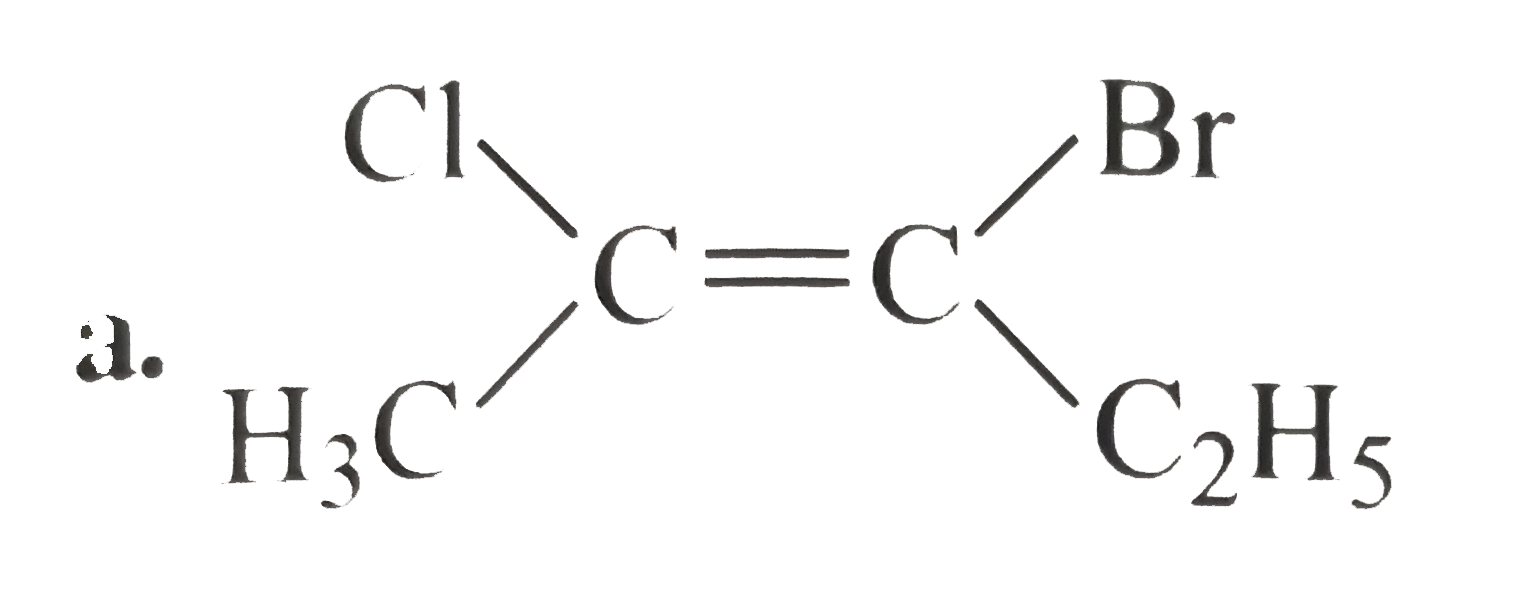
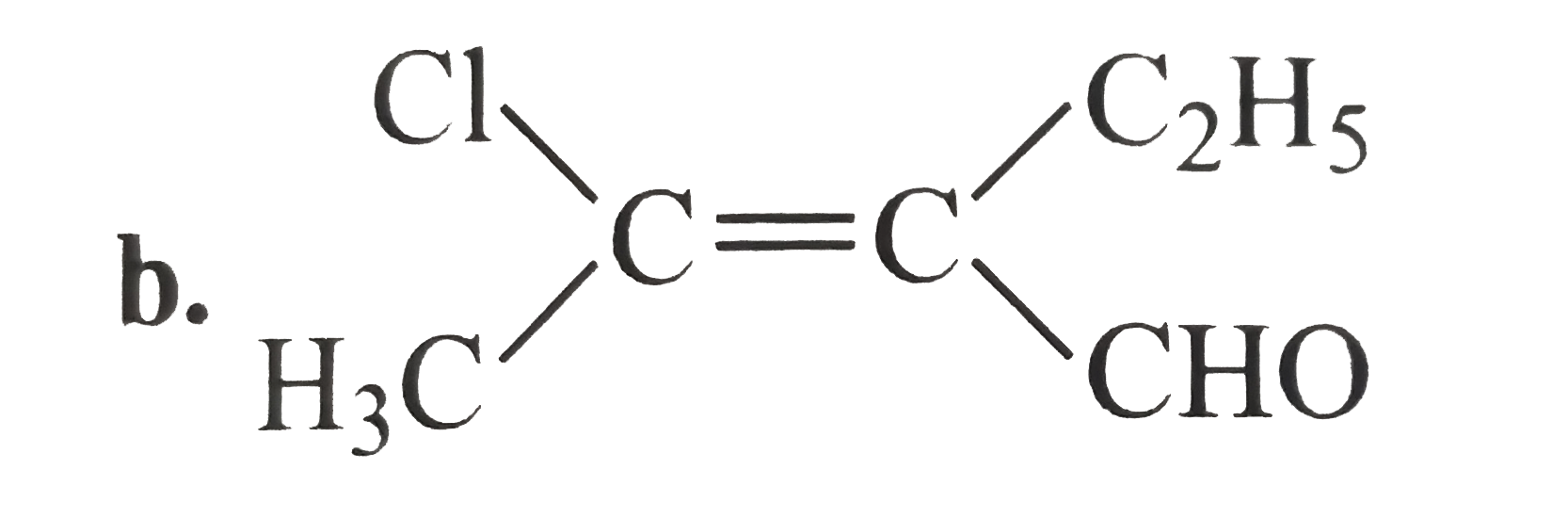
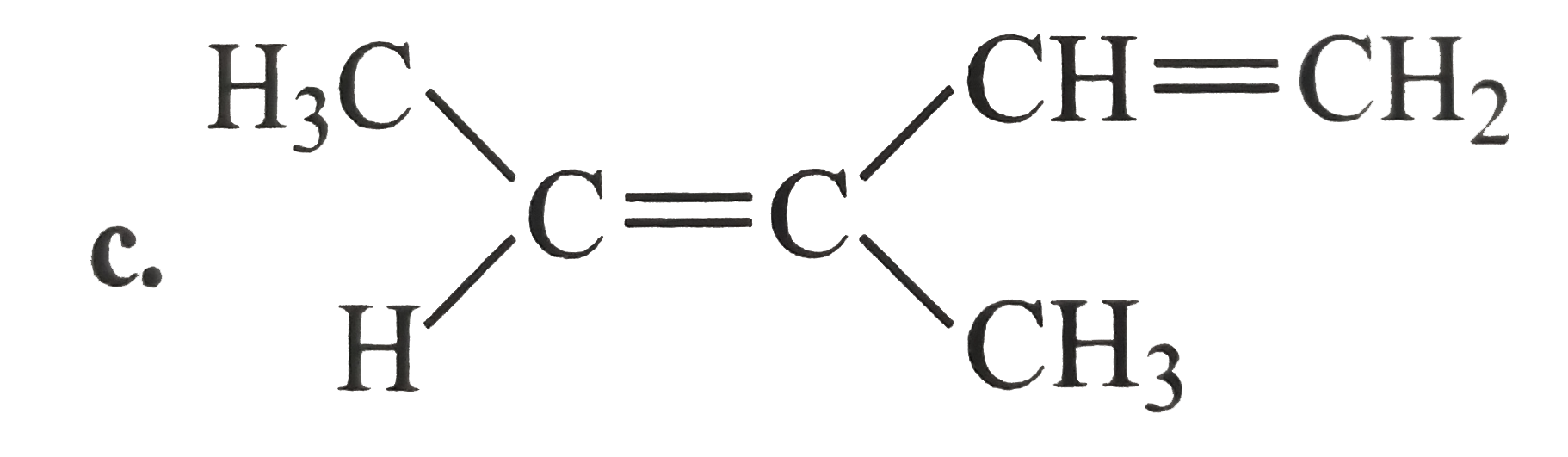
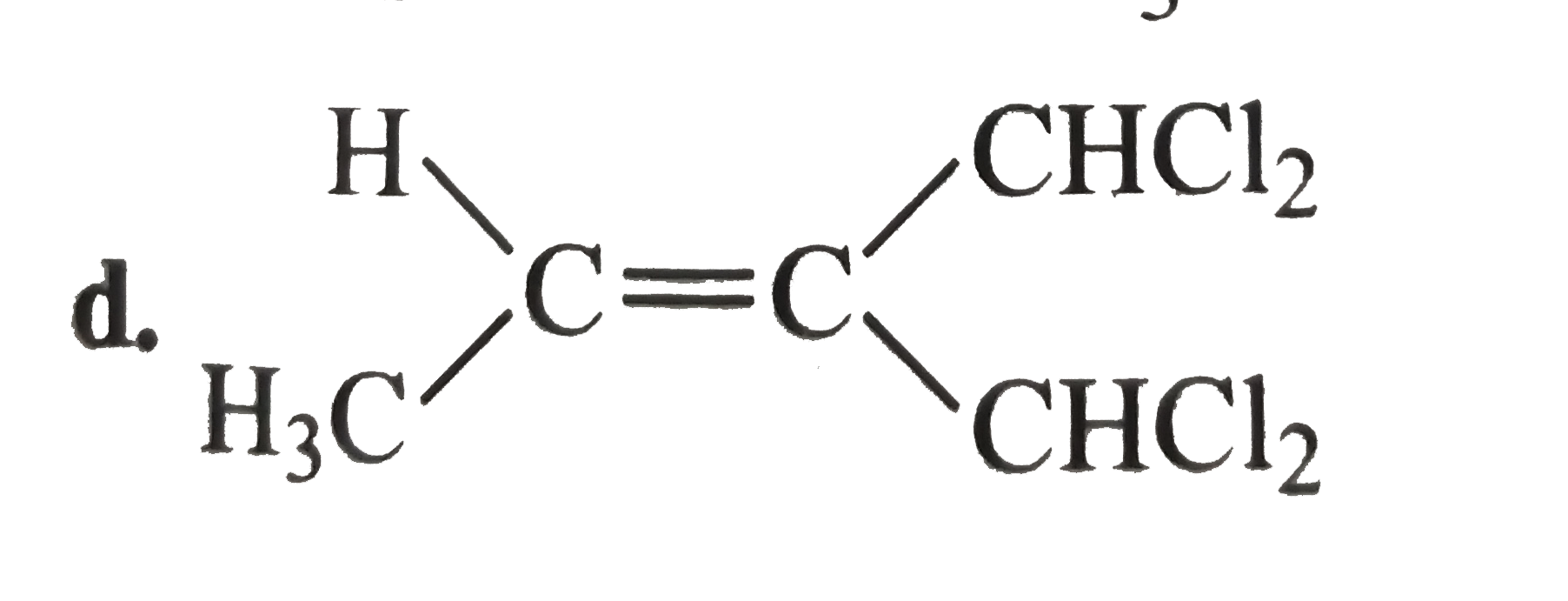
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ISOMERISM
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Single correct answer type (Exercise)|65 VideosISOMERISM
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion-Reasoning Type (Exercise)|5 VideosISOMERISM
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple choice questions (Exercise)|38 VideosIONIC EQUILIBRIUM
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Subjective|28 VideosNCERT BASED EXERCISE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Chemical Equilibrium|73 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-ISOMERISM-Single correct answer type
- Which of the following will not be able to show optical isomerism (ena...
Text Solution
|
- The type of isomerism exihibited by the compound with formula C(4)H(10...
Text Solution
|
- Acids and ester having the same number of carbon atoms are:
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following kinds of isomerism can nitroethane exhibit?
Text Solution
|
- Which among the following is likely to show geometrical isomerism?
Text Solution
|
- How many gem dihalides with different formulas are possible for C(3)H(...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement is correct?
Text Solution
|
- The total number of halogenated products likely to be formed by ethanc...
Text Solution
|
- If the optical rotation produced by the compound (A) is +52^(@), the o...
Text Solution
|
- The E-isomer among the following is:
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following will not show geometrical isomerism?
Text Solution
|
- The dihedral angle between the hydrogen atoms of two methyl groups is ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following object is chiral?
Text Solution
|