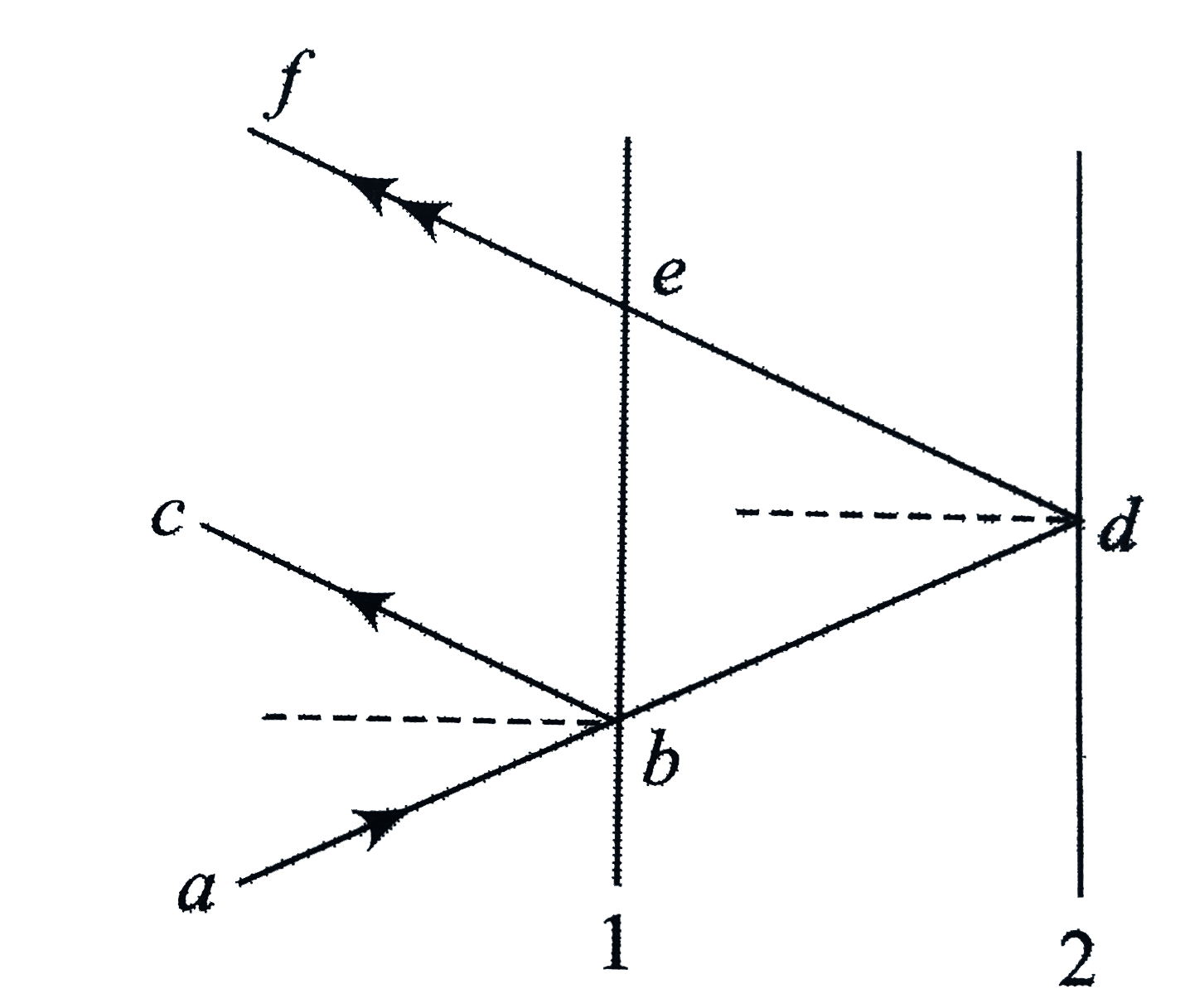
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-WAVE OPTICS-Solved Examples
- In a modified Young's double-slit experiment, a monochromatic uniform ...
Text Solution
|
- A narrow monochromatic beam of light of intensity 1 is incident on a g...
Text Solution
|
- In figure S is a monochromatic point source emitting light of waveleng...
Text Solution
|
- A double - slit apparatus is immersed in a liquid of refractive index ...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's experiment the upper slit is covered by a thin glass plate ...
Text Solution
|
- The Young's double-slit experiment is done in a medium of refractive i...
Text Solution
|
- A glass of refractive index 1.5 is coated with a thin layer of thickne...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel ABCD of 10 cm width has two small slits S(1) and S(2) sealed ...
Text Solution
|
- A point sources S emitting light of wavelength 600nm is placed at a ve...
Text Solution
|
- A prism (mu(P)=sqrt(3)) has an angle of prism A=30^(@).A thin film (mu...
Text Solution
|