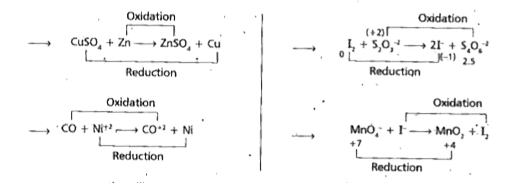
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
STOICHIOMETRY
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS |6 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise Important Question |39 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise VERY SHORT Answer questions |13 VideosSTATES OF MATTER GASES AND LIQUIDS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS|22 VideosTHE P-BLOCK ELEMENTS GROUP-13
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise Long Answer Questions|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)-STOICHIOMETRY -SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
- Consider the reactions a) 6CO(2)(g)+6H(2)O(I)toC(6)H(12)O(6)(aq)+6O(...
Text Solution
|
- The compound AgF(2) is unstable compound. However, if formed, the comp...
Text Solution
|
- Whenever a reaction between an oxidising agent and a reducing agent is...
Text Solution
|
- How do you count the following observations? a) Though alkaline pota...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the substance oxidised, reduced, oxidising agent and reducing...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the substance oxidised, reduced, oxidising agent and reducing...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the substance oxidised, reduced, oxidising agent and reducing...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the substance oxidised, reduced, oxidising agent and reducing...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the substance oxidised, reduced, oxidising agent and reducing...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the reactions 2S(2)O(3)^(2-)(aq)+I(2)(s)toS(4)O(6)^(2-)(aq)...
Text Solution
|
- Justify giving reactions that among halogens, fluorine is the best oxi...
Text Solution
|
- Why does the following reaction occur ? XeO(6)^(4-)(aq)+2F^(-)(aq)+6...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the reactions : a) H(3)PO(2)(aq)+4AgNO(3)(aq)+2H(2)O(l)toH(...
Text Solution
|
- Balance the following redox reaction in basic medium by ion-electron m...
Text Solution
|
- Balance the following redox reactions by ion-electron method : MnO...
Text Solution
|
- Balance the following redox reactions by ion-electron method : H(2...
Text Solution
|
- Balance the following Relox reaction by ion-electron method an acidie ...
Text Solution
|
- Balance the following equations in basic medium by ion-electron method...
Text Solution
|
- What sorts of information can you draw from the following reaction ? ...
Text Solution
|
- The Mn^(3+) ion is unstable solution and undergoes disproportionation ...
Text Solution
|