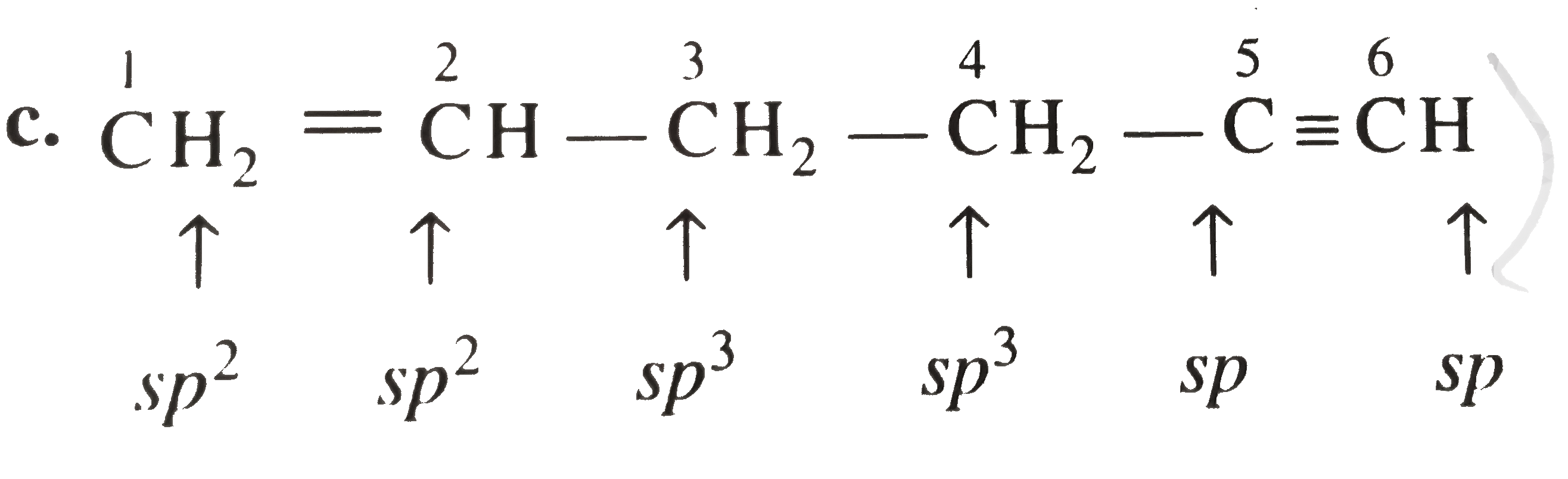A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
PURIFICATION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS AND QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Linked Comprehension Type|25 VideosPURIFICATION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS AND QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct Answers Type|10 VideosPURIFICATION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS AND QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective Type|11 VideosPERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND GENERAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises (Archives )Subjective|4 VideosREDOX REACTIONS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives (Integers)|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-PURIFICATION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS AND QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS-Concept Application Type
- Discuss the chemistry of Lassaigne’s test.
Text Solution
|
- Differentiate between the principle of estimation of nitrogen in an or...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the principle of estimation of halogens, sulphur and phosphoru...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the principle of paper chromatography.
Text Solution
|
- Why is nitric acid added to sodium extract before adding silver nitrat...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the reason for the fusion of an organic compound with metallic...
Text Solution
|
- Name a suitable technique of separation of the components from a mixtu...
Text Solution
|
- Explain, why an organic liquid vaporises at a temperature below its bo...
Text Solution
|
- Will "CC"l(4) give white precipitate of AgCl on heating it with silver...
Text Solution
|
- Why is a solution of potassium hydroxide used to absorb carbon dioxide...
Text Solution
|
- Why is it necessary to use acetic acid and not sulphuric acid for acid...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound contains 69% carbon and 4.8% hydrogen, the remaind...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of 0.50 g of an organic compound was treated according to Kje...
Text Solution
|
- 0.3080 gm of and organic chloro compound gave 0.5740 gm of silver chlo...
Text Solution
|
- In the estimation of sulphur by Carius method, 0.468 g of an organic s...
Text Solution
|
- In the organic compound CH(2) = CH – CH(2) – CH(2) – C equivCH, the pa...
Text Solution
|
- In the Lassaigne’s test for nitrogen in an organic compound, the Pruss...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following carbocation is most stable?
Text Solution
|
- The best and latest technique for isolation, purification and separati...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction: CH(3)CH(2)I + KOH(aq)toCH(3)CH(2)OH+KI is classified...
Text Solution
|