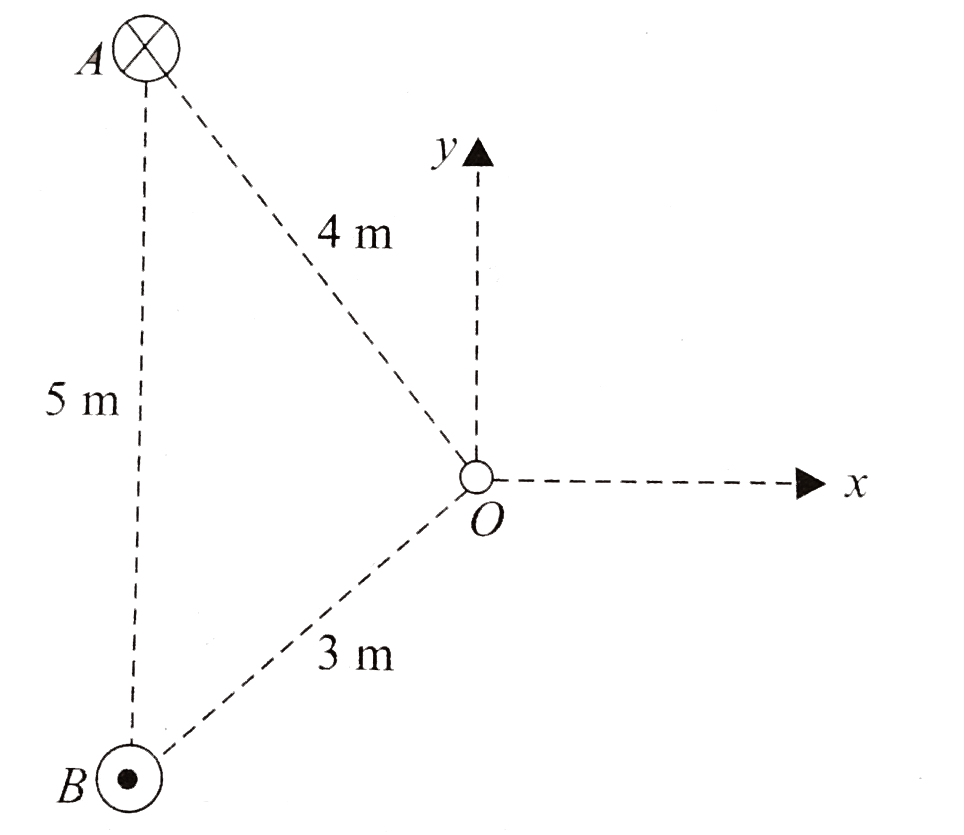
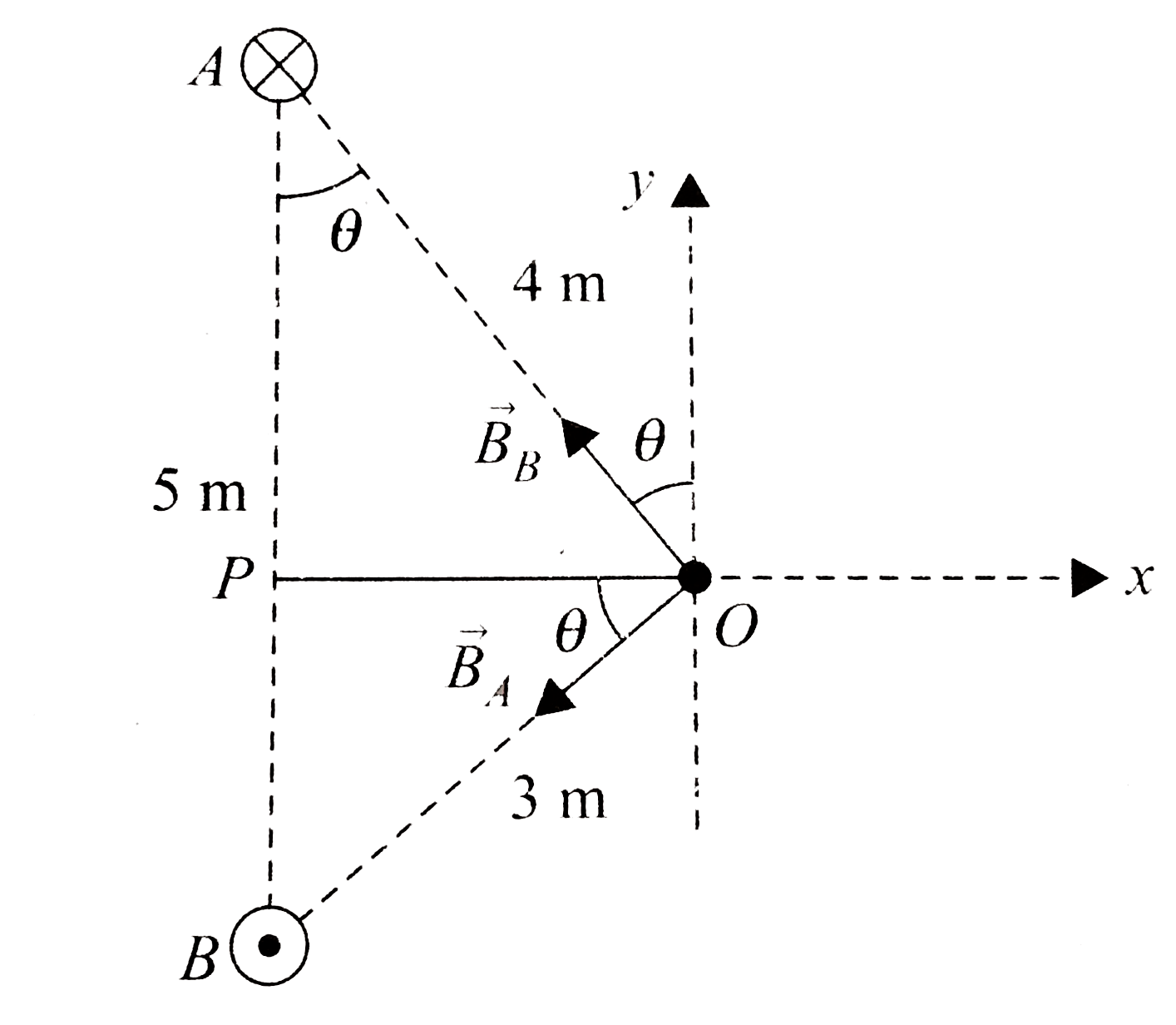
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 5
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct|34 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 5
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Linked Comprehension|84 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 3
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise True and False|3 VideosNUCLEAR PHYSICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise ddp.5.5|14 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 5-Integer
- Two infinitely long straight parallel wire are 5 m apart, perpendicula...
Text Solution
|
- A charged particle enters a uniform magnetic field with velocity v(0) ...
Text Solution
|
- A charged particle of mass m = 1 mg and charge q = 1 (mu) C enter alon...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel wires carrying equal currents i(1) and i(2) with i(1)gti(...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod of mass 200 gm and length 10 cm can slide without fri...
Text Solution
|
- An infinitely long conductor PQR is bent to form a right angle as show...
Text Solution
|
- A magnetic field vec(B)=-B(0)hat(i) exists within a sphere of radius R...
Text Solution
|
- In the given circuit, what is the current I (in A) drawn from battery ...
Text Solution
|
- A coil of inductance L = 5//8 H and of resistance R = 62.8 (Omega) is ...
Text Solution
|
- In the given LCR series circuit find the reading (in A) of the hot wir...
Text Solution
|
- At any instant a current of 2 A is increasing at a rate of 1 A//s thro...
Text Solution
|
- The diagram shows a circuit having a coil of resistance R = 2.5 (Omega...
Text Solution
|
- A thin wire AC shaped as a semi-circle of diameter d rotates with a co...
Text Solution
|