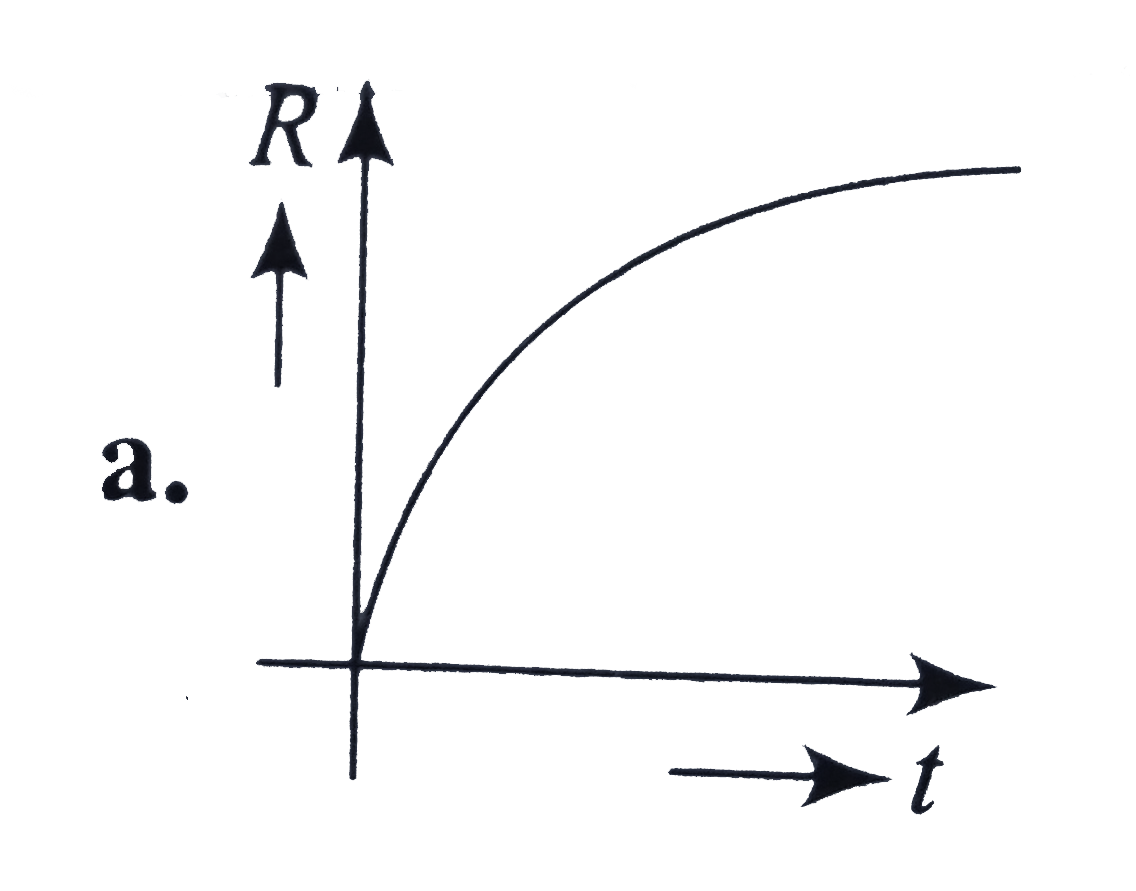
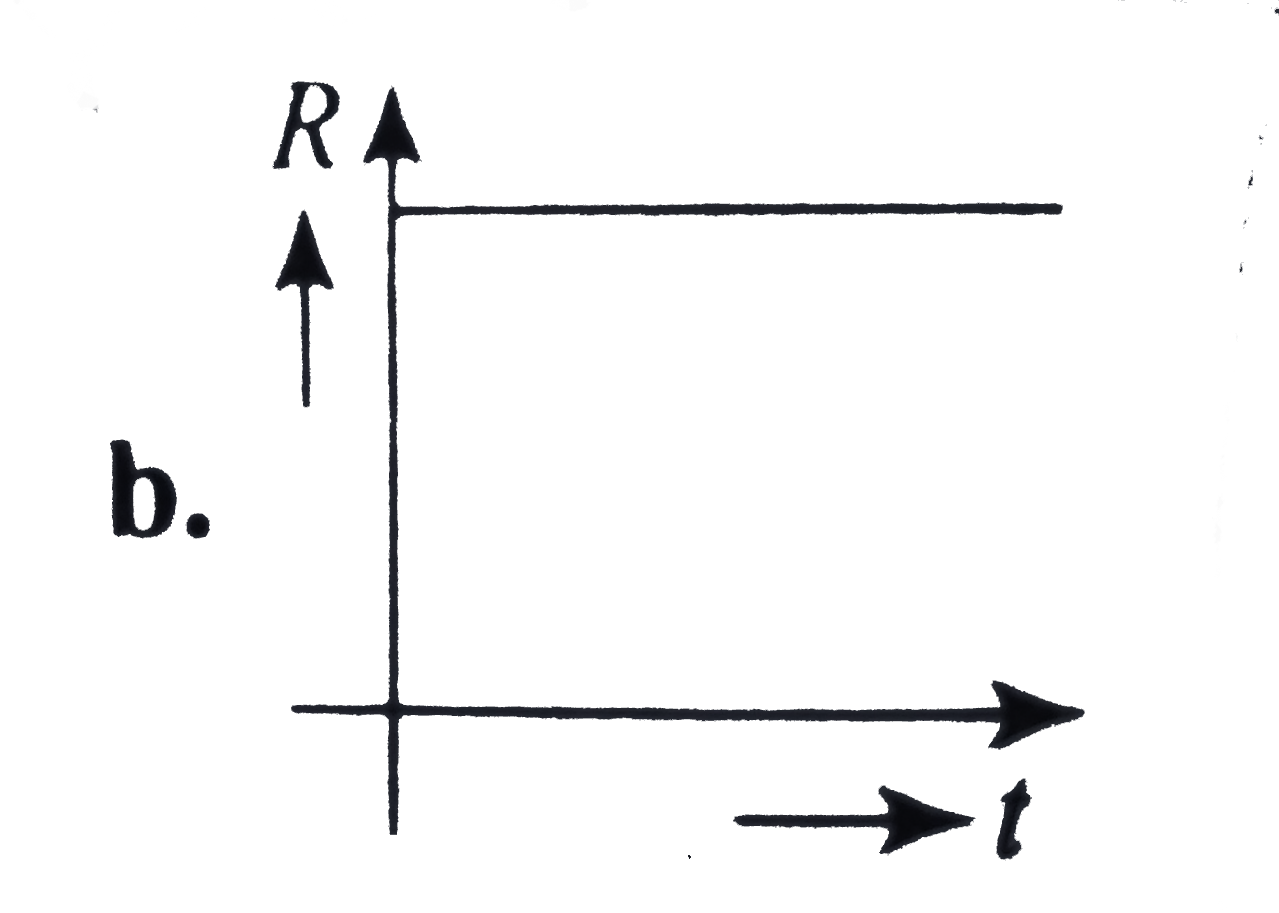
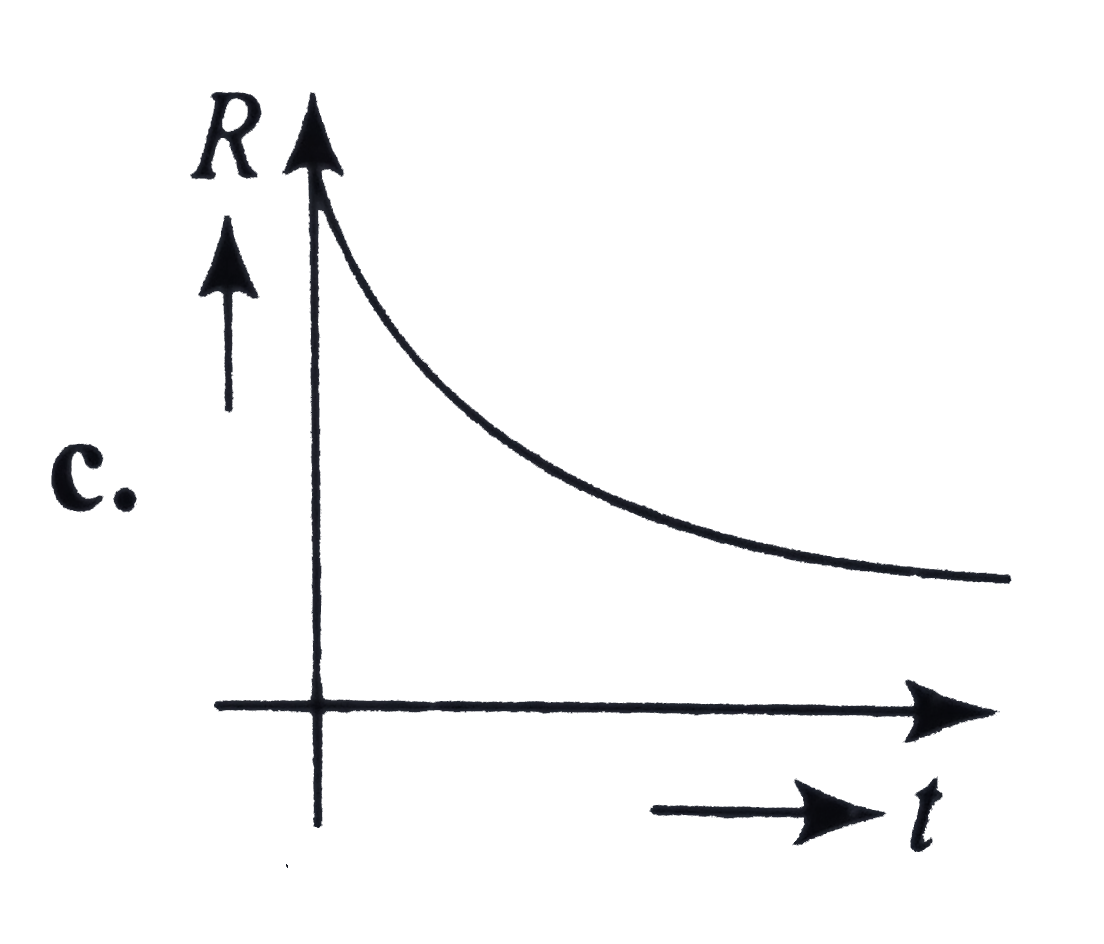
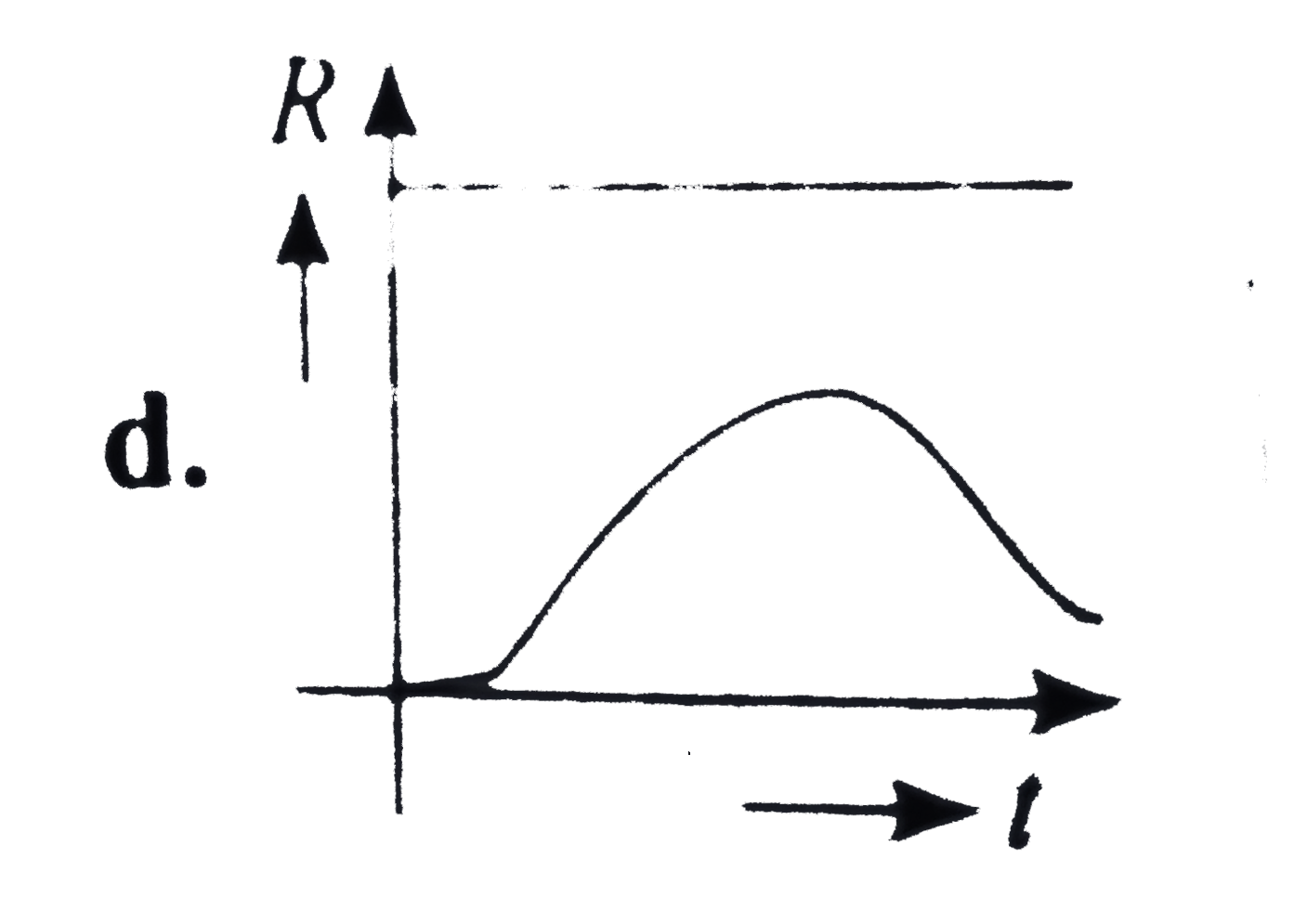
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
NUCLEAR PHYSICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Linked Comprehension|29 VideosNUCLEAR PHYSICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|6 VideosNUCLEAR PHYSICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective|35 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 5
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|12 VideosPHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer Type|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-NUCLEAR PHYSICS-Single Correct Option
- A sample of radioactive material decays simultaneouly by two processes...
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following processes, the number of protons in the nule...
Text Solution
|
- A radioactiev nuleus X deays to a stable nuleus Y. Then, time graph of...
Text Solution
|
- A heavy nuleus having mass number 200 gets disintegrated into two smal...
Text Solution
|
- An element X decays , first by positron emission and then two alpha-pa...
Text Solution
|
- 90% of a radioactive sample is left undecayed after time t has elapsed...
Text Solution
|
- A radioactive element X converts into another stable element. Y half-l...
Text Solution
|
- A radioactive element P disintegrates into Q which further disintegrat...
Text Solution
|
- The binding energy of an electron in the ground state of He is equal t...
Text Solution
|
- The mean life time of a radionuclide, if the activity decrease by 4% ...
Text Solution
|
- On an average, a neutron loses half of its energy per collision with a...
Text Solution
|
- Masses of two isobars .(29)Cu^(64) and .(30)Zn^(64) are 63.9298 u and ...
Text Solution
|
- If a nucleus such as .^(226)Ra that is initially at rest undergoes al...
Text Solution
|
- If the Q value of an endothermic reaction is 11.32 MeV, then the minim...
Text Solution
|
- 1.00 kg of .^(235)U undergoes fission process. If energy released per ...
Text Solution
|
- Mark out the incoreect statemnet.
Text Solution
|
- U-235 can decay by many ways , let us here consider only two ways, A a...
Text Solution
|
- A radio isotope X with a half life 1.4xx10^(9) yr decays of Y which is...
Text Solution
|
- What is the probability of a radioactive nucleus to survive one mean l...
Text Solution
|
- Consider one of fission reactions of ^(235)U by thermal neutrons .(92)...
Text Solution
|