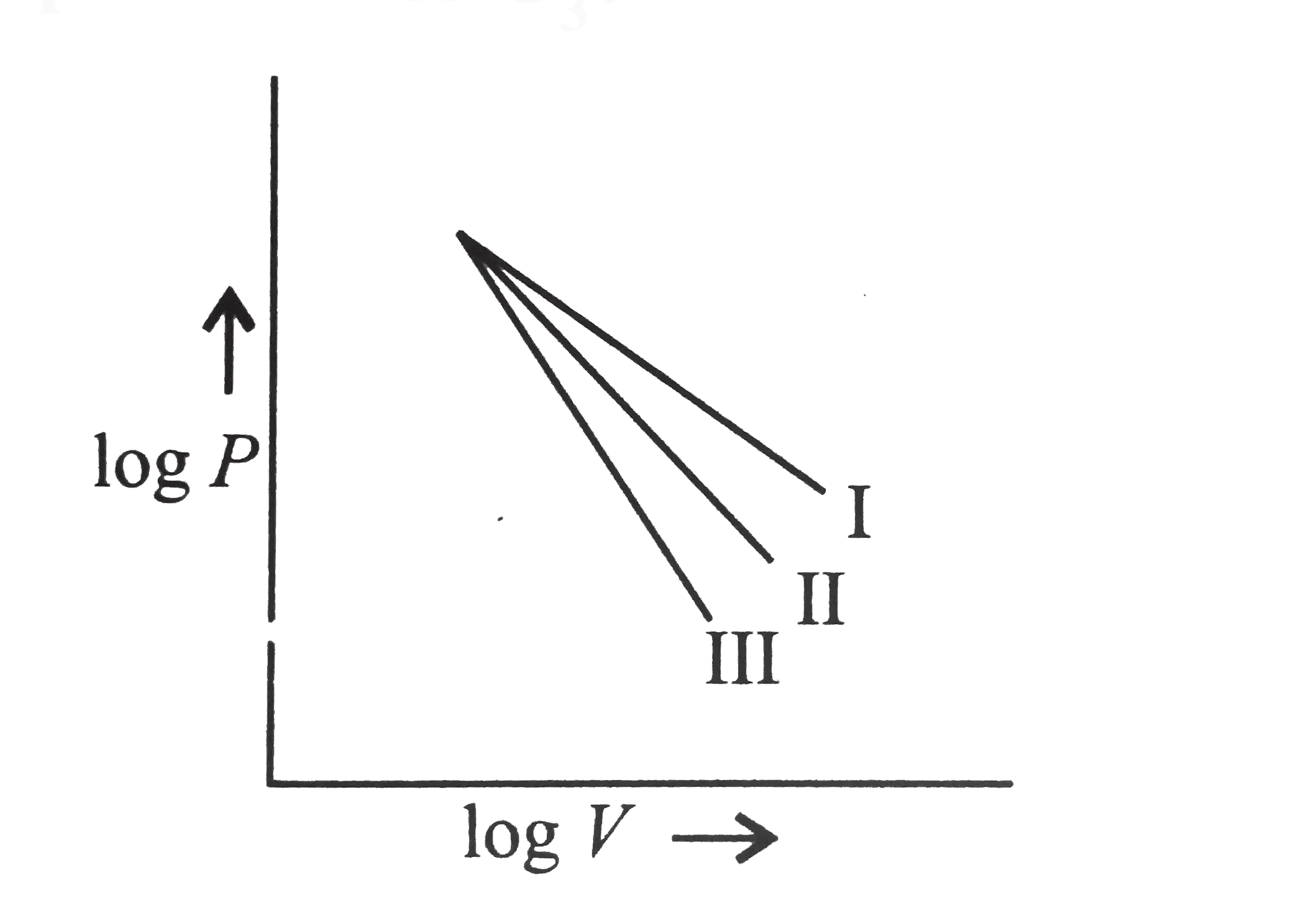
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-THERMODYNAMICS-Archives (Subjective)
- The following curve represent adiabatic expansions of gases He,O(2),an...
Text Solution
|
- The enthalpies for the following reactions (DeltaH^(Theta)) at 25^(@)C...
Text Solution
|
- The standared enthalpies of formation at 298K for C C1(g), H(2)O(g), C...
Text Solution
|
- Given that: i. C(s) + O(2)(g) rarr CO(2)(g) , DeltaH =- 94.05 kcal ...
Text Solution
|
- The following statement is true only under some specific conditions. W...
Text Solution
|
- The bond dissociation energies of gaseous H(2),Cl(2), and HCl are 100,...
Text Solution
|
- The standard molar heat of formation of ethane, carbon dioxide and wat...
Text Solution
|
- An intimate mixture of ferric oxide and aluminium is used as solid fue...
Text Solution
|
- The enthalpy of combustion of H(2), cyclohexene (C(6)H(10)) and cycloh...
Text Solution
|
- CsOH +HCI rarr CsCI +H(2)O, DeltaH =- 13.4 kcal mol^(-1)……….(i) CsOH...
Text Solution
|
- Determine enthalpy change for, C(3)H(8(g))+H(2(g))rarr C(2)H(6(g))+C...
Text Solution
|
- Compute the heat of formation of liquid methyl alcohol in kilojoule pe...
Text Solution
|
- From the following data, calculate the enthalpy change for the combust...
Text Solution
|
- The standard heat of formation values of SF(6)(g), S(g), and F(g) are ...
Text Solution
|
- Show that the reaction CO(g) +(1//2)O(2)(g) rarr CO(2)(g) at 300K ...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of argon gas at 1atm pressure and 27^(@)C expands reversibly ...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the enthalpy of formation of B(2)H(6)(g) in kJ/mol of the fo...
Text Solution
|
- The standart potential of the following cell is 0.23 at 15^(@)C and 0....
Text Solution
|
- When 1pentyne (A) is treated with 4N alcoholic KOH at 175^(@)C, it is ...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of a perfect gas undergo the following processes: a. A rev...
Text Solution
|
- C(v) values of He is always (3R)/(2) but C(v) values of H(2) is (3R)/(...
Text Solution
|