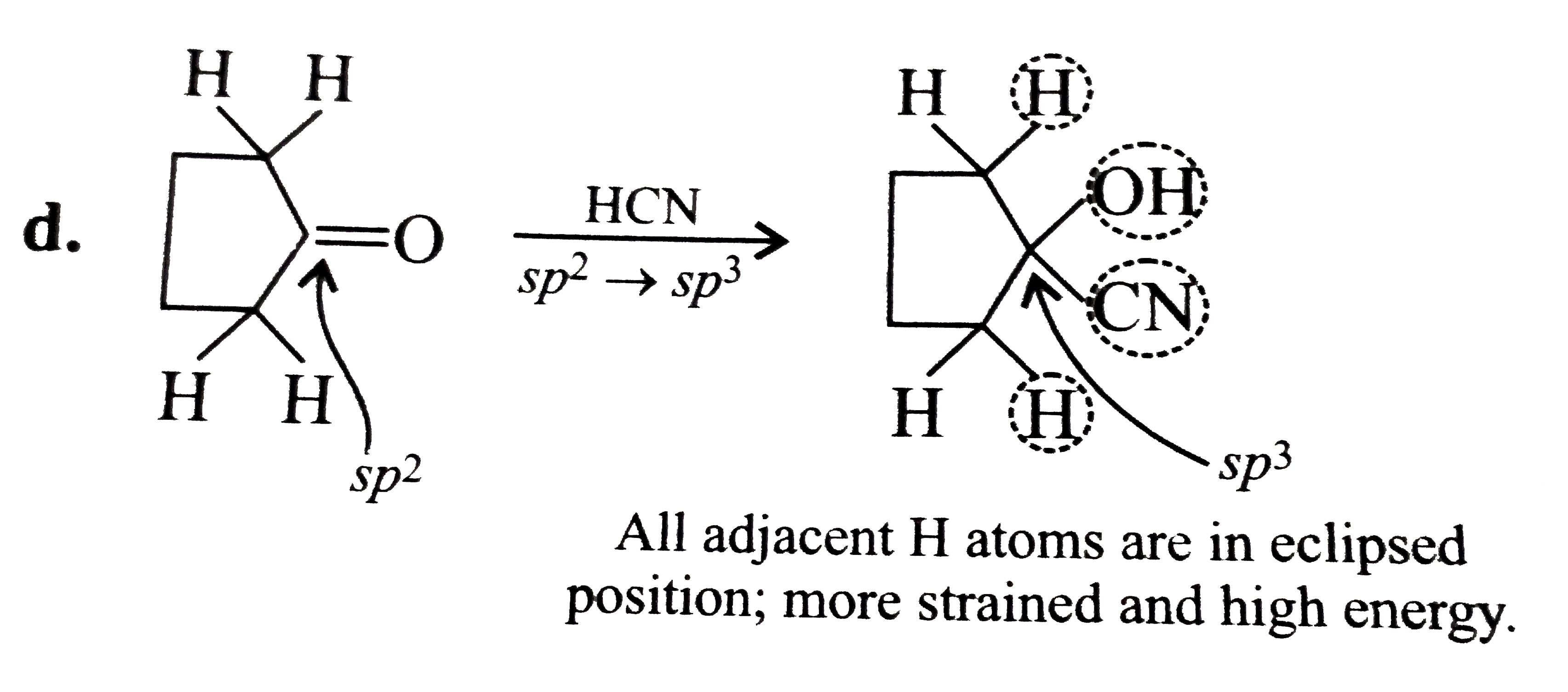
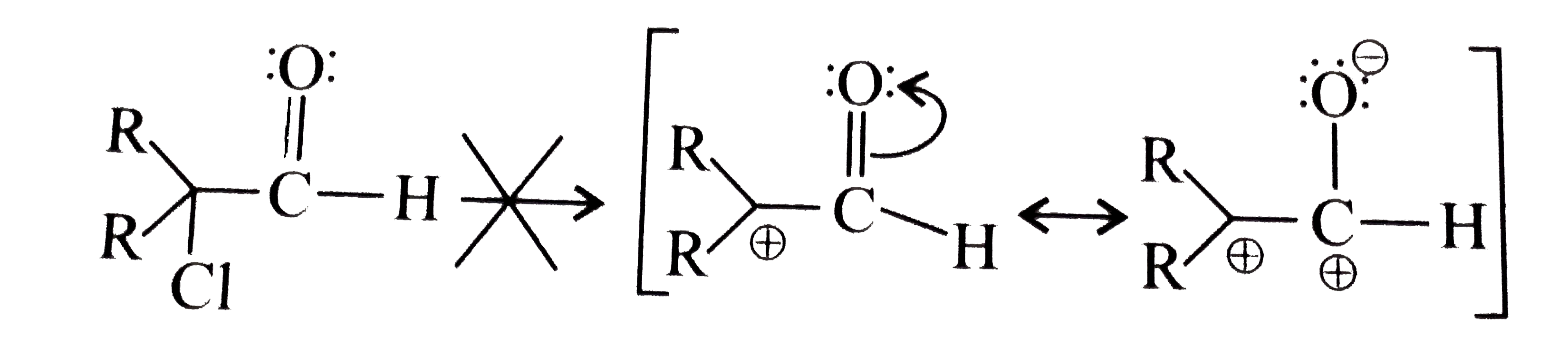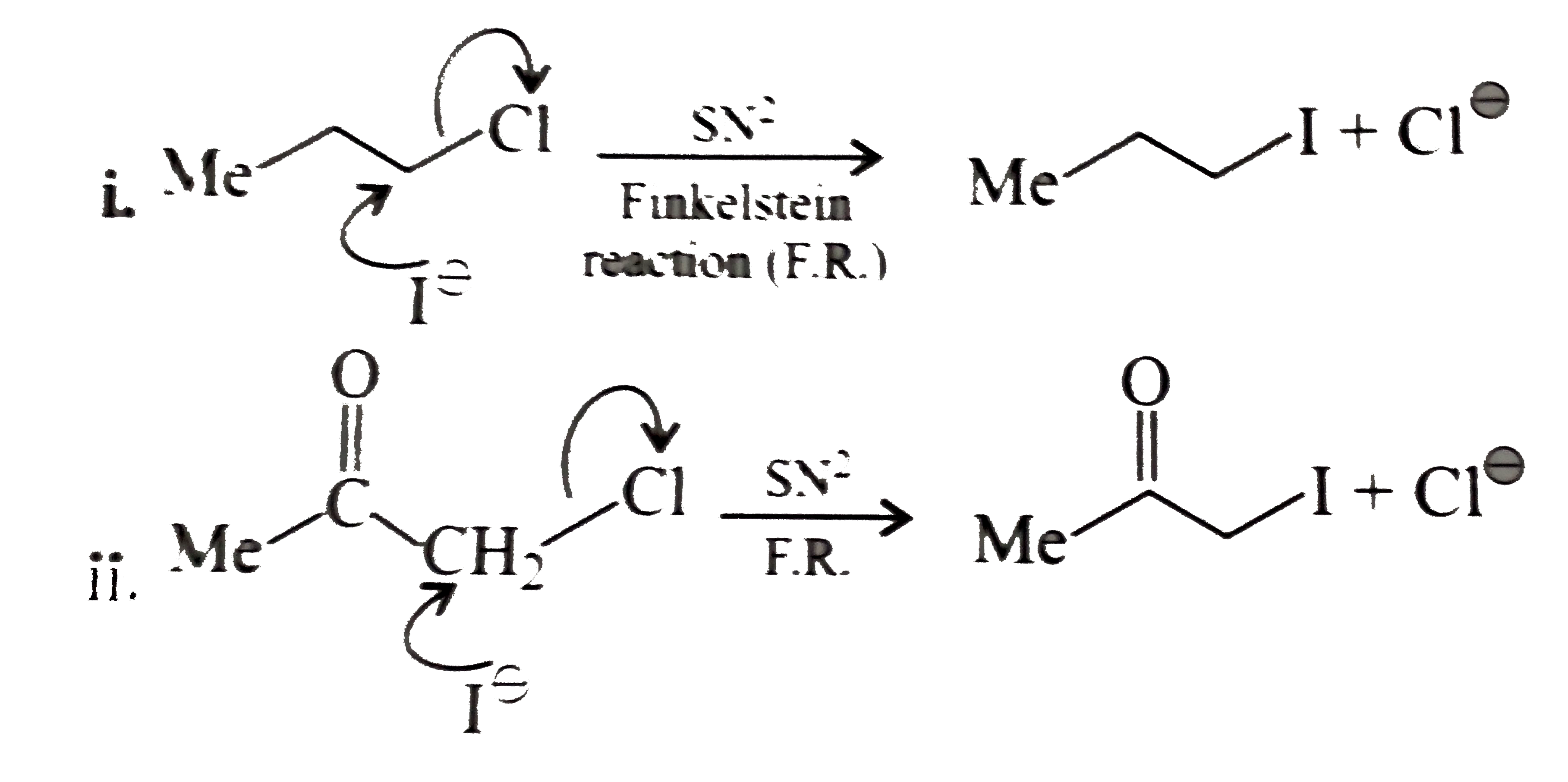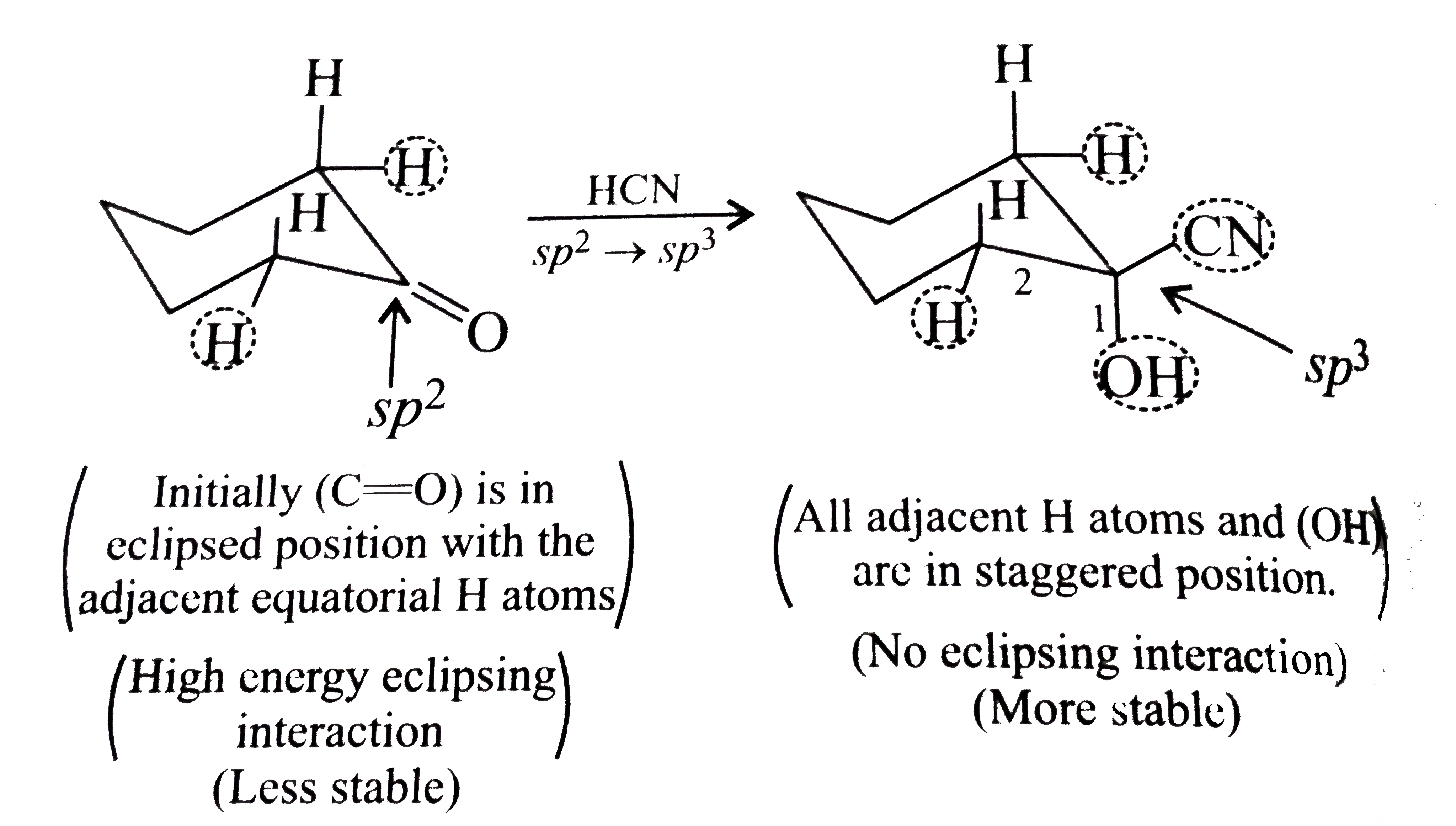Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALIPHATIC AND AROMATIC ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Subjective|52 VideosALIPHATIC AND AROMATIC ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Concept Application|20 VideosALIPHATIC AND AROMATIC ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Subjective|26 VideosALCOHOL,PHENOL AND ETHERS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Analytical And Descriptive|15 VideosAPPENDIX INORGANIC VOLUME 2
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Short Answer Type|179 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-ALIPHATIC AND AROMATIC ALDEHYDES AND KETONES-Solved Examples
- Write the structure of various isomers formed in the reaction given be...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the compounds (A) and (B). (A)underset("Iodoform test")unde...
Text Solution
|
- Explain: a. alpha-Halocarbonyl compounds, even the 3^(@) types like ...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reactions: a. b. c.
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between the following: a.
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reactions: a.
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reactions: a. b. c. d. e.
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reactions: a. b. c.
Text Solution
|
- Identify (A) to (C ):
Text Solution
|
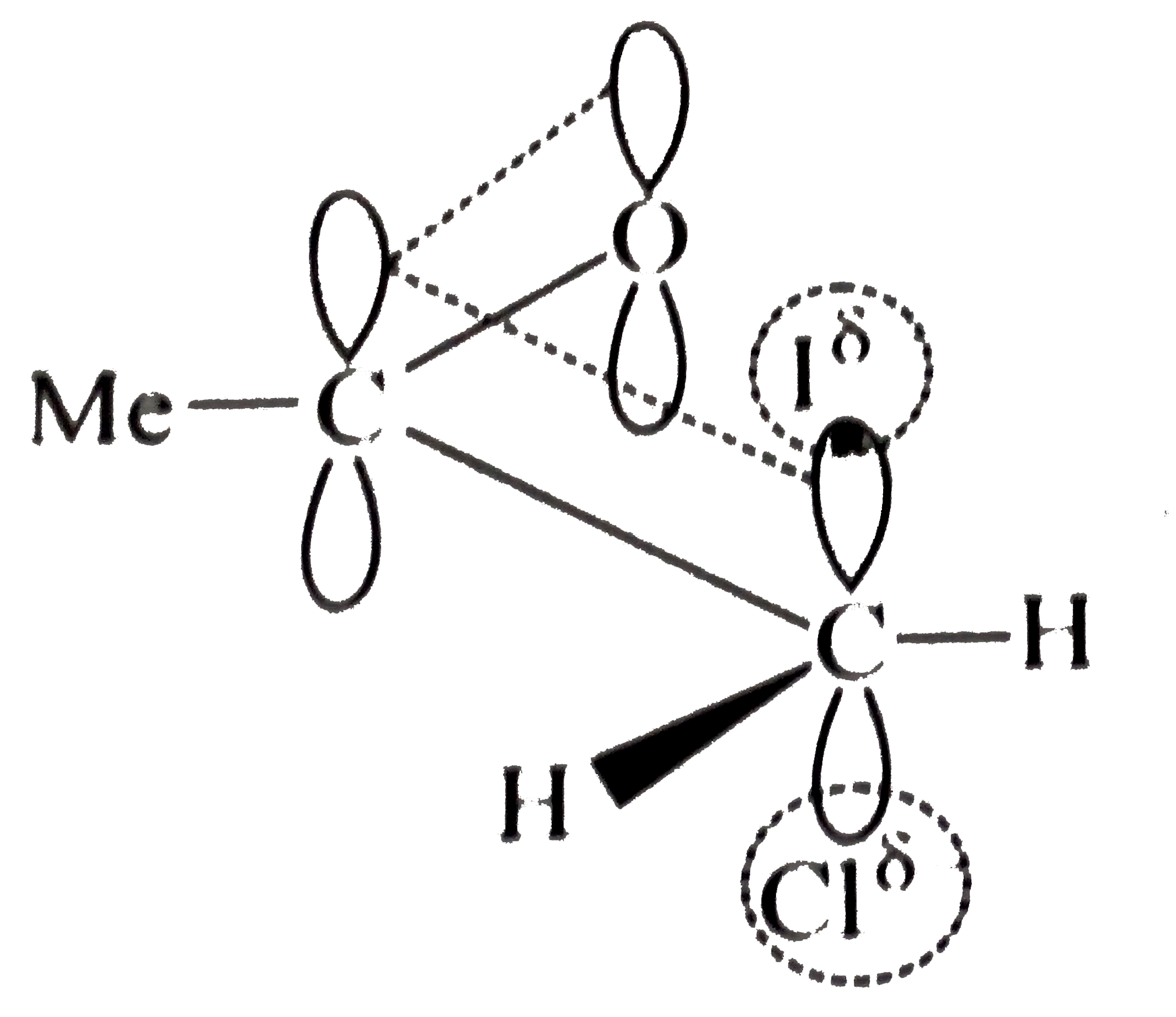
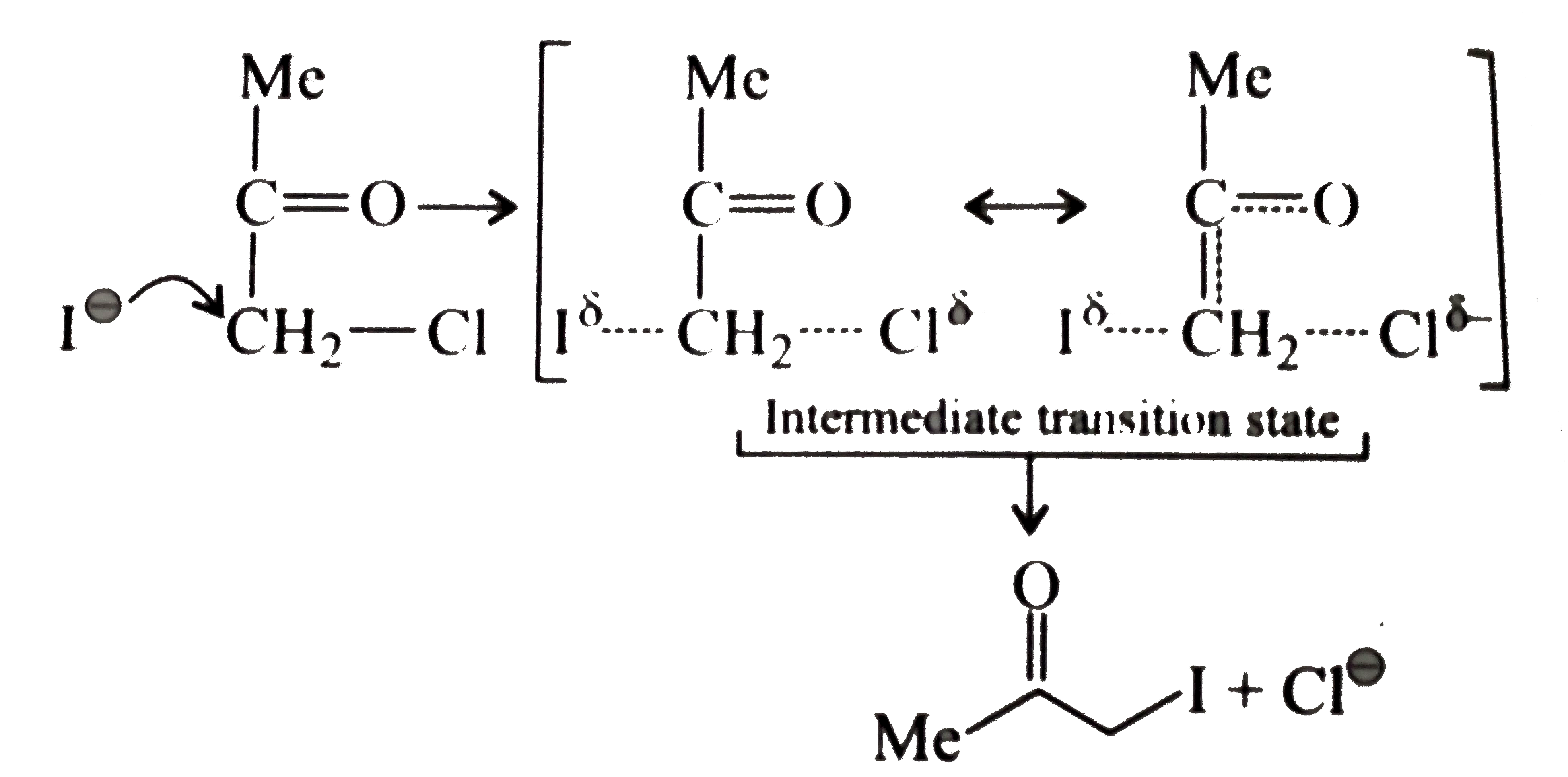
- Explain the mechanism of the following reaction:
Text Solution
|
- Explain the formation of (B), (C ) and (D) in the given reaction:
Text Solution
|
- Name the following reactants also give names of reactions involved. ...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reactions: a.
Text Solution
|
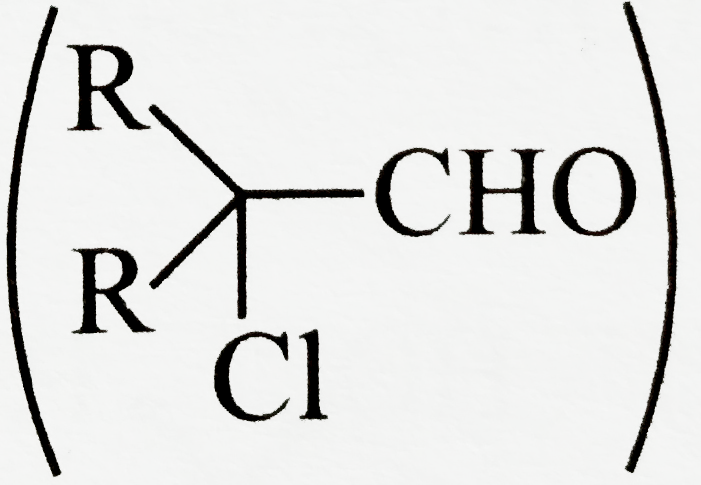 , do not undergo `SN^(1)` reaction.
, do not undergo `SN^(1)` reaction.