Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Single Correct|252 VideosSOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct|44 VideosSOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 6.2|72 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Interger|2 VideosSUPERPOSITION AND STANDING WAVES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Comprehension Type|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-SOUND WAVES AND DOPPLER EFFECT-Subjective
- A window whose area is 2m^2 opens on street where the street noise res...
Text Solution
|
- Two tuning forks A and B are vibrating at the same frequency 256 Hz. A...
Text Solution
|
- A driver in a stationary car horns which produces monochromatic sound ...
Text Solution
|
- The speed of sound in hydrogen gas at certain temperature is v (m)/(s)...
Text Solution
|
- A source of sound of frequency 256 Hz moves rapidly towards a wall wit...
Text Solution
|
- A vibrating tuning fork tied to the end of a string 1.988 m long is wh...
Text Solution
|
- A source of sonic oscillations with frequency n=1700Hz and a receiver ...
Text Solution
|
- A locomotive approaching a crossing at a speed of 80 mi/h sounds a whi...
Text Solution
|
- A whistle of frequency 540 Hz is moving in a circle of radius 2 ft at ...
Text Solution
|
- In a car race sound signals emitted by two cars are detected by the de...
Text Solution
|
- Airport authority has made the regulation that maximum allowable inten...
Text Solution
|
- (a) The power of sound from the speaker of a radio is 20 mW. By turnin...
Text Solution
|
- The sound level at a point is increased by 30 dB. What is factor is th...
Text Solution
|
- What is the maximum possible sound level in dB of sound waves in air? ...
Text Solution
|
- A window whose area is 2m^2 opens on street where the street noise res...
Text Solution
|
- Two tuning forks A and B are vibrating at the same frequency 256 Hz. A...
Text Solution
|
- A driver in a stationary car horns which produces monochromatic sound ...
Text Solution
|
- The speed of sound in hydrogen gas at certain temperature is v (m)/(s)...
Text Solution
|
- A source of sound of frequency 256 Hz moves rapidly towards a wall wit...
Text Solution
|
- A vibrating tuning fork tied to the end of a string 1.988 m long is wh...
Text Solution
|
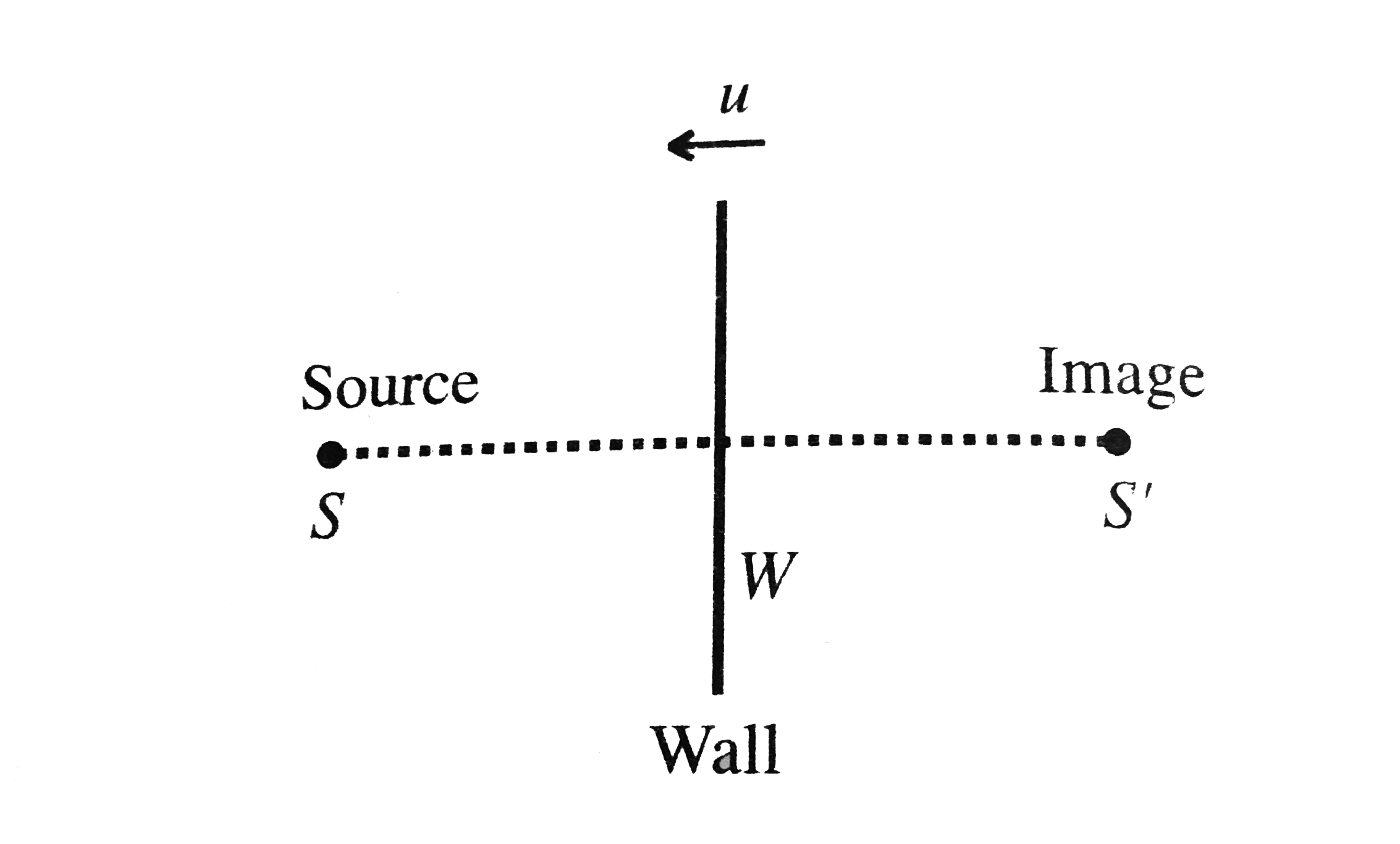 A driver in a stationary car horns which produces monochromatic sound waves of frequency `n=1000Hz`, normally towards a reflecting wall. If the wall approaches the car will a velocity `u=3.3(m)/(s)`, calculate the frequency of sound reflected from wall and heard by the driver. What is the percentage change of sound frequency of reflection from the wall?
A driver in a stationary car horns which produces monochromatic sound waves of frequency `n=1000Hz`, normally towards a reflecting wall. If the wall approaches the car will a velocity `u=3.3(m)/(s)`, calculate the frequency of sound reflected from wall and heard by the driver. What is the percentage change of sound frequency of reflection from the wall?