The acetyl CoA enters into the [mitochondrial matrix] a cyclic pathway tricarboxylic acid cycle, more commonly called krebs cycle after the scientist Hans Krebs who first elucidated it.
1) Condensation: In this acetyl CoA condenses with oxaloacetic acid and water to yield citric acid in the presence of citrate synthetase and CoA is released.
OAA + A.CoA + water `overset("Citrate synthesis")to CA + "Co.A"`
2) Dehydration : Citric acid looses water molecule to yield cisaconitic acid in the presence of aconitase.
`CA overset("Aconitase") to` Cis-aconitic acid + `H_(2)O`
3) Hydration : A water molecule is added to cis aconic acid to yield isocitric acid in the presence of a conitase.
Cis-aconitic acid `+ H_(2)O overset("Aconitase") to` isocitric acid.
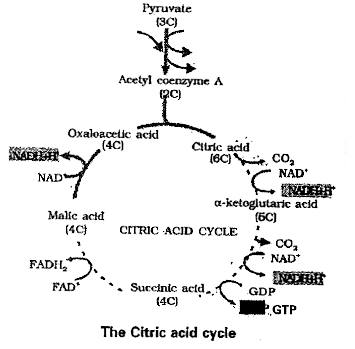
4) Oxidation I: Isocitric acid undergoes oxidation in the presence of dehydrogenase to yield succinic acid:
Isocitric acid + `NADP^(+) overset("dehydrogenase")to` oxalosuccinic acid + NADPH + `H^(+)`
5) Decarboxylation : Oxalosuccinic acid undergoes decarboxylation in the presence ofdecarboxylase to form a-keto glutaric acid.
Oxalosuccinic acid `overset("de carboxylase") to` a keto glutaric acid + `CO_(2)`
6) Oxidation n, decarboxylation and keto glutaric acid undergoes oxidation- and decarboxylation in the presence of dehydrogenase and condenses with co. A to form succinyl co. A
`alpha`-keto glutaric acid + NADP + co.A `overset("dehydrogenase") to` succinyl co.A + NADPH + `H^(+) + CO_(2)`
Cleavage : Succinyl co.A splits-into succinic acid and co.A in the presence of thiokinase to form succinic acid. The energy released is utilised to from ATP from ADP and PI.
Succinyl co A + ADP + Pi `overset("thiokinase") to` Succinic acid + ATP + co.A
Oxidation - III: Succinic acid undergoes oxidation and forms Fumaric acid in the presence of succinic dehydrogenase.
Succinic acid + FAD `overset("succinic dehydrogenase") to` Fumaric acid + `FADH_(2)`
9) Hydration: A water molecule isalcohol to Fumaric acid in the presence of Fumarase to form Malic acid.
Fumaric acid + `H_(2)O overset("Fumerase") to` Malic acid
10) Oxidation IV : Malic acid undergoes oxidation in the presence of malic dehydrogenase to form oxaloacetic acid.
Malic acid + NADP `overset("Malic dehydrogenase") to` Oxaloacetic acid + NADPH + `H^(+)`
In TCA cycle, for every 2 molecules of Acetyl co.A undergoing oxidation, 2 ATP, 8 `NADPH^+ H^+, 2FADH_(2)` molecules are formed.
