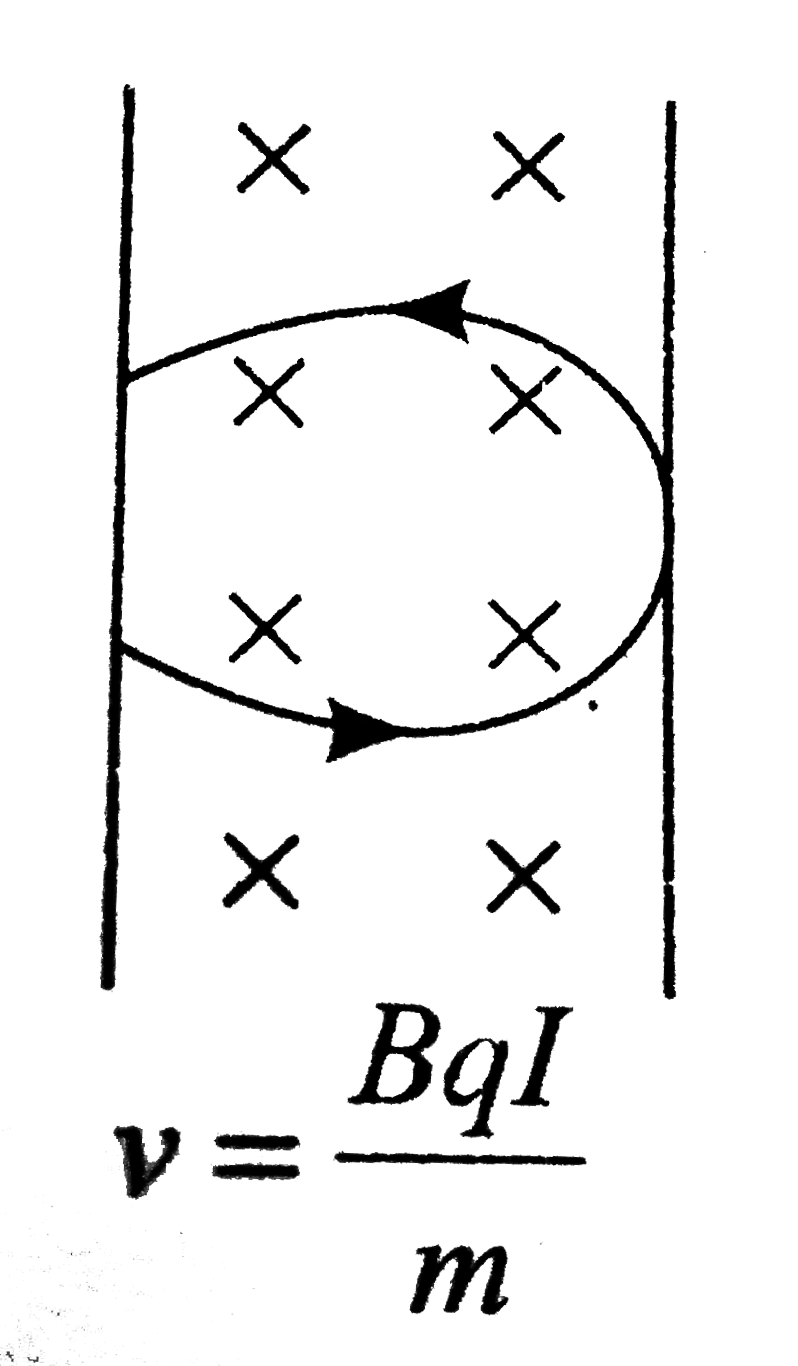
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Comprehension|2 VideosMAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Integer|1 VideosMAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Single Correct|18 VideosINDUCTANCE
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Concept Based|8 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise True and False|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-MAGNETIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC FORCES-Archives Multiple Correct
- A proton moving with a constant velocity passes through a region of sp...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of charge +q and mass m moving under the influence of unifo...
Text Solution
|
- H^(+), He^(+) and O^(2+) ions having same kinetic energy pass through ...
Text Solution
|
- A long current carrying wire, carrying current such that it is flowing...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass mand charge q, moving with velocity v enters Region...
Text Solution
|
- An electron and a proton are moving on straight parallel paths with sa...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the motion of a positive point charge in a region where there...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of massM and positive charge Q, moving with a constant velo...
Text Solution
|
- A conductor (shown in the figure) carrying constant current I is kept ...
Text Solution
|