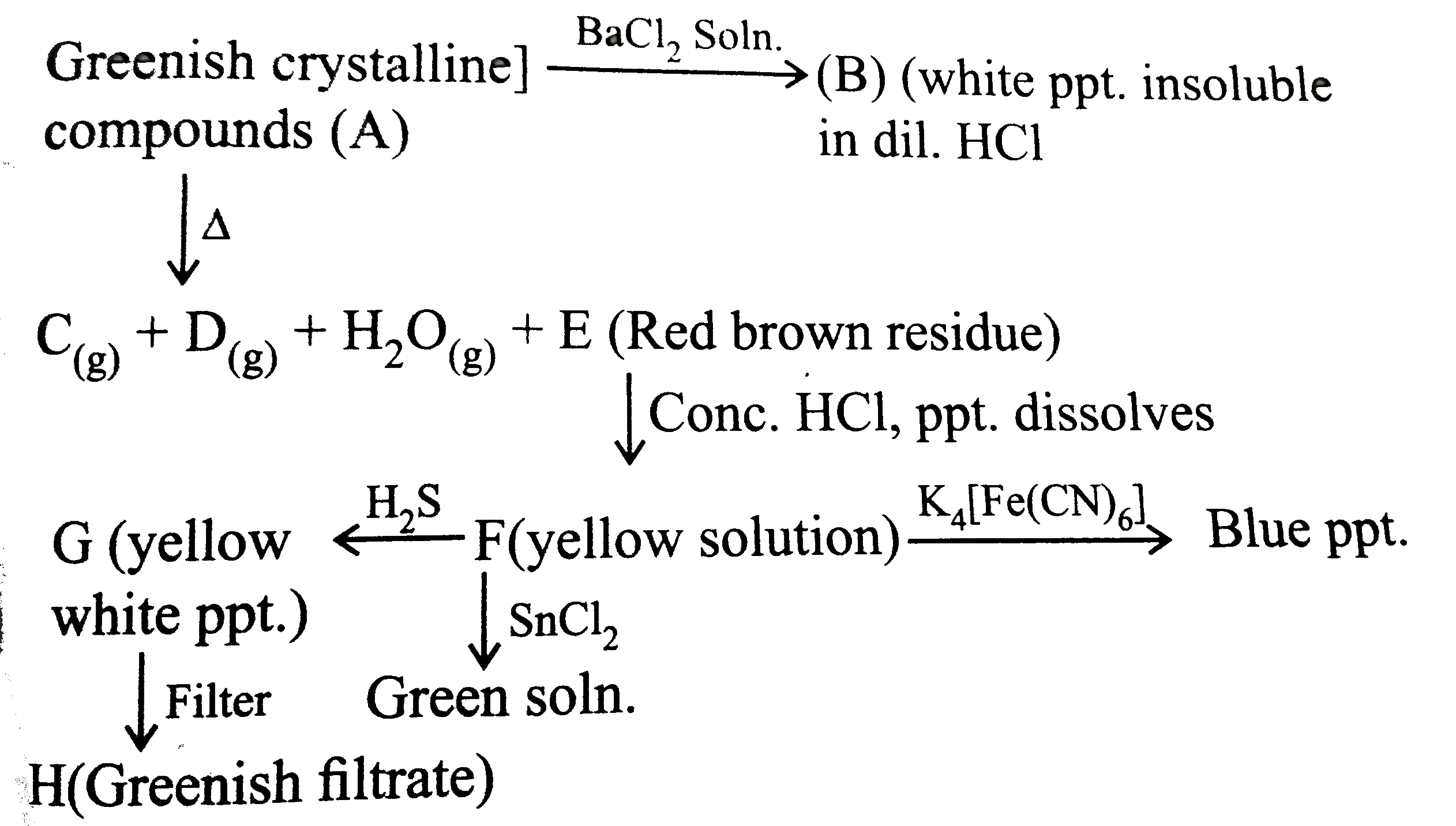A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
QUALITATIVE INORGANIC SALT ANALYSIS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises (Multiple Correct) Part-A (Analysis Of Anions)|30 VideosQUALITATIVE INORGANIC SALT ANALYSIS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises (Multiple Correct) Part-B (Analysis Of Cations)|28 VideosQUALITATIVE INORGANIC SALT ANALYSIS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Example|11 VideosP-BLOCK GROUP 18 ELEMENTS - THE INERT GASES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Ex 5.1 (Objective)|14 VideosREDUCTION AND OXIDATION REACTION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise SUBJECTIVE TYPE|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-QUALITATIVE INORGANIC SALT ANALYSIS-Exercises (Linked Comprehension)
- Solid A + H(2)O rarr (B) (while turbity which dissolves in HCI) Ide...
Text Solution
|
- Identify compound A
Text Solution
|
- Gases C and D are
Text Solution
|
- Identify yellow solution F
Text Solution
|
Text Solution
|
- Identify X
Text Solution
|
- What is the formula of chocolate coloured ppt ?
Text Solution
|
- What is the formula of brown ppt ?
Text Solution
|
- Identify C
Text Solution
|
- Identify B
Text Solution
|
- Identify D
Text Solution
|
- Compound (A) is
Text Solution
|
- Oxidation state of Fe in compound (F) is
Text Solution
|
- underset("in basic medium")((D))+(NH(4))(2)SO(4)rarr brown ppt (G) ...
Text Solution
|
- What ppt (B) + NH(3) rarr Black ppt . (H). Hence, (H) is due to the...
Text Solution
|
- Gas (B) on passing through CaSO(4) solution will give
Text Solution
|
- Compound (A),(B) and(E ) are respectively
Text Solution
|
- Compound (C ) and (D) are respectively
Text Solution
|
- i.(A)underset(Delta)overset(NaOH)rarr(B)(g) overset(HCI)rarr While fum...
Text Solution
|
- i.(A)underset(Delta)overset(NaOH)rarr(B)(g) overset(HCI)rarr While fum...
Text Solution
|