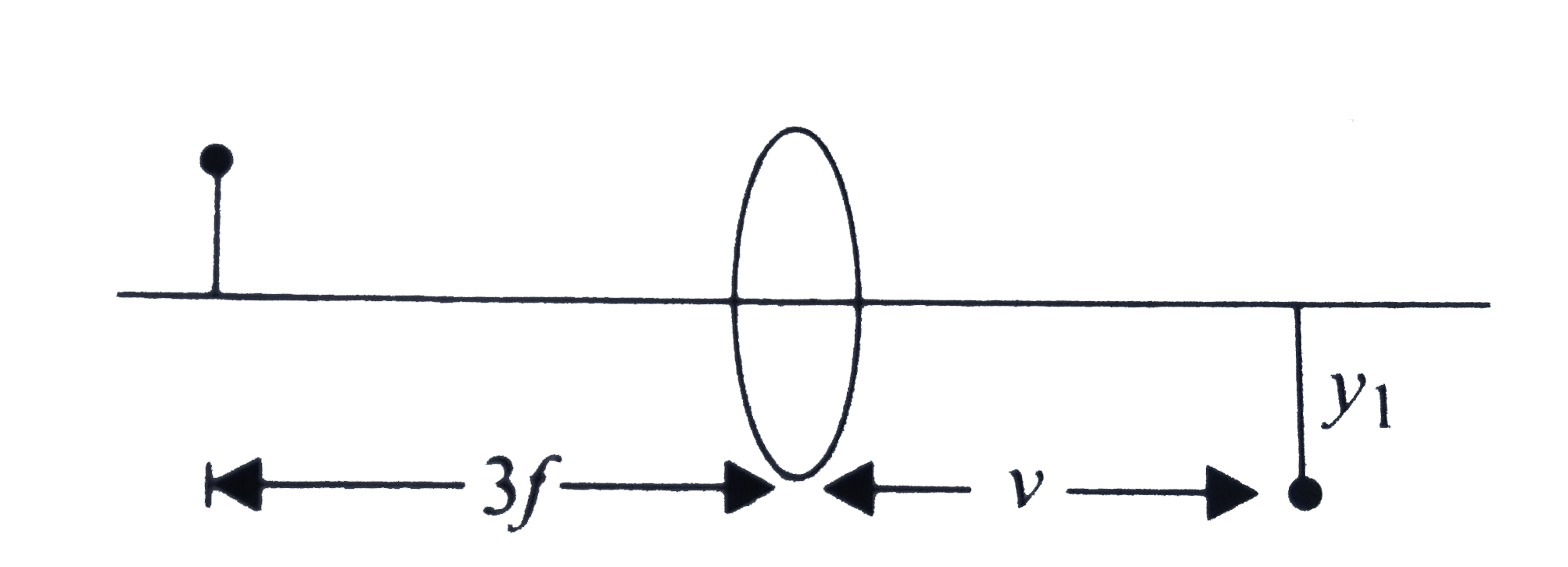
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|15 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Archives|7 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion-Reasoninig|2 VideosELECTRON,PHONTS,PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT & X-RAYS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 3.3|15 VideosHEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Thermal Power in Resistance Connected in Circuit|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Linked Comprehension
- A parallel beam of light falls on a solid tranparent sphere. Q. W...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light falls on a solid tranparent sphere. Q. I...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light falls on a solid tranparent sphere. Q. F...
Text Solution
|
- Pulfrich refractometer is used to measure the refractive index of soli...
Text Solution
|
- Pulfrich refractometer is used to measure the refractive index of soli...
Text Solution
|
- Pulfrich refractometer is used to measure the refractive index of soli...
Text Solution
|
- An object is present on the principal axis of a concave mirror at a di...
Text Solution
|
- An object is placed between a plane mirror and a concave mirror of foc...
Text Solution
|
- An object is present on the principal axis of a concave mirror at a di...
Text Solution
|
- An object kept near a convex lens of focal length f, executes SHM betw...
Text Solution
|
- An object kept near a convex lens of focal length f, executes SHM betw...
Text Solution
|
- An object kept near a convex lens of focal length f, executes SHM betw...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length 40cm is held at a distance 12cm coaxiall...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length 40cm is held at a distance 12cm coaxiall...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length 40cm is held at a distance 12cm coaxiall...
Text Solution
|
- A concave mirror forms real image of a point source lying on the optic...
Text Solution
|
- A concave mirror forms real image of a point source lying on the optic...
Text Solution
|
- A concave mirror forms real image of a point source lying on the optic...
Text Solution
|
- An object AB of height 1cm lying on the axis of convex mirror of focal...
Text Solution
|
- An object AB of height 1cm lying on the axis of convex mirror of focal...
Text Solution
|