A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise DPP 1.3|14 VideosRAY OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise DPP 1.4|15 VideosRAY OPTICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Matching Column Type|1 VideosPHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer Type|4 VideosSOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise single correct Ansewer type|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-RAY OPTICS-DPP 1.2
- One side of a glass slab is silvered as shown. A ray of light is incid...
Text Solution
|
- When the rectangular metal tank is filled to the top with an unkown li...
Text Solution
|
- A transparent cube of 15 cm edge contains a small air bubble. Its appa...
Text Solution
|
- A plane mirror is placed at the bottom of a tank containing a liquid o...
Text Solution
|
- One face of a rectangular glass plate 6 cm thick is silvered. An objec...
Text Solution
|
- A concave mirror is placed at the bottom of an empty tank with face up...
Text Solution
|
- A slab of glass, of thickness 6 cm and refractive index mu=1.5 is plac...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travels from an optically denser to rarer medium. The c...
Text Solution
|
- A point source of light S is placed at the bottom of a vessel containg...
Text Solution
|
- Light enters at an angle of incidence in a transparent rod of refracti...
Text Solution
|
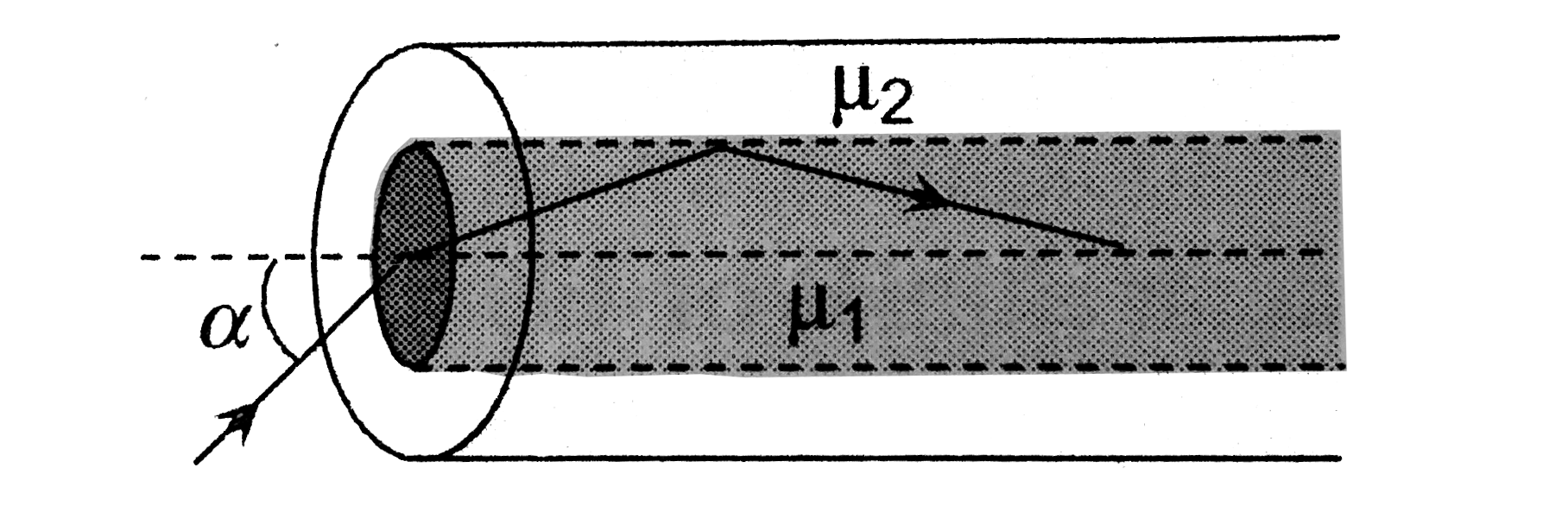
- An optical fibre consists of core of mu(1) surrounded by a cladding of...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of glass ( mu = 1.5) and of square cross section is bent into t...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travels from a medium of refractive index mu to air. It...
Text Solution
|
- The apparent depth of water in cylindrical water tank of diameter 2R i...
Text Solution
|
- When light is incident on a medium at angle i and refracted into a sec...
Text Solution
|