A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-MISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 5-Linked Comprehension
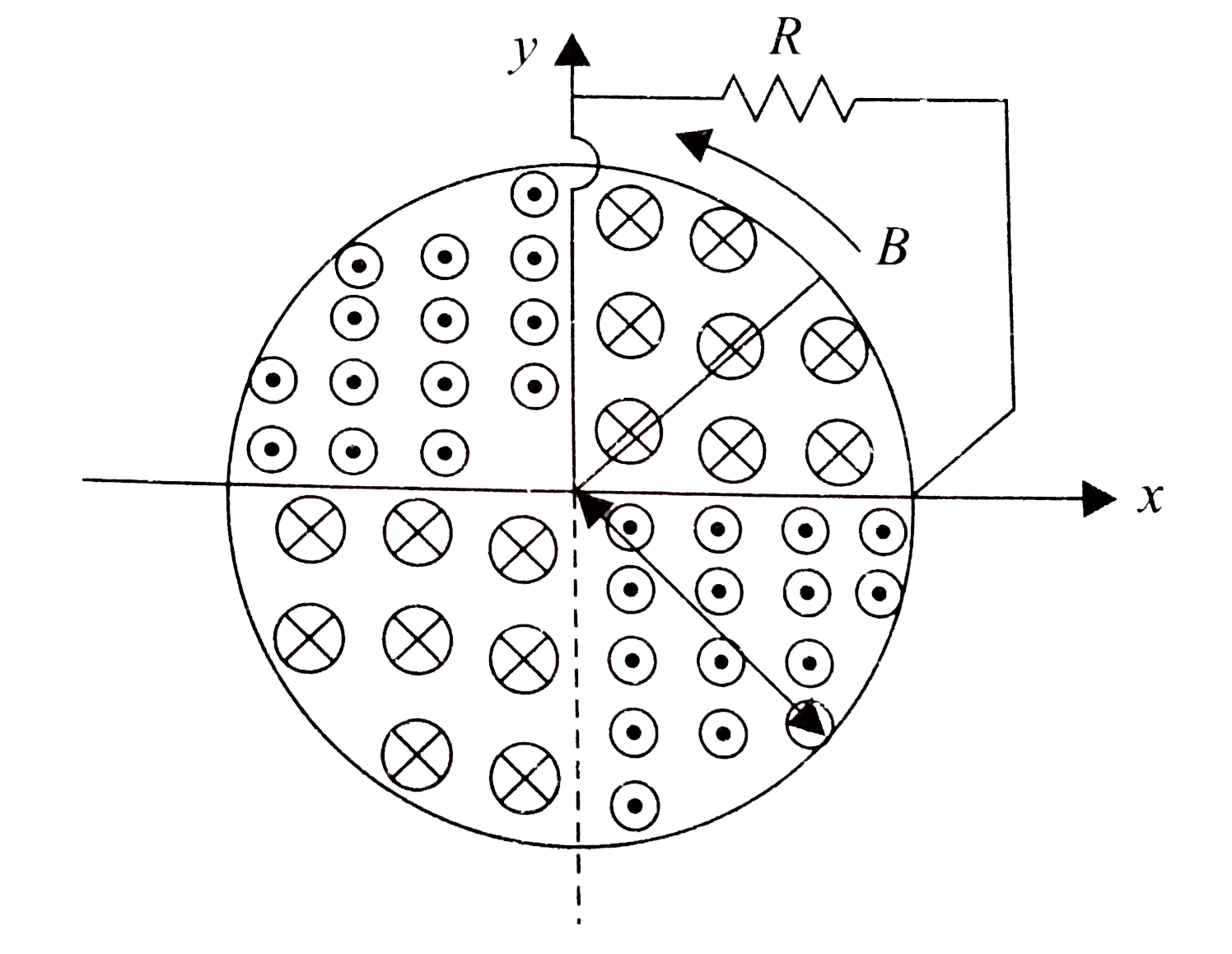
- In a cylindrical region of radius a, magnetic field exists along its a...
Text Solution
|
- In a cylindrical region of radius a, magnetic field exists along its a...
Text Solution
|
- In a cylindrical region of radius a, magnetic field exists along its a...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular wire frame of dimensions (0.25 xx 2.0 m) and mass 0.5 kg...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular wire frame of dimensions (0.25 xx 2.0 m) and mass 0.5 kg...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of mass m and resistance R is sliding over the 2 conduc...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of mass m and resistance R is sliding over the 2 conduc...
Text Solution
|
- A stationary circular loop of radius a is located in a magnetic field ...
Text Solution
|
- A stationary circular loop of radius a is located in a magnetic field ...
Text Solution
|
- A circular ring of radius a is made from a wire having resistance (lam...
Text Solution
|
- A circular ring of radius a is made from a wire having resistance (lam...
Text Solution
|
- A long solenoid having n = 200 turns per metre has a circular cross-se...
Text Solution
|
- A long solenoid having n = 200 turns per metre has a circular cross-se...
Text Solution
|
- A long solenoid having n = 200 turns per metre has a circular cross-se...
Text Solution
|
- A long solenoid having n = 200 turns per metre has a circular cross-se...
Text Solution
|
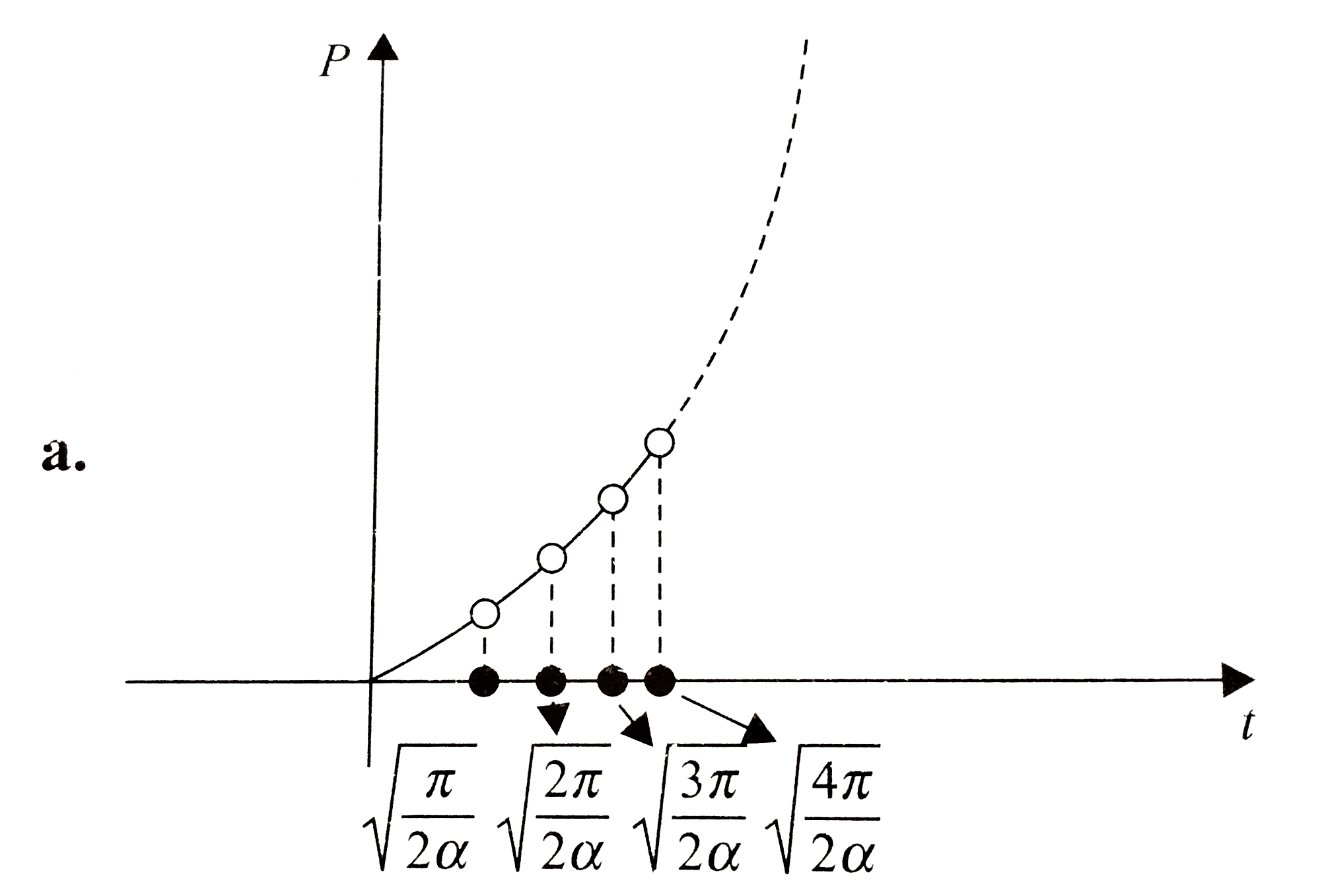
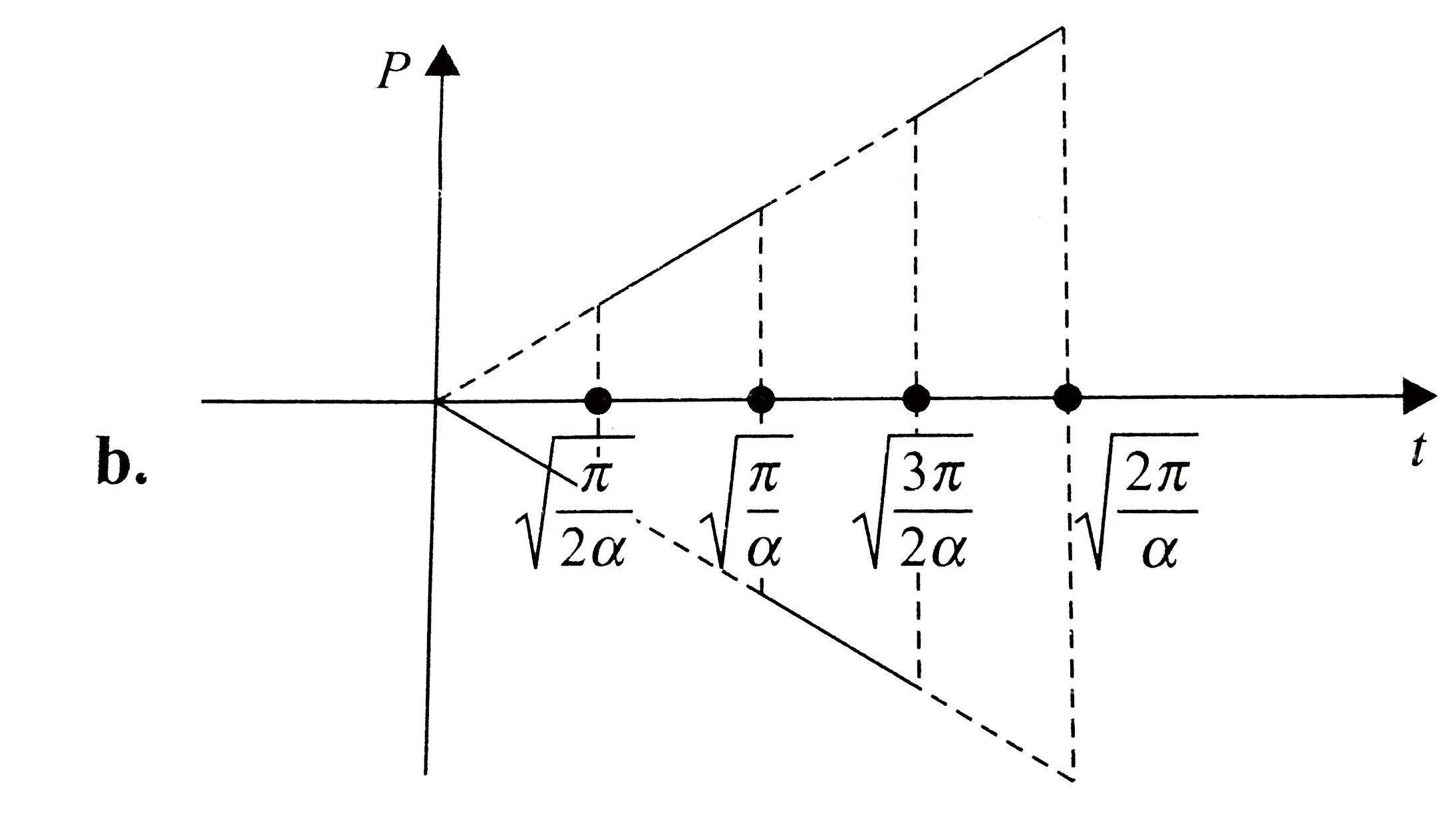
- The potential difference across a 2-H inductor as a function of time i...
Text Solution
|
- The potential difference across a 2-H inductor as a function of time i...
Text Solution
|
- The potential difference across a 2-H inductor as a function of time i...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the circuit shown below. When switch S(1) is closed, let I be...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the circuit shown below. When switch S(1) is closed, let I be...
Text Solution
|

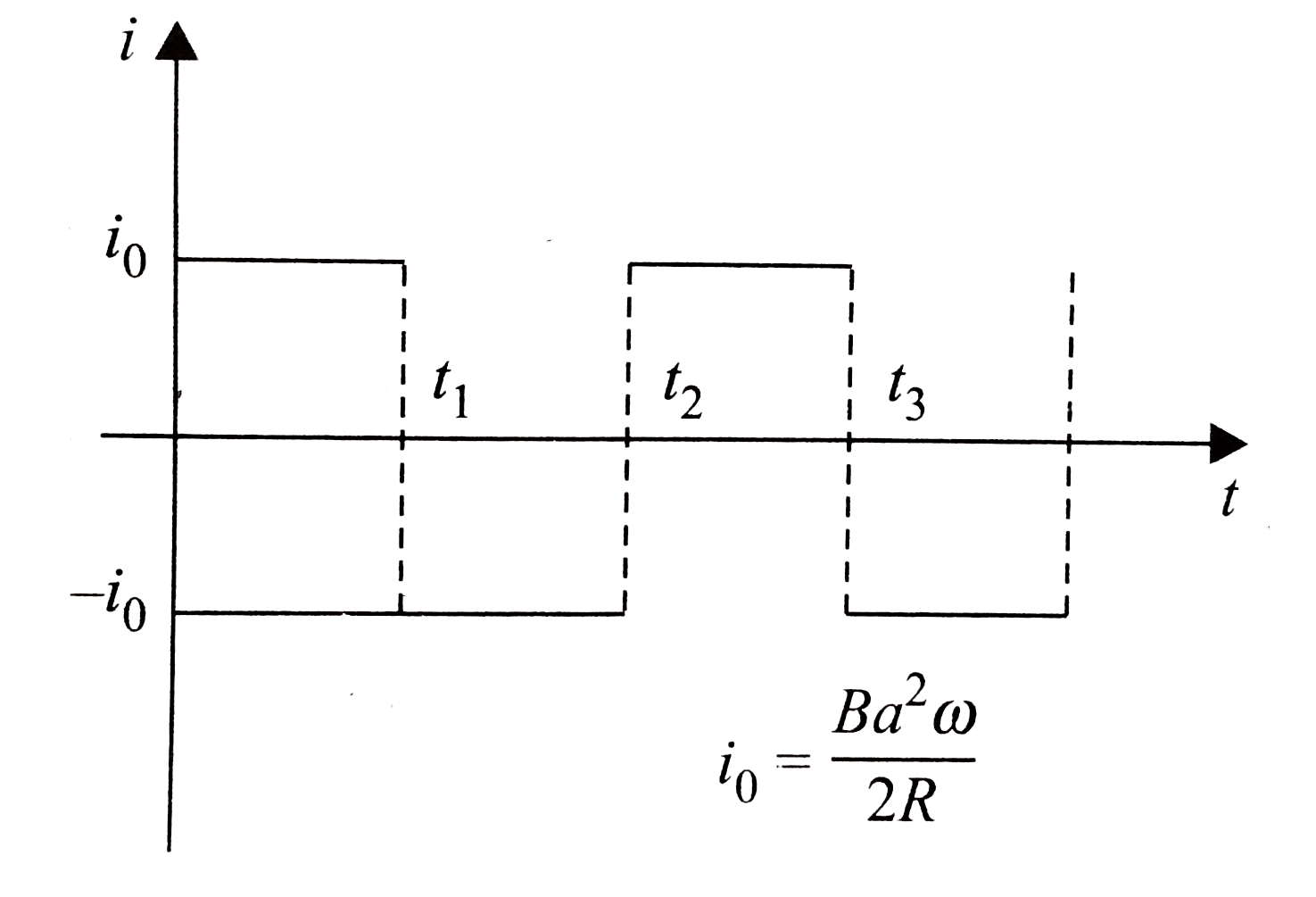
 .
.