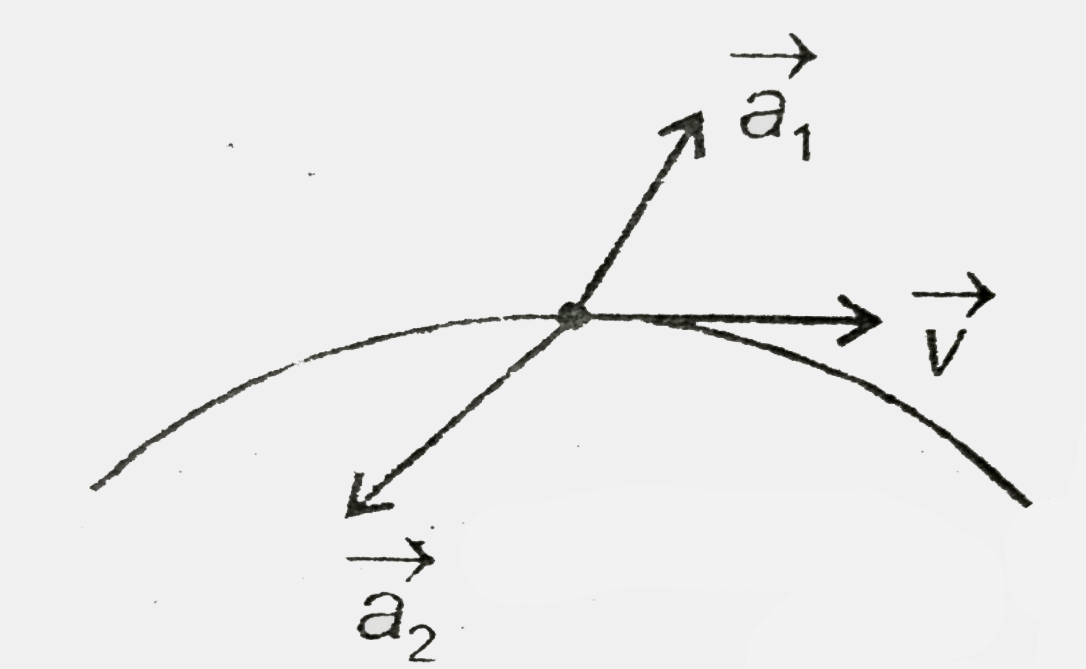
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MOTION IN A PLANE
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignement section -F (Matrix-Match)|2 VideosMOTION IN A PLANE
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignement section -G (Integer)|4 VideosMOTION IN A PLANE
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignement section -D (Linked Comprehension)|12 VideosMOCK_TEST_17
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Example|15 VideosMOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise ASSIGNMENT (SECTION - D)|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-MOTION IN A PLANE-Assignement section -E (Assertion-Reason)
- Statement -1 : A food packet is dropped from a rescue plane . Path of ...
Text Solution
|
- Statemetnt - 1 : In circular motion, acceleration may be in any direct...
Text Solution
|
- Statement -1 : A man standing on the ground has to hold his umbrella a...
Text Solution
|
- A body moves in a curved path as show : Statement -1 : Its accel...
Text Solution
|