Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Example|25 VideosMAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 1.1|22 VideosINDUCTANCE
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Concept Based|8 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise True and False|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
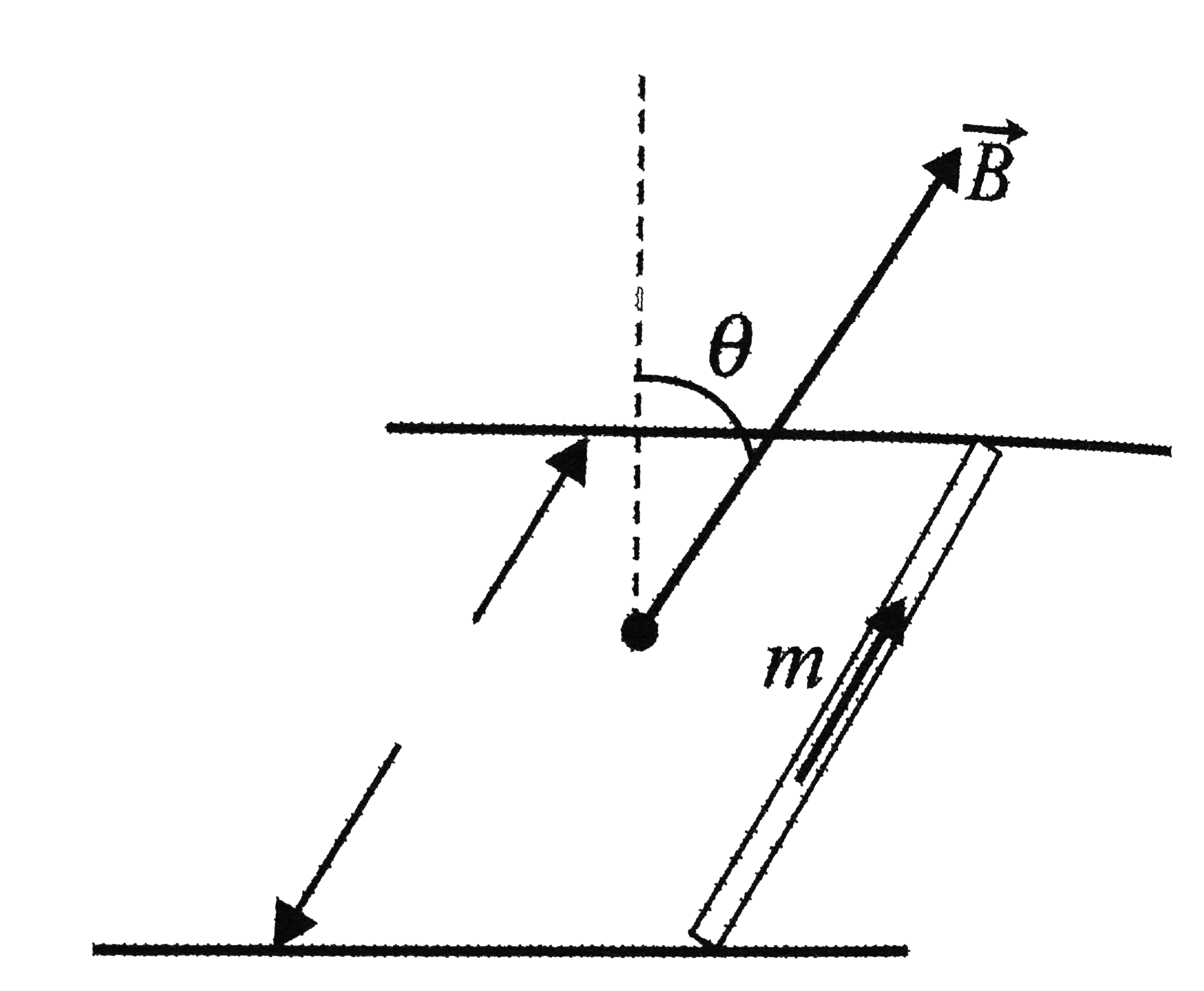
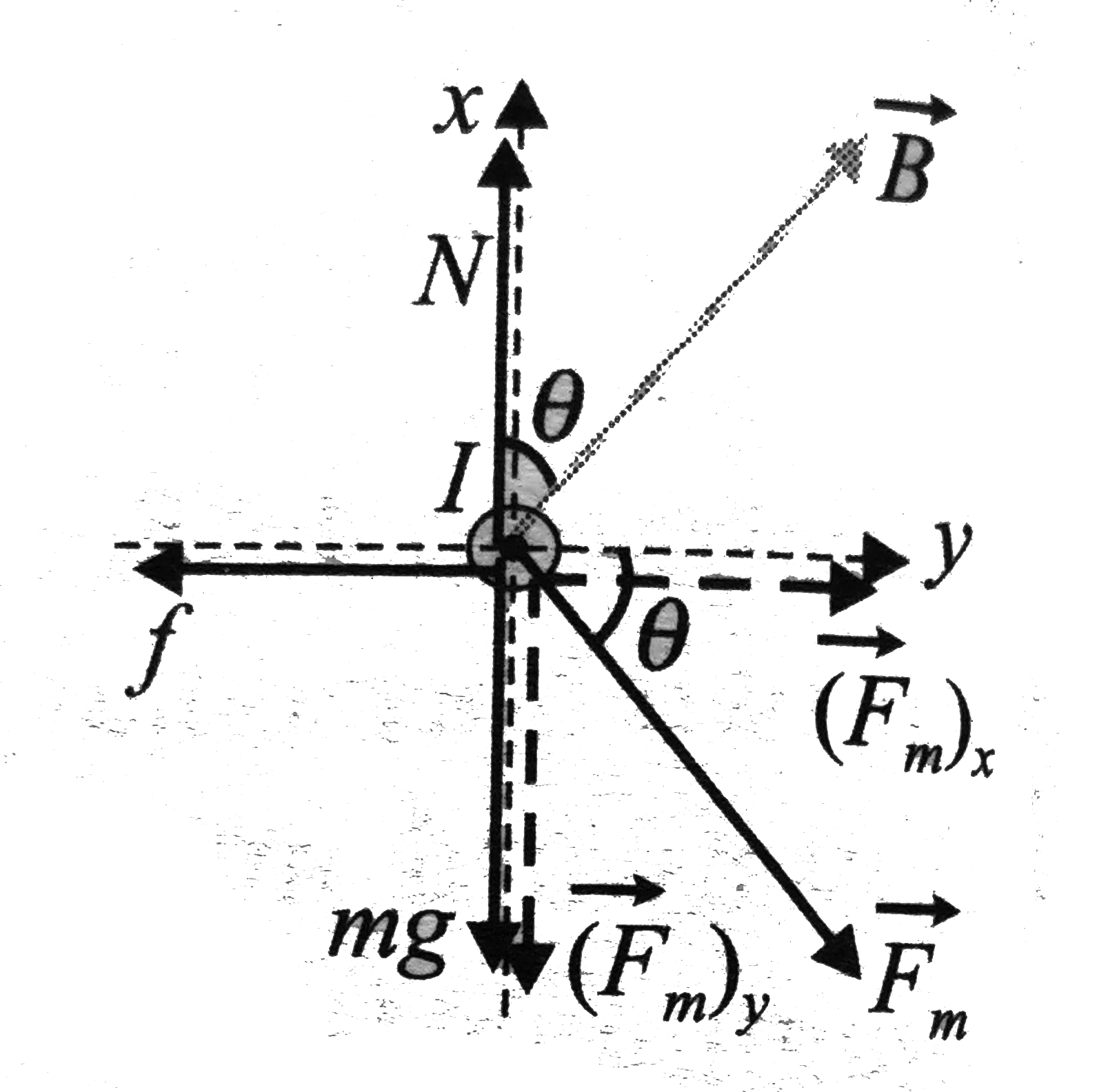 .
.