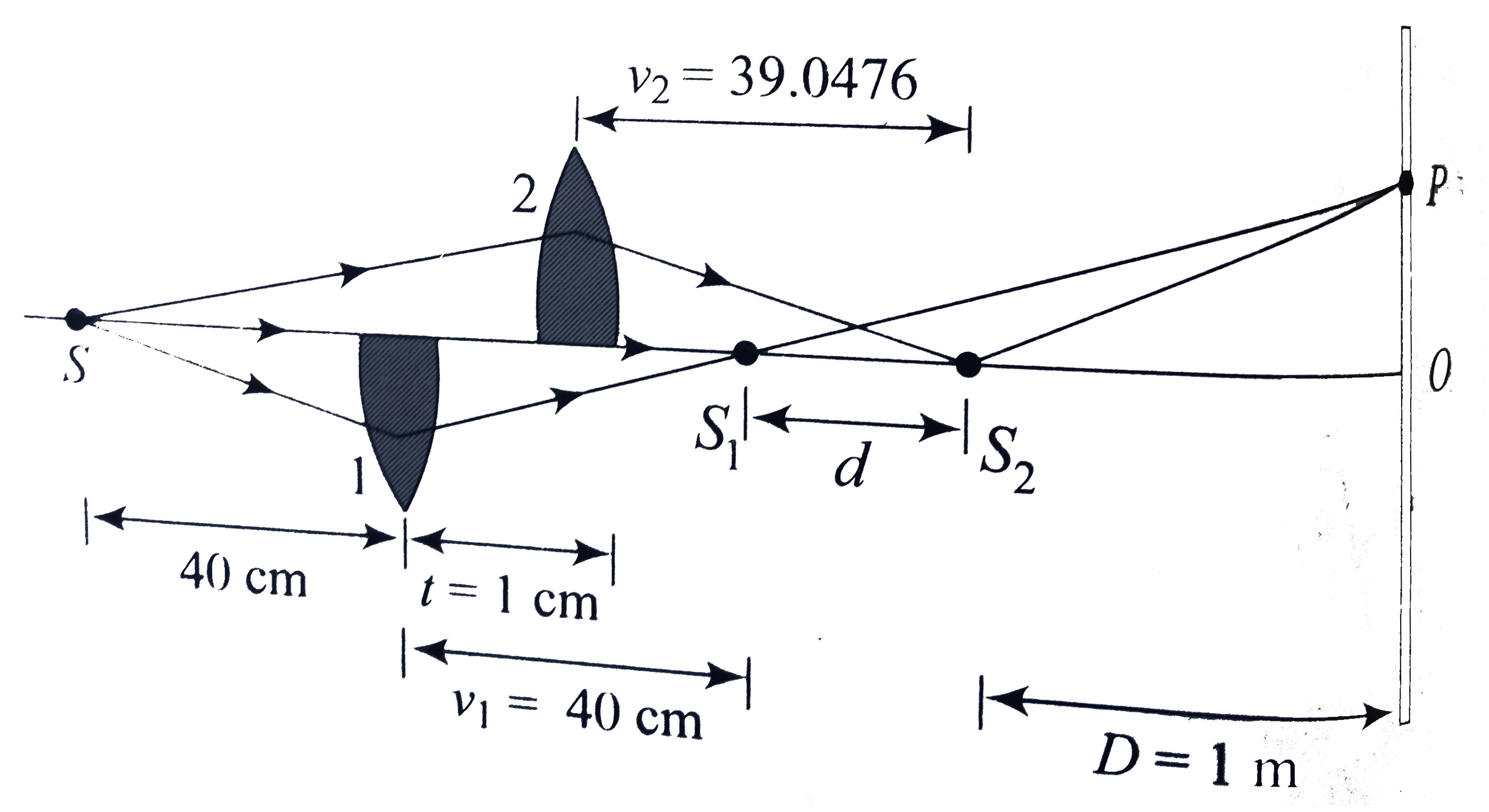
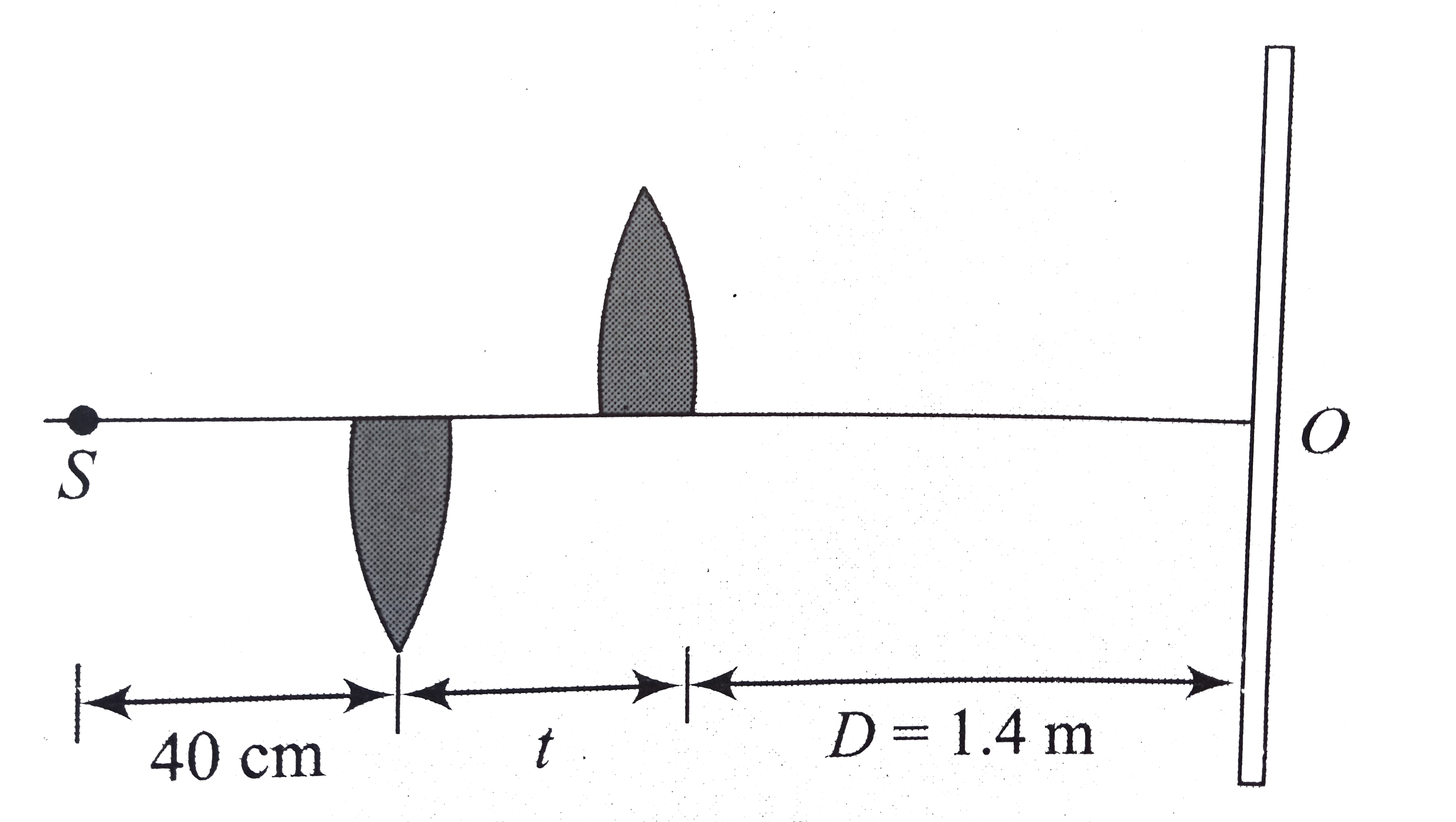Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-WAVE OPTICS-Comprehension Type
- A convex lens of focal length 20 cm is cut long its diameter and the ...
Text Solution
|
- Fig. shows a surface XY separating two transparent media, medium 1 and...
Text Solution
|
- Fig. shows a surface XY separating two transparent media, medium 1 and...
Text Solution
|
- Fig. shows a surface XY separating two transparent media, medium 1 and...
Text Solution
|
- What is the specific heat ratio of diatomic gases ?
Text Solution
|
- What is the specific heat ratio of triatomic gases ?
Text Solution
|
- If I1/I2 =4 then find the value of (Imax - Imin)/ (Imax+Imin)
Text Solution
|
- A rod of mass m and length L is pivoted at a point O and kept in horiz...
Text Solution
|
- If I1/I2 =9 then find the value of (Imax - Imin)/ (Imax+Imin) A ̅
Text Solution
|
- A point source S emits light of wavelength 600 nm. It is palced at a v...
Text Solution
|
- A point source S emits light of wavelength 600 nm. It is palced at a v...
Text Solution
|
- A point source S emits light of wavelength 600 nm. It is palced at a v...
Text Solution
|
- A YDSE is performed in a medium of refractive index 4 // 3, A light of...
Text Solution
|
- A YDSE is performed in a medium of refractive index 4 // 3, A light of...
Text Solution
|
- In YDSE's experiment performed in a medium of refractive index (4/3), ...
Text Solution
|