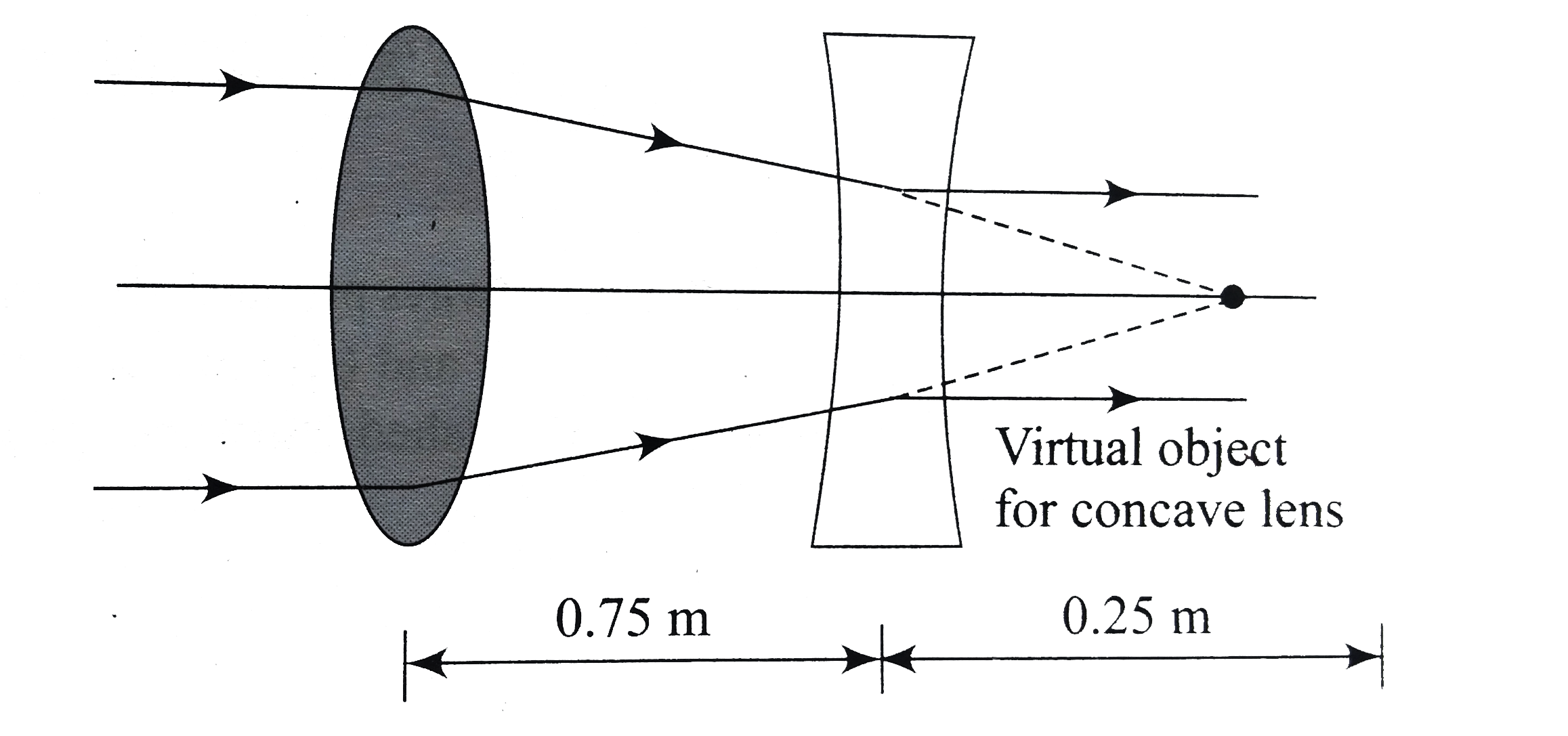
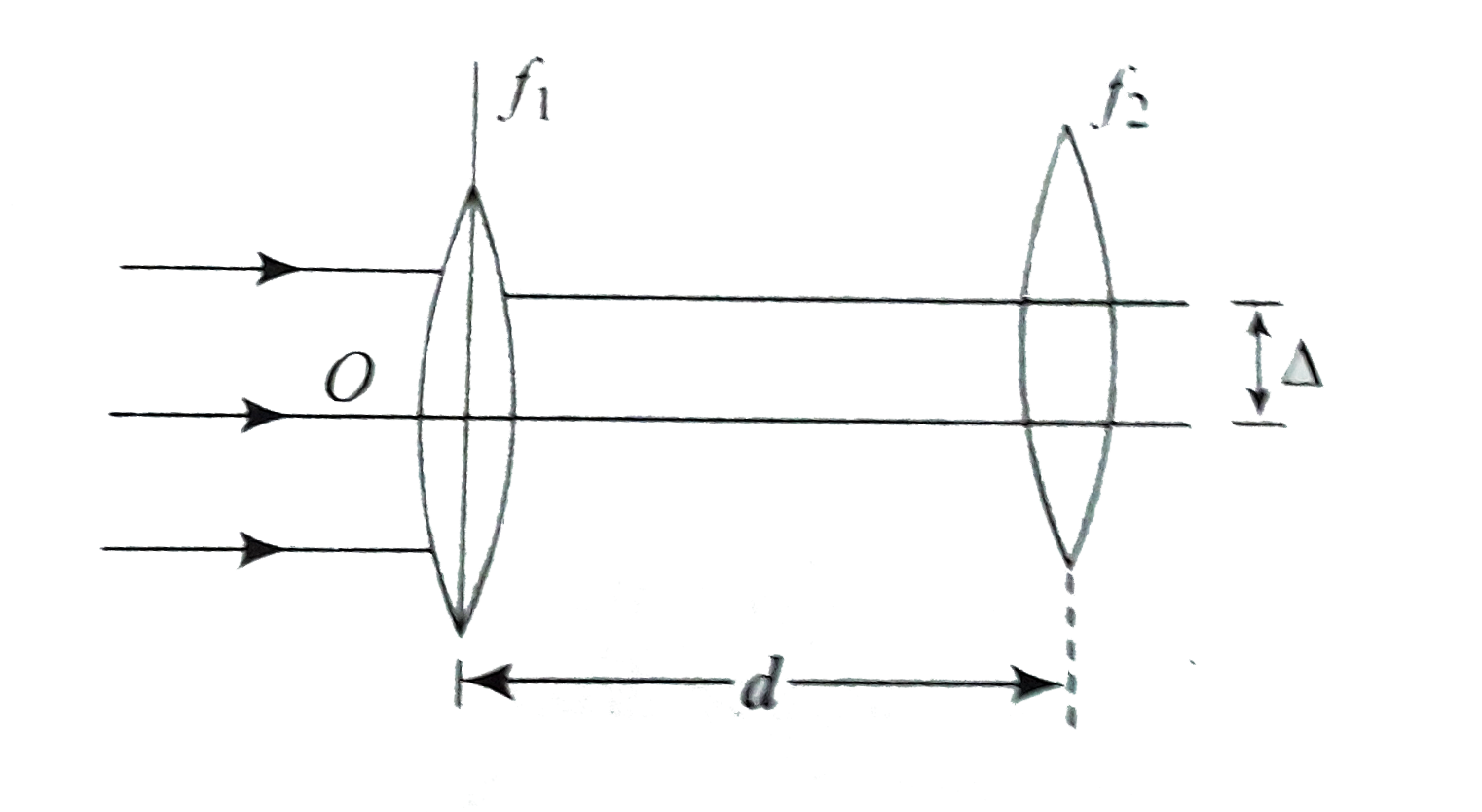A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct Answers Type|8 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion-Reasoninig Type|2 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise True/False|5 VideosELECTRON,PHONTS,PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT & X-RAYS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 3.3|15 VideosHEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Thermal Power in Resistance Connected in Circuit|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Single Correct Answer Type
- A beam of light consisting of red, green and blue colurs is incident o...
Text Solution
|
- A thin prism P(1) with angle 4^(@) and made from glass of refractive i...
Text Solution
|
- Two thin convex lenses of focal lengths f(1) and f(2) are separated by...
Text Solution
|
- Spherical aberration in a thin lens can be reduced by
Text Solution
|
- A beam of light of wavelength 600nm from a distance source falls on a ...
Text Solution
|
- An isosceles prism of angle 120degree has a refractive index 1.44. Two...
Text Solution
|
- A diminished image of an object is to be obtained on a screen 1.0 m fr...
Text Solution
|
- The focal lengths of the objective and the eyepiece of a compound mic...
Text Solution
|
- An eye specialist prescribes spectacles having a combination of a conv...
Text Solution
|
- A real image of a distant object is formed by a plano-convex lens on i...
Text Solution
|
- A concave mirror is placed on a horizontal table with its axis directe...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical surface of radius of curvature R separates air (refractive...
Text Solution
|
- A concave lens of glass, refractive index 1.5, has both surfaces of sa...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow double concave lens is made of very thin transparent materia...
Text Solution
|
- A point source of light S, placed at a distance L in front of the cen...
Text Solution
|
- A diverging beam of light from a point source S having divergence angl...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular slab ABCD, of refractive index n1 , is immersed in water...
Text Solution
|
- In a compound microscope, the intermediate image is
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light passes through four transparent media with refractive i...
Text Solution
|
- A given ray of light suffers minimum deviation in an equilateral prism...
Text Solution
|