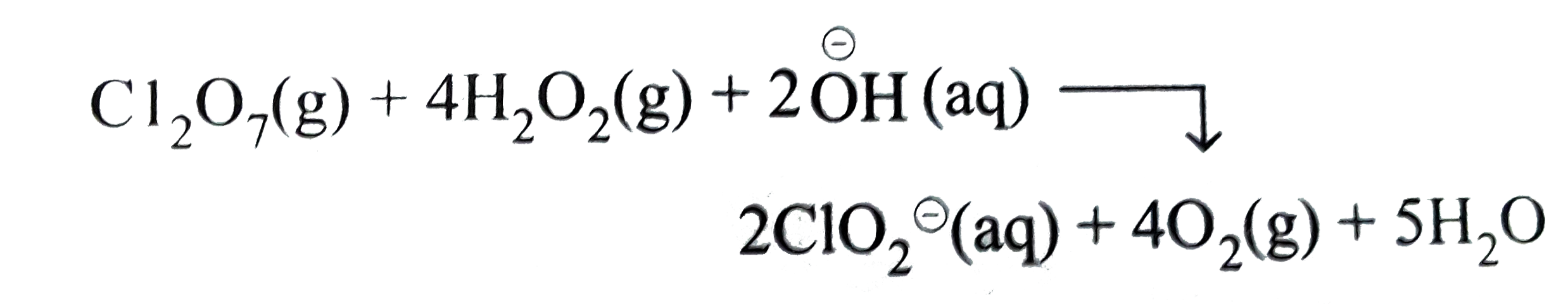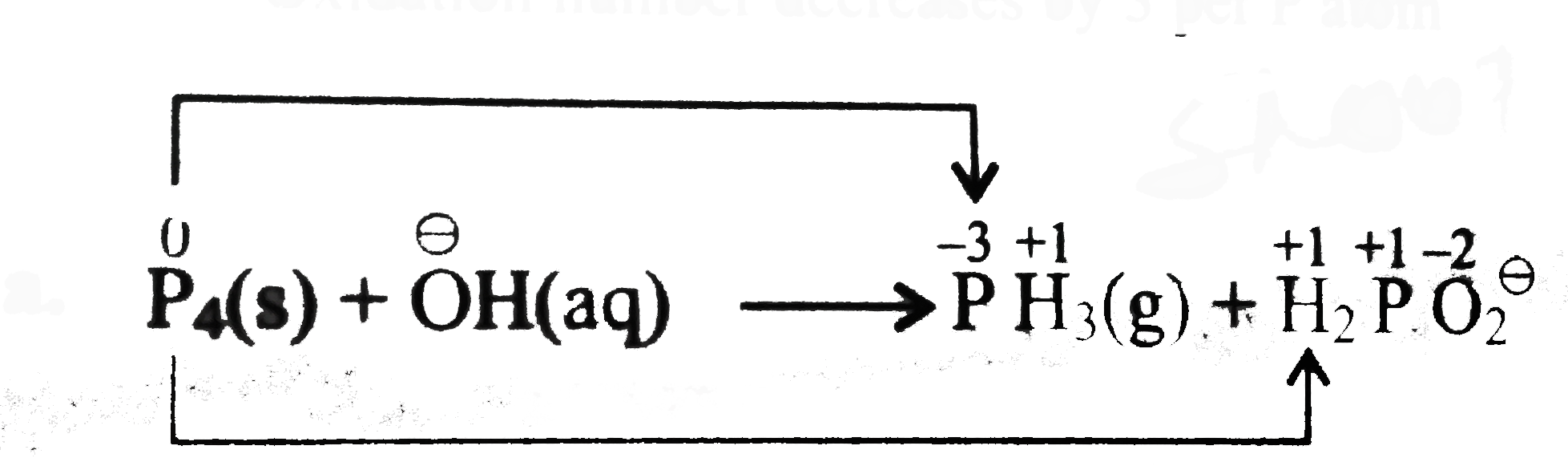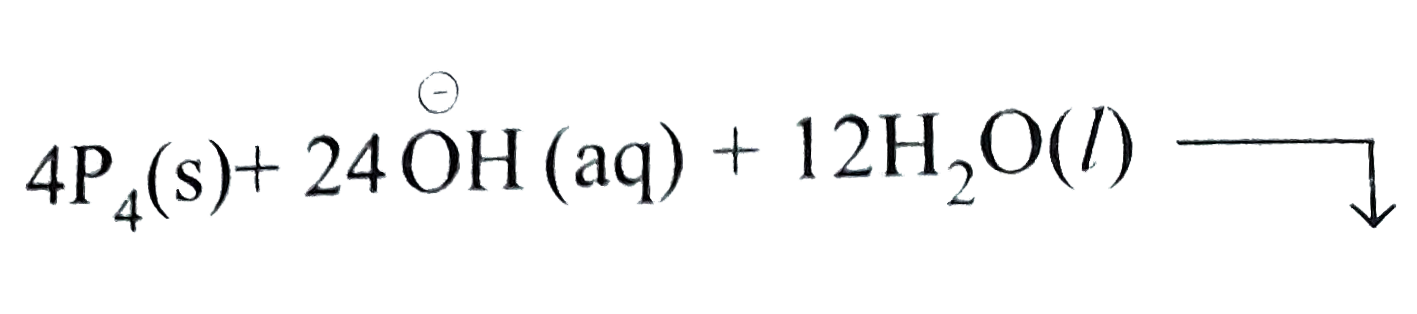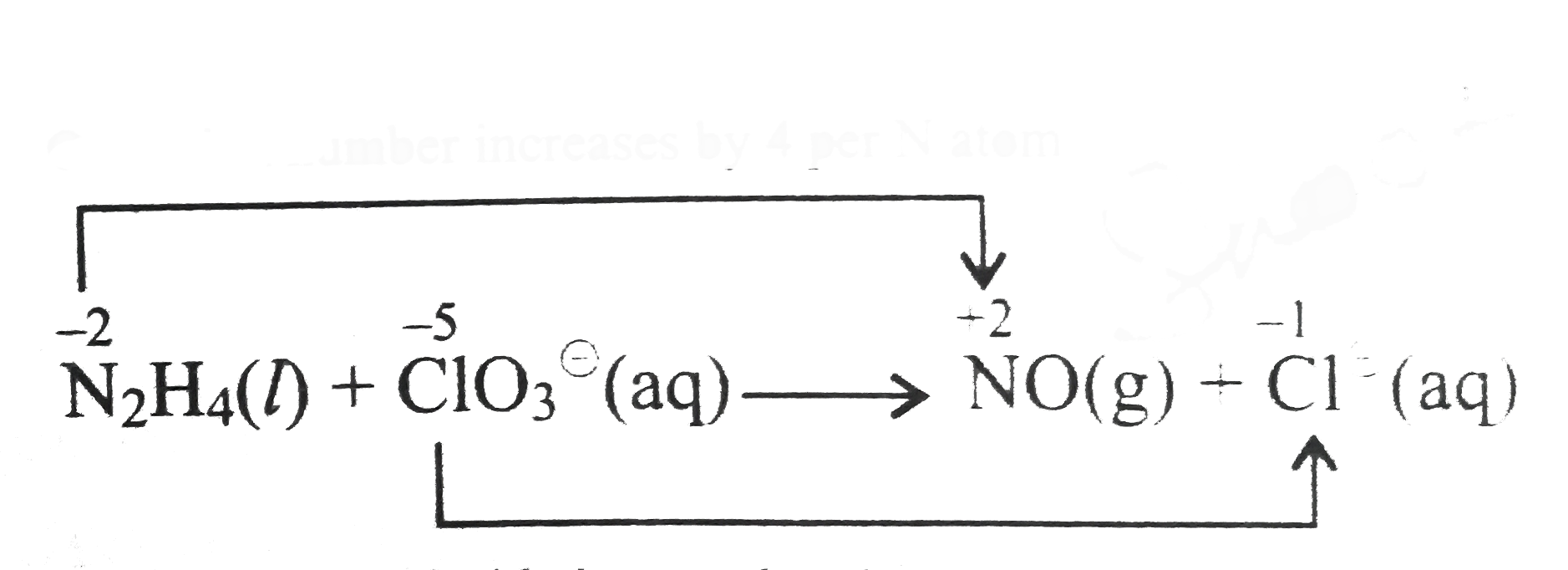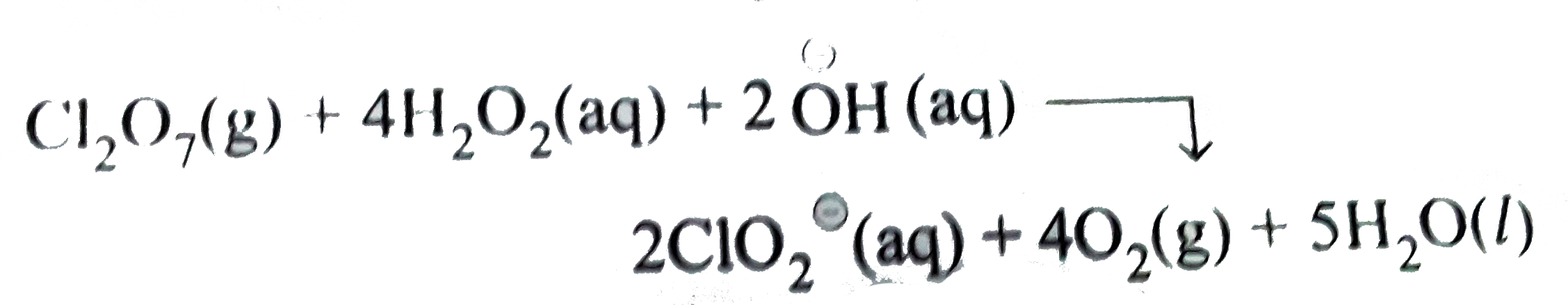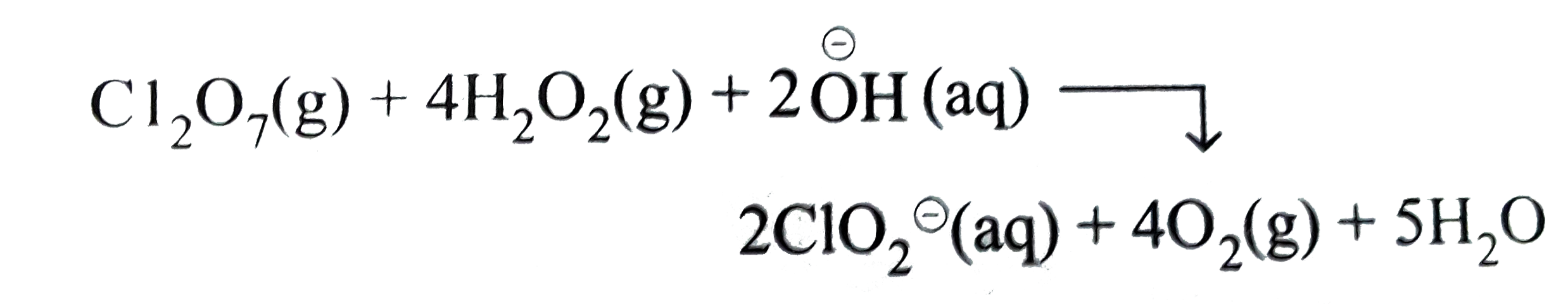a.
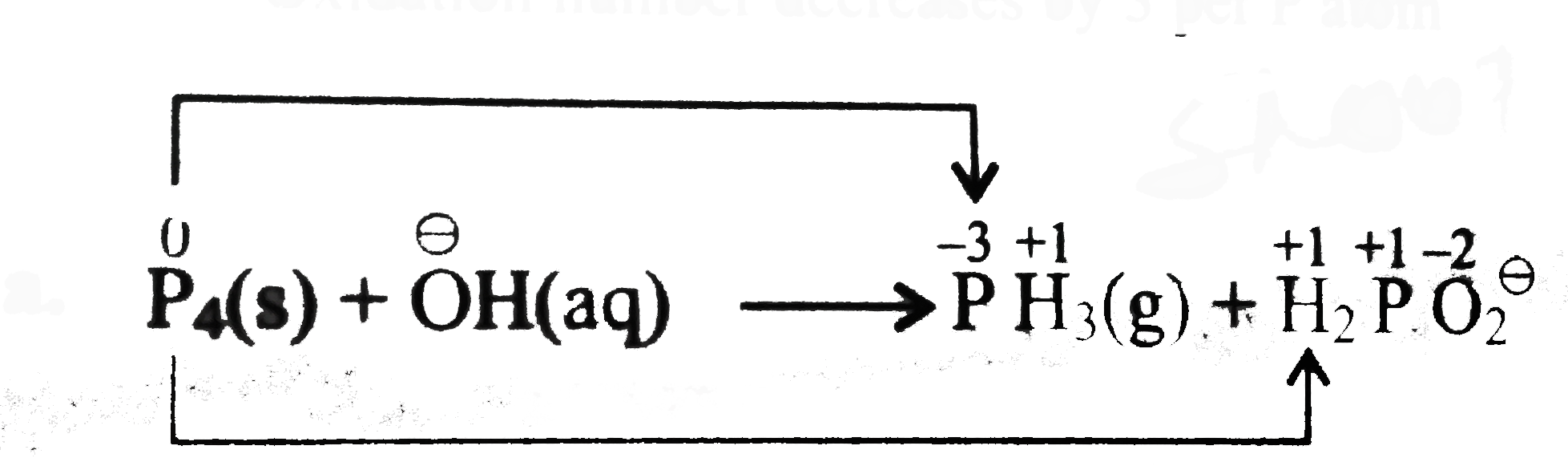
`P_(4)` acts both as an oxidising as well as a reducing agent.
Oxidising number method:
Total decrease in oxidation number of `P_(4)` in
`PH_(3)= 3xx4=12`
Total increase in oxidation number of `P_(4)` in
`H_(2)PO_(2)^(Θ)=1xx4=4`
Therefore, to balance increase`//`decreases in oxidation numer multiply `PH_(3)` by `1` and `H_(2)PO_(2)^(Θ)` by `3`, we have,
`P_(4)(s)+overset(Θ)OH(aq)rarrPH_(3)(g)+3H_(2)PO_(2)^(Θ)(aq)`
To balance `H` atoms, add `3H_(2)O` to L.H.S and `3overset(Θ)OH` to the R.H.S we have,
`P_(4)(s)+6overset(Θ)OH+3H_(2)O(l)rarrPH_(3)(g)+3H_(2)PO_(2)^(Θ)(aq)+3overset(Θ)OH(aq)`
or
`P_(4)(s)+3overset(Θ)OH(aq)+3H_(2)O(l)rarrPH_(3)(g)+3H_(2)PO_(2)^(Θ)(aq)`....(i)
Thus, Eq (i) represents the correct balanced equation.
Ion electron method:
Oxidation half equation
`P_(4)(s)rarrH_(2)PO_(2)^(Θ)(aq)`....(ii)
Balancing `P` atoms, we have,
`overset(0)(P_(4)(s)rarr4H_(2)overset(+1)(PO_(2)^(Θ)(aq)`
Balancing oxidation number by adding electrons,
`P_(4)(s)rarr4H_(2)PO_(2)^(Θ)(aq)+4e^(-)`
balance charged by adding `overset(Θ)OH` ions
`P_(4)(s)+8overset(Θ)OH(aq)rarr4H_(2)PO_(2)^(Θ)(aq)+4e^(-)`....(iii)
`O` and `H` get automatically balanced. Thus, equation (iii) represents the balanced oxidation half reaction.
Reduction half equation
`overset(0)P_(4)(s)rarroverset(-3)(PH_(3))(g)`.....(i)
Balancing `P` atoms, we have,
`P_(4)(s)rarr4PH_(3)(g)`
Balance oxidation number by adding electrons,
`P_(4)(s)+12e^(-)rarr4PH_(3)(g)+12overset(Θ)OH(aq)`....(v)
To cancel out electrons, multiply equation (iii) by `3` and add it to equation (v) we have,
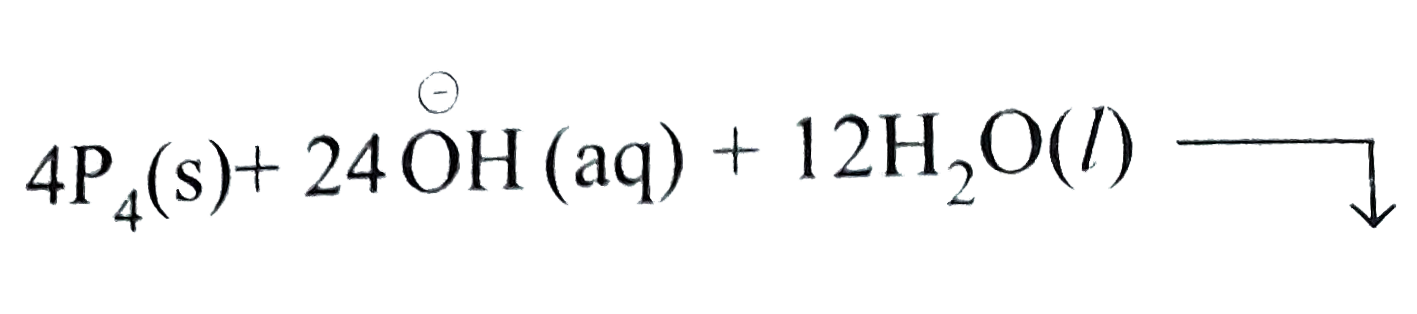
or `P_(4)(g)+3overset(Θ)OH(g)+3H_(2)O(l)rarrPH_(3)(aq)+3H_(2)PO_(2)^(Θ)(aq)`....(vi)
Thus, equation (vi) represents the correct balanced equation.
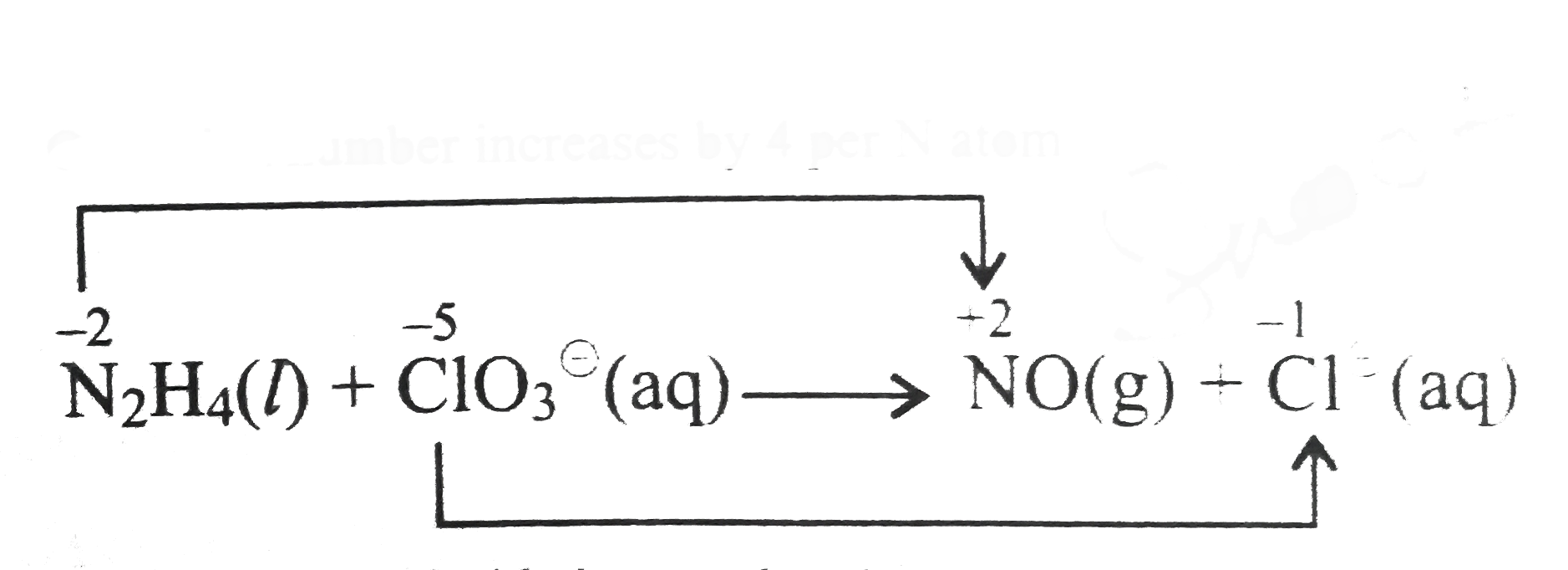
Therefore, `N_(2)H_(4)` acts as the reducing agent while `ClO_(3)^(Θ)` acts as the oxidising agent.
Oxidation number method:
Total increase in oxidation number of `N=2xx4=8`
Total decrease in oxidation number of `Cl= 1xx6=6`
Therefore, to balance the increase`//`decrease in oxidation number multiply `N_(2)H_(4)` by `3` and `ClO_(3)^(Θ)` by `4` we have,
`3N_(2)H_(4)(l)+4ClO_(3)^(Θ)(aq)rarr6NO(g)+Cl^(Θ)(aq)`
To balance `N` and `Cl` atoms, multiply `NO` by `6` and `Cl^(Θ)` by `4` we have,
`3N_(2)H_(4)(l)+4ClO_(3)^(Θ)(aq)rarr6NO(g)+4Cl^(Θ)(aq)`
Balance `O` atoms by adding `6H_(2)O`,
`3N_(2)H_(4)(l)+4ClO_(3)^(Θ)(aq)rarr6NO(g)+4Cl^(Θ)(aq)+6H_(2)O(l)`....(i)
`H` atoms get automatically balanced and thus equation
(i) represents the correct balanced equation.
Ion electron methd.
Oxidation half equation
`overset(-2)N_(2)(l)rarroverset(+2)NO(g)`
Balance `N` atoms,
`N_(2)H_(4)(l)rarr2NO(g)+8e^(-)`
Balance charge by adding `overset(Θ)OH` ions.
`N_(2)H_(4)(l)+8overset(Θ)OH(aq)rarr2NO(l)+8e^(-)`
Balance `O` atoms by adding `6H_(2)O`,
`N_(2)H_(4)(l)+8overset(Θ)OH(aq)rarr2NO(g)+6H_(2)O(l)+8e^(-)`....(ii)
Thus, equation (ii) represents the correct balanced oxidation half equation.
Reduction half equation
`overset(+5)(ClO_(3)^(Θ))(aq)rarroverset(-1)(Cl^(Θ))(aq)`
Balance oxidation number by adding electrons,
`ClO_(3)^(Θ)(aq)+5e^(-) rarr Cl^(Θ)(aq)`
Balance charge by adding `overset(Θ)(O)H` ions,
`CiO_(3)^(Θ)(aq)+6e^(-) rarr Cl^(Θ)(aq)+6 overset(Θ)(O)H(aq)`
Balance `O` atoms by adding `3H_(2)O`,
`ClO_(3)^(Θ)(aq)+3H_(2)O(l)+6^(-) rarr Cl^(Θ)(aq)+6overset(Θ)(O)H(aq) ...(iii)`
Thus, equation (iii) reprsents the correct balanced reduction half equation.
To cancel out electrons gained and lost, multiply equation out electrons gained and lost, multiply equation (ii) by 3 and equation (iii) by `4` and add, we have,
`3N_(2)H_(4)(l)+4ClO_(3)^(Θ)(aq)rarr 6NO(g)+4Cl^(Θ)(aq)+6H_(2)O(l)`
This represents the correct balanced equation
c.

Thus, `Cl_(2)O_(7)(g)` acts an oxidising agent while `H_(2)O_(2)(aq)` as the reducing agent.
Oxidation number method:
Total decrease in oxidation number of `Cl_(2)O_(7) =4xx2=8`
Total increase on oxidation number of `H_(2)O_(2)=2xx1=2`
Therefore to balance the increase//decrease in oxidation number multiply `H_(2)O_(2)` and `O_(2) by 4`, we have,
`Cl_(2)O_(7)(g)+4H_(2)O_(2)(aq)rarr ClO_(2)^(Θ)(aq)+4O_(2)(g)`
To balance `Cl` atoms multiply `ClO_(2)^(Θ)` by `2`, we have,
`Cl_(2)O_(7)(g)+4 H_(2)O_(2)(aq)rarr 2ClO_(2)^(Θ)(aq)+4O_(2)(g)`
To balance `O` atoms, add `3H_(2)O` to `RHS`, we have
`Cl_(2)O_(7)(g)+4H_(2)O_(2_(aq) rarr 2ClO_(2)^(Θ)(aq)+40_(2)(g)+3H_(2)O(l)`
To balance `H` atoms, add `2H_(2)O` to `R.H.S` and `2overset(Θ)OH` to L.H.S, we have
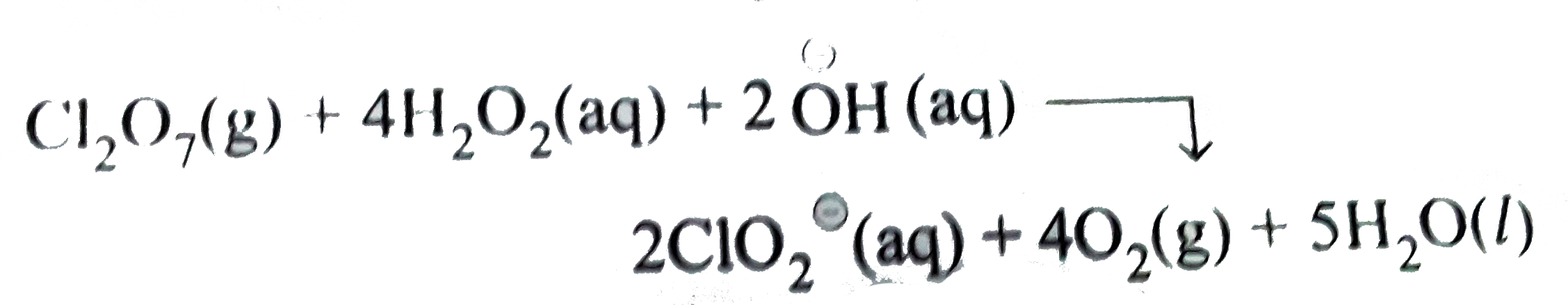
This represents the balanced redox equation.
Ion electron method:
Oxidation half equation
`H_(2)overset(-1)O_(2)(aq)rarroverset(0)O_(2)(g)`
Balance oxidation number by adding electrons,
`H_(2)O_(2)(aq)rarrO_(2)(g)+2e^(-)`
Balance charge by adding `overset(Θ)OH` ions.
`H_(2)O_(2)(aq)+2overset(Θ)OH(aq)rarrO_(2)(g)+2H_(2)O(l)+2H_(2)O(l)+2e^(-)`
Balance `O` atoms by adding `H_(2)O`
`H_(2)O_(2)(aq)+2overset(Θ)OH(aq)rarrO_(2)(g)+2H_(2)O(l)+2e^(-)`....(i)
Reduction half equation:
`overset(+7)(Cl_(2))O_(7)(g)rarroverset(+3)(Cl)O_(2)^(Θ)(aq)`
Balance `Cl` atoms
`Cl_(2)O_(7)(g)rarr2ClO_(2)^(Θ)(aq)`
Balance oxidation number by adding electrons,
`Cl_(2)O_(7)(g)+8e^(-)rarr2ClO_(2)^(Θ)(aq)`....(ii)
Add `overset(Θ)OH` ions to balance charge
`Cl_(2)O_(7)(g)+8e^(-)rarr2ClO_(2)^(Θ)(aq)+6overset(Θ)OH`
Balance `O` atom by adding `3H_(2)O` to L.H.S, we have, `Cl_(2)O_(7)(g)+3H_(2)O(l)+8e^(-)rarr2ClO_(2)^(Θ)(aq)+6overset(Θ)OH(aq)`..(ii)
To cancel out electrons, multiply equation (i) by `4` and add it to equation (ii), we have , `4H_(2)O_(2)(aq)+8overset(Θ)OH(aq)+Cl_(2)O_(7)(g)Cl_(2)O_(7)(g)+3H_(2)O(l)rarr2ClO_(2)^(Θ)+(aq)+6overset(Θ)OH(aq)+4O_(2)(g)+8H_(2)O(l)`