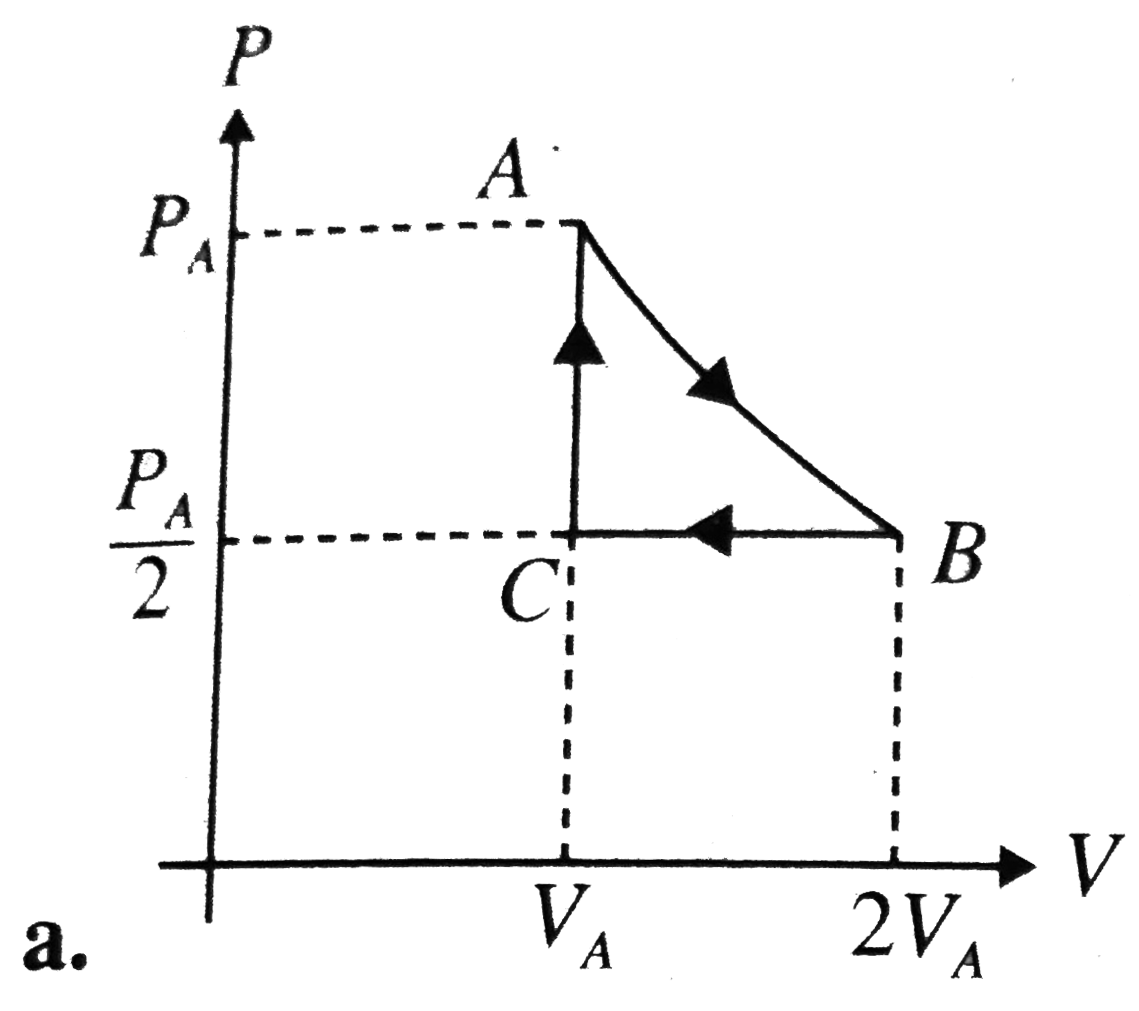
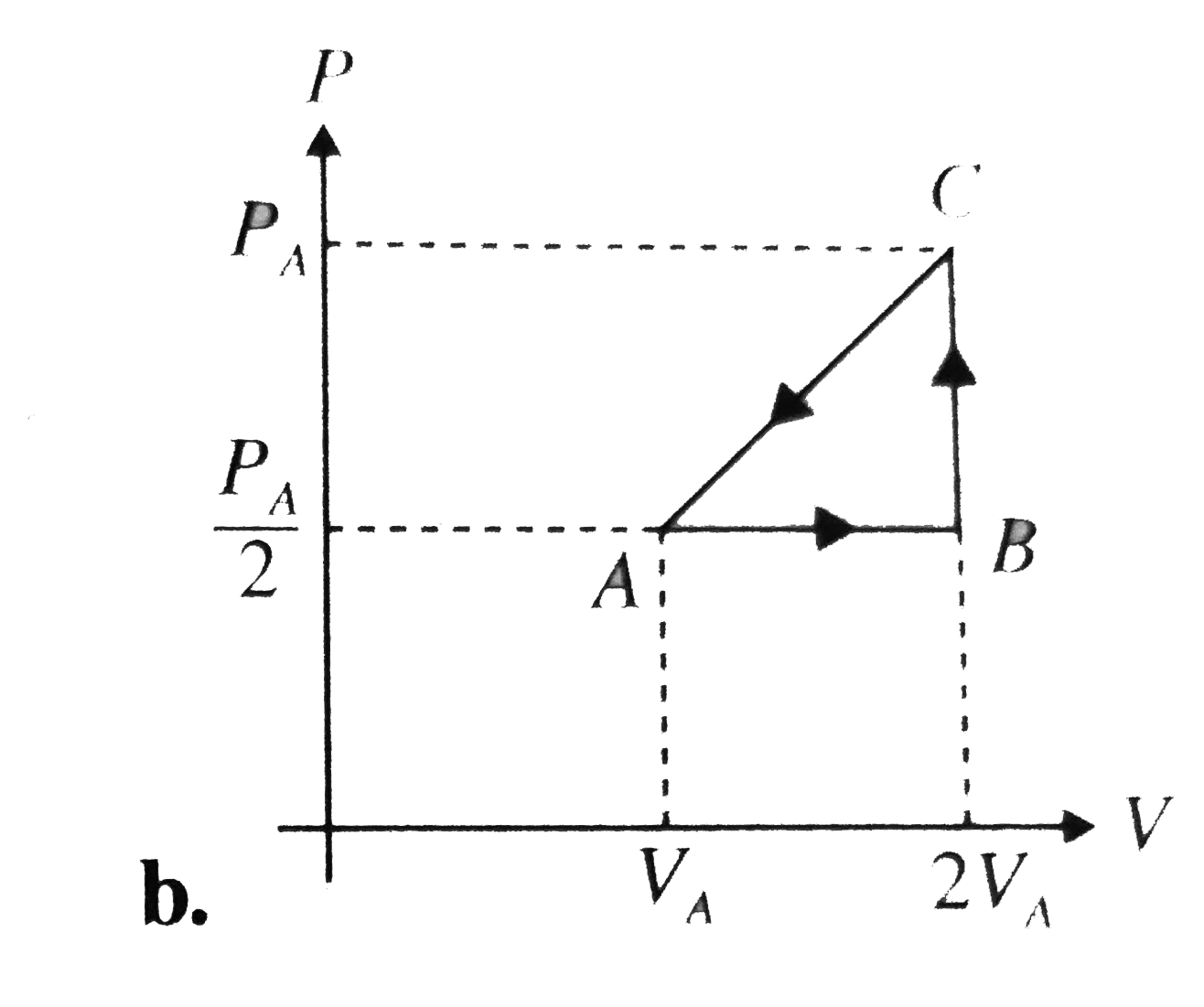
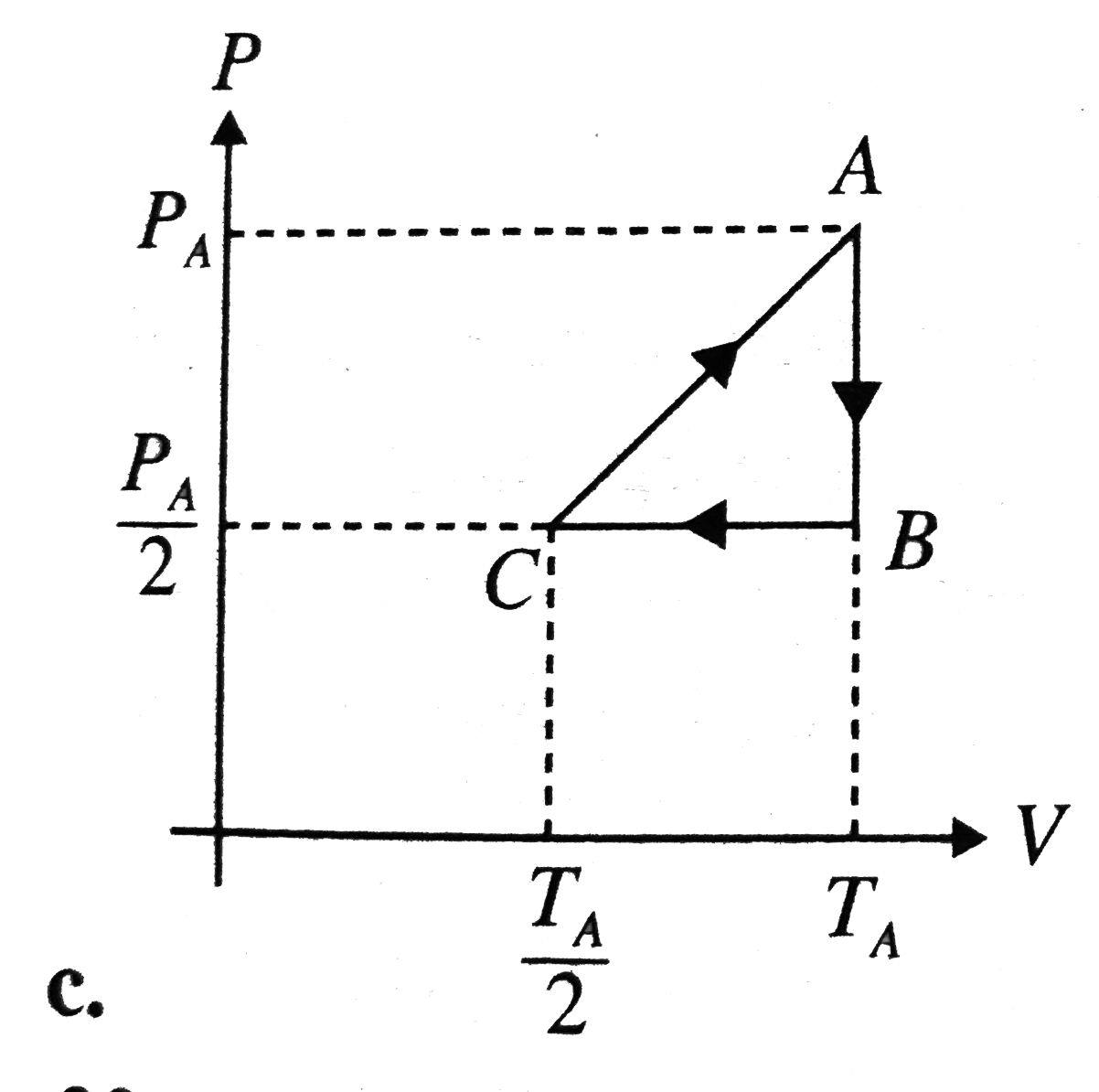
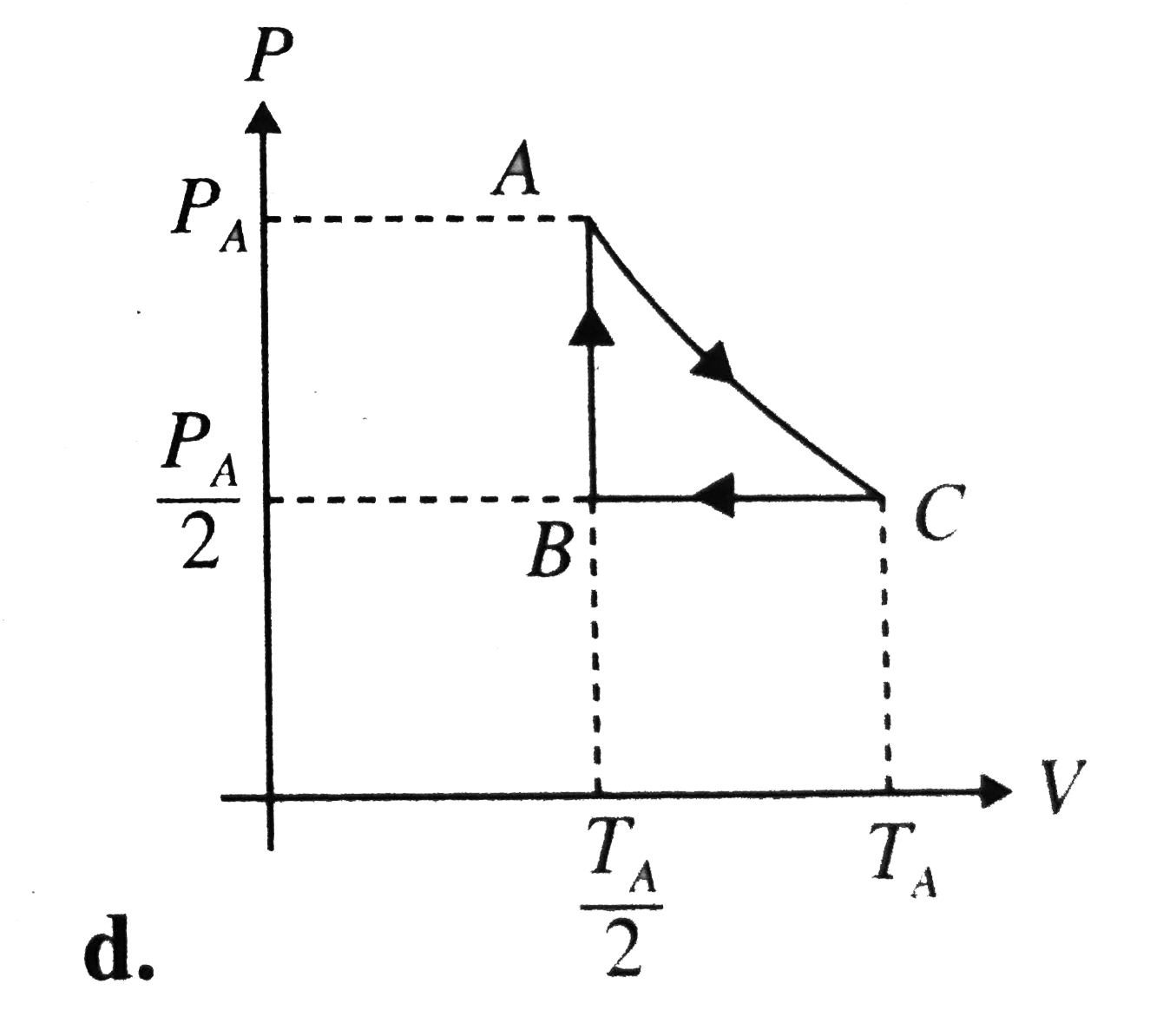
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion-Reasoning|6 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Comprehension|56 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Single Correct|140 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Compression|2 VideosLINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Single correct anwer type|14 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-KINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS-Multiple Corrects
- A closed vessel contains a mixture of two diatomic gases A and B. Mola...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas undergoes a thermodynamic cycle as shown in figure: ...
Text Solution
|
- Which the following statements are correct ?
Text Solution
|
- Figure. Shows the P-V diagram for a Carnot cycle. In this diagram
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows an indicator diagram. During path 1-2-3, 100 cal is given...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal monatomic gas has initial temperature T(0), is ma...
Text Solution
|
- P - V diagram of a cyclic process ABCA is as shown in Fig. Choose the ...
Text Solution
|
- During the process AB of an ideal gas
Text Solution
|
- Temperature versus pressure graph of an ideal gas is shown in figure. ...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas undergoes the cyclic process shown in a graph below :
Text Solution
|
- The indicator diagram for two processes 1(isothermal) and 2(adiabatic)...
Text Solution
|
- Three moles of an ideal gas (Cp=7/2R) at pressure, PA and temperature ...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is taken from the state A (pressure p, volume V) to the s...
Text Solution
|
- A partition divides a container having insulated walls into two compar...
Text Solution
|
- During an experiment, an ideal gas is found to obey a condition (p^2)/...
Text Solution
|
- Pick the correct statement (s) :
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas undergoes an expansion from a state with temperature T(1)...
Text Solution
|
- A system undergoes three quasi-static process sequentially as indicate...
Text Solution
|
- An insulated 0.2 m^(3) tank contains helium at 1200 kPa and 47^(@)C. A...
Text Solution
|
- A gas in container A is in thermal equilibrium with another gas in con...
Text Solution
|